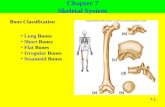
Eardrum Membrane that vibrates the bones of the middle ear.
-
Upload
tiffany-nash -
Category
Documents
-
view
222 -
download
1
Transcript of Eardrum Membrane that vibrates the bones of the middle ear.

Eardrum
• Membrane that vibrates the bones of the middle ear.

Cochlea
• Fluid-filled structure of the inner ear that contains hair cells.

Intensity
• Amount of sound energy that flows through a given area at a given time
• Beethovoven’s music had a lot of intensity.

Loudness
• The way the brain perceives the intensity of a sound. IPods are usually played loudly.

Frequency
• Frequency is a measure of the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit time. It is also referred to as temporal frequency. The period is the duration of one cycle in a repeating event. So the period is the reciprocal of the frequency.

Pitch
• The highness or lowness of a sound.
• Opera singers can have a high pitch or a low pitch.

Ultrasonic waves
• Sounds with frequencies above 20,000 Hz

Doppler Effect• The change in pitch of a
sound caused by motion of either the sound source or reciever.

Noise
• noise means unwanted sound or noise pollution.
• Kids can make a lot of unwanted noise.

Quality
• Difference between sounds of the same frequency caused by overtones.

Music
• A combination of sounds and distinct pitches following a specified pattern.

Overtones
• Multiples of the fundamental frequency

Resonator
• The part of the violin that amplifies the sound of the strings

Echo• A true echo is a single
reflection of the sound source. The time delay is the extra distance divided by the speed of sound.
• If so many reflections arrive at a listener that they are unable to distinguish between them, the proper term is reverberation

Reverberation
Unpleasant echo effect caused by many by different circumstances (happens in caves),

Acoustics
• The study of sound

Echolocation
• Finding objects by emitting sound waves and interpreting the reflected sound.

Sonar
• Used to locate objects underwater by reflection of sound waves.