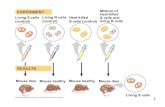
DNA Replication Replication is semi-conservative (one strand is old, one strand new) Each strand...
-
Upload
annice-weaver -
Category
Documents
-
view
220 -
download
1
Transcript of DNA Replication Replication is semi-conservative (one strand is old, one strand new) Each strand...



DNA Replication• Replication is semi-conservative (one strand
is old, one strand new)
• Each strand serves as a template (or pattern) for the new strand

Origins of Replication
• Where DNA Replication starts
• Differs between organisms– Prokaryotes = 1 origin
of replication– Eukaryotes = many
different origins of replication

General Process of DNA Replication
• Step 1:
– DNA Helicase separates the DNA helix
• Step 2: – DNA Polymerase III builds the new strand
of DNA


-Nitrogenous bases are located in the cytoplasm
-They enter the nucleus through the pores in the nuclear membrane



Thymine is added accidentally.
DNA polymerase cuts the damaged DNA.
The proper base is added.
Ligase joins the two spots.

DNA Ligase
• DNA Ligase – Forms covalent bonds between
nucleotides to create a continuous strand of DNA
– When DNA Polymerase I edits the DNA strand, DNA Ligase attaches the bases on one side of the DNA strand together.


DNA Replication
• Replicate the following DNA strand:
• A – G – G – C – T – T – C – A – G – T
• T – C – C – G – A – A – G – T – C - A