Do Now YOU NEED YOUR NUA NOTEBOOK TODAY What is the main difference between a prokaryotic and...
-
Upload
caitlin-reed -
Category
Documents
-
view
212 -
download
0
description
Transcript of Do Now YOU NEED YOUR NUA NOTEBOOK TODAY What is the main difference between a prokaryotic and...
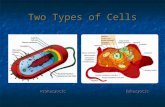
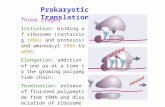
Do Now YOU NEED YOUR NUA NOTEBOOK TODAY What is the main difference between a prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell? Do bacteria cells contain a nucleus? What is the main difference between a prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell? Do bacteria cells contain a nucleus? Topic Ch. 7 Cell Structure & Function The Discovery of the Cell Robert Hooke used compound light microscope to view cork, a plant material Cork had 1000s of chambers in it - named the chambers cells Robert Hooke used compound light microscope to view cork, a plant material Cork had 1000s of chambers in it - named the chambers cells The Cell Theory Cells - the basic unit of life Developed the cell theory: All living things are made of cells Cells are the basic units of structure & function in living things New cells are produced from preexisting cells Cells - the basic unit of life Developed the cell theory: All living things are made of cells Cells are the basic units of structure & function in living things New cells are produced from preexisting cells Exploring the Cell Prokaryotes & Eukaryotes Cells are in 2 broad categories depending on whether they have a nucleus Nucleus - a membrane-enclosed structure that contains the cells DNA Controls the cells activities Cells are in 2 broad categories depending on whether they have a nucleus Nucleus - a membrane-enclosed structure that contains the cells DNA Controls the cells activities Prokaryotes & Eukaryotes Eukaryotes - cells that have a nucleus Prokaryotes - cells that do not have a nucleus Eukaryotes - cells that have a nucleus Prokaryotes - cells that do not have a nucleus Comparing the Cell to a Factory Organelles - little organs, structures within a cell Cytoplasm - portion of the cell outside the nucleus Organelles - little organs, structures within a cell Cytoplasm - portion of the cell outside the nucleus Nucleus Nucleus - contains cells DNA, & with it, the instructions for making proteins Nuclear envelope - membrane that surrounds the nucleus Nucleolus - center of nucleus, where ribosomes are formed Nucleus - contains cells DNA, & with it, the instructions for making proteins Nuclear envelope - membrane that surrounds the nucleus Nucleolus - center of nucleus, where ribosomes are formed Ribosomes Proteins are made on ribosomes Ribosomes - small particles of RNA & protein found throughout the cytoplasm Site of protein synthesis (to make) Proteins are made on ribosomes Ribosomes - small particles of RNA & protein found throughout the cytoplasm Site of protein synthesis (to make) Endoplasmic Reticulum Endoplasmic reticulum - ER - site where proteins are assembled Golgi Apparatus Golgi apparatus - function is to package proteins from the ER The packaging center of the cell Golgi apparatus - function is to package proteins from the ER The packaging center of the cell Lysosomes Lysosomes - small organelles filled with enzymes They break down (digest) lipids, carbohydrates, & proteins into molecules that can be used by the cell Lysosomes - small organelles filled with enzymes They break down (digest) lipids, carbohydrates, & proteins into molecules that can be used by the cell Vacuoles Vacuoles - saclike structures that store materials like water, salts, proteins, & carbs. Mitochondria & Chloroplasts Mitochondria - organelles that convert chemical energy stored in food to compounds that can be used by the cell The powerhouse of the cell Mitochondria - organelles that convert chemical energy stored in food to compounds that can be used by the cell The powerhouse of the cell Mitochondria & Chloroplasts Chloroplasts - organelles that capture energy from sun & convert it into chemical energy, during photosynthesis Green structures, only found in PLANT cells Chloroplasts - organelles that capture energy from sun & convert it into chemical energy, during photosynthesis Green structures, only found in PLANT cells Cytoskeleton Cytoskeleton - a network of protein filaments that help the cell maintain its shape Cell Membrane Cell membrane - regulates what enters & leaves the cell, also provide protection & support Contains lipid bilayer - 2 layers of lipids Cell membrane - regulates what enters & leaves the cell, also provide protection & support Contains lipid bilayer - 2 layers of lipids Cell Boundaries Cell wall - found in plant cells, fungi, algae, & many prokaryotes (NOT in animal cells) Provides support & protection for the cell Cell wall - found in plant cells, fungi, algae, & many prokaryotes (NOT in animal cells) Provides support & protection for the cell Home Work Use the organelles in your NUA notebook discussed during class and compare those functions as they relate to daily operation of Malcolm X Shabazz High School. Example; DNA would be the principals office. Use the organelles in your NUA notebook discussed during class and compare those functions as they relate to daily operation of Malcolm X Shabazz High School. Example; DNA would be the principals office. Diffusion Through Cell Boundaries Every living cell exists in a liquid environment that it needs to survive Cells have a different concentration or amount of substances within them Every living cell exists in a liquid environment that it needs to survive Cells have a different concentration or amount of substances within them Diffusion Through Cell Boundaries Diffusion - movement of molecules from an area of greater concentration to lesser concentration to create equilibrium Does NOT require energy Equilibrium - when the concentration of a substance is the same on both sides of a membrane Diffusion - movement of molecules from an area of greater concentration to lesser concentration to create equilibrium Does NOT require energy Equilibrium - when the concentration of a substance is the same on both sides of a membrane Osmosis Osmosis - diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane, until equilibrium is reached The Effects of Osmosis on Cells Facilitated Diffusion Facilitated diffusion - molecules that cant diffuse across the cells lipid bilayer on their own, move through protein channels instead Active Transport Active transport - requires energy moves against the concentration gradient from low to high Unicellular Organisms Cells are the basic units of all organisms, but sometimes a cell is the organism A single-celled organism is also called a unicellular organism Cells are the basic units of all organisms, but sometimes a cell is the organism A single-celled organism is also called a unicellular organism Multicellular Organisms Organisms made up of many cells are multicellular Cell specialization - cells throughout an organism can develop in different ways to perform different tasks Organisms made up of many cells are multicellular Cell specialization - cells throughout an organism can develop in different ways to perform different tasks Cell Specialization Levels of Organization The levels of organization in a multicellular organism are individual cells, tissues, organs, & organ systems Levels of Organization Tissue - a group of similar cells that perform a particular function Organ - many groups of tissue working together Organ system - a group of organs working together to perform a specific function Tissue - a group of similar cells that perform a particular function Organ - many groups of tissue working together Organ system - a group of organs working together to perform a specific function