Drugs for Adrenal Steroid Disease-2009
-
Upload
areef-muarif -
Category
Documents
-
view
220 -
download
0
Transcript of Drugs for Adrenal Steroid Disease-2009
-
8/13/2019 Drugs for Adrenal Steroid Disease-2009
1/22
Drugs for Adrenal Steroid Disease
Thianti Sylviningrum
-
8/13/2019 Drugs for Adrenal Steroid Disease-2009
2/22
Learning Objectives
By the end of this lectures,students will be able to :
1. Explain the anatomy,physiology and histology
of adrenal glands.
2. Explain patophysiology of adrenal disease
3. Explain drug of choice for adrenal disease
4. Explain the drug mechanism for adrenal disease
and its side effect
-
8/13/2019 Drugs for Adrenal Steroid Disease-2009
3/22
Introduction
The extracellular environment :
a. must contain the correct concentrations of ions
b. adequate supply of metabolic substrates for cellsto generate ATP
The adrenal glands play a key role in making
these adjustments
-
8/13/2019 Drugs for Adrenal Steroid Disease-2009
4/22
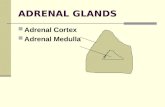
The adrenal gland
outer cortex
inner medulla
The cortex contains three histologically distinctzones (from outside to inside):
a. Glomerulosa
b. Fasciculata
c. reticularis
-
8/13/2019 Drugs for Adrenal Steroid Disease-2009
5/22
Hormones secreted by the adrenal cortex include
glucocorticoids,aldosterone, and adrenal androgens
The glucocorticoid hormones, cortisol and
corticosterone adjusting the metabolism ofcarbohydrates, lipids, and proteins in liver, muscle, and
adipose tissues during fasting, enable the body to cope
with physical and emotional traumas or stresses, immune
response
-
8/13/2019 Drugs for Adrenal Steroid Disease-2009
6/22
The mineralocorticoid hormone : aldosterone
stimulates the kidneys to conserve sodium and,
hence, body fluid volume
the catecholamines, epinephrine &
norepinephrine, widespread effects on the
cardiovascular system and muscular system,and
on carbohydrate and lipid metabolism in liver,muscle,and adipose tissues.
-
8/13/2019 Drugs for Adrenal Steroid Disease-2009
7/22
-
8/13/2019 Drugs for Adrenal Steroid Disease-2009
8/22
Adrenal Steroid Hormones Are Synthesized
From Cholesterol
Sources of Cholesterol : lipid droplets in adrenal
cortical cells
contained in low-density lipoprotein
-
8/13/2019 Drugs for Adrenal Steroid Disease-2009
9/22
Adrenal disease
Addisons Disease : muscular weakness, low blood
pressure, depression, anorexia, loss of weight and
hypoglycaemia
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia : genetic defectsaffecting the steroidogenic enzymes impair the formation
of cortisol
Cushings Disease : hypersecretion from the adrenal
glands or by prolonged therapeutic glucocorticoidregimens
-
8/13/2019 Drugs for Adrenal Steroid Disease-2009
10/22
An excessive production of mineralocorticoids results in
disturbances of Na+ and K+ balance :
a. hyperactivity of the adrenals or tumours of the glands
(primary hyperaldosteronism, or Conn's syndrome)b. excessive renin-angiotensin action such as occurs in
kidney disease, cirrhosis of the liver or congestive
cardiac failure (secondary hyperaldosteronism).
-
8/13/2019 Drugs for Adrenal Steroid Disease-2009
11/22
-
8/13/2019 Drugs for Adrenal Steroid Disease-2009
12/22
-
8/13/2019 Drugs for Adrenal Steroid Disease-2009
13/22
-
8/13/2019 Drugs for Adrenal Steroid Disease-2009
14/22
-
8/13/2019 Drugs for Adrenal Steroid Disease-2009
15/22
Both endogenous and exogenous glucocorticoids have a
negative feedback effect on the secretion of CRF and
ACTH.
Administration of exogenous glucocorticoids depressesthe secretion of CRF and ACTH, thus inhibiting the
secretion of endogenous glucocorticoids and potentially
causing atrophy of the adrenal cortex.
If therapy is prolonged, it may take many months toreturn to normal function when the drugs are stopped.
-
8/13/2019 Drugs for Adrenal Steroid Disease-2009
16/22
-
8/13/2019 Drugs for Adrenal Steroid Disease-2009
17/22
Unwanted effects : large doses or prolongedadministration rather than replacement therapy.
Possible unwanted effects include suppression of theresponse to infection or injury
an opportunistic infection can be potentially very seriousunless quickly treated with antimicrobial agents alongwith an increase in the dose of steroid.
Wound healing may be impaired, and peptic ulceration
may also occur.
-
8/13/2019 Drugs for Adrenal Steroid Disease-2009
18/22
-
8/13/2019 Drugs for Adrenal Steroid Disease-2009
19/22
The regulation of the synthesis and release of aldosterone
is complex.
Low plasma Na+ or high plasma K+ concentrations
affect thezona glomerulosacells of the adrenal directly,stimulating aldosterone release.
Depletion of body Na+ also activates the renin-
angiotensin system. One of the effects of angiotensin II is
to increase the synthesis and release of aldosterone.
-
8/13/2019 Drugs for Adrenal Steroid Disease-2009
20/22
As with the glucocorticoids, the interaction ofaldosterone with its receptor initiates transcription andtranslation of specific proteins, resulting in an increase inthe number of sodium channels in the apical membrane
of the cell, and subsequently an increase in the number ofNa+/K+ ATPase molecules in the basolateral membrane
The ensuing increased K+ excretion into the tubuleresults from an influx of K+ into the cell by the action of
the basal Na+/K+ ATPase, coupled with an increasedefflux of K+ through apical potassium channels.
-
8/13/2019 Drugs for Adrenal Steroid Disease-2009
21/22
Clinical use of mineralocorticoids
and antagonists
Clinical use of mineralocorticoids and antagonists
a. The main clinical use of mineralocorticoids is in replacementtherapy
b. The most commonly used drug is fludrocortisonewhich can betaken orally
c. Spironolactone is a competitive antagonist of aldosterone, and italso prevents the mineralocorticoid effects of other adrenalsteroids on the renal tubule. Side effects include gynaecomastiaand impotence, because spironolactone also has some blockingaction on androgen andprogesterone receptors.
d. Eplerenone has a similar indication and mechanism of action,although fewer side effects.
-
8/13/2019 Drugs for Adrenal Steroid Disease-2009
22/22