Diff Biology Ch. 7 A View of the Cell. CH. 7 A View of the Cell A.History -before 1600 ’s -...
-
Upload
harry-randall -
Category
Documents
-
view
227 -
download
0
Transcript of Diff Biology Ch. 7 A View of the Cell. CH. 7 A View of the Cell A.History -before 1600 ’s -...

DiffDiffBiologyBiologyCh. 7Ch. 7
DiffDiffBiologyBiologyCh. 7Ch. 7
A View of the Cell
A View of the Cell

CH. 7 A View of the Cell
CH. 7 A View of the Cell
A.A. HistoryHistory- before 1600’s - fiber/tissue
thought to be the basic unit of life
- spontaneous generation
1. Robert Hooke (1665)- observed cork cells
I. The Cell Theory:
I.The Cell Theory:

Robert Hooke (1665)- Coined term ‘Cell’
Robert Hooke (1665)- Coined term ‘Cell’

2. Van Leeuwenhoek
(1683) 2. Van Leeuwenhoek
(1683) - first to
see living cells

Von Leeuwenhoek (1683)- first to see living cells
Von Leeuwenhoek (1683)- first to see living cells

3.Mathias Schleiden (1838)
3.Mathias Schleiden (1838)- plants made
up of cells

4.4.Theodor SchwannTheodor Schwann (1838)
4.4.Theodor SchwannTheodor Schwann (1838)- animals made
up of cells

5.5.Rudolph VirchowRudolph Virchow (1855)
5.5.Rudolph VirchowRudolph Virchow (1855)
- cells come from other cells

B.The Cell Theory(3 parts):
B.The Cell Theory(3 parts):1.All living things are made
of cells.2.All cells come from
preexisting cells.3.Cells are the basic units
of structure and function.

- developed over several hundred years involving many scientists
- followed the development of the microscope

Research Method: Light Microscopy
Research Method: Light Microscopy
TECHNIQUE RESULTS
Brightfield (unstained specimen). Passes light directly through specimen. Unless cell is naturally pigmented or artificially stained, image has little contrast. [Parts (a)–(d) show a human cheek epithelial cell.]
(a)
Brightfield (stained specimen). Staining with various dyes enhances contrast, but most staining procedures require that cells be fixed (preserved).
(b)
Phase-contrast. Enhances contrast in unstained cells by amplifying variations in density within specimen; especially useful for examining living, unpigmented cells.
(c)
50 µm

Differential-interference-contrast (Nomarski). Like phase-contrast microscopy, it uses optical modifications to exaggerate differences indensity, making the image appear almost 3D.
Fluorescence. Shows the locations of specific molecules in the cell by tagging the molecules with fluorescent dyes or antibodies. These fluorescent substances absorb ultraviolet radiation and emit visible light, as shown here in a cell from an artery.
Confocal. Uses lasers and special optics for “optical sectioning” of fluorescently-stained specimens. Only a single plane of focus is illuminated; out-of-focus fluorescence above and below the plane is subtracted by a computer. A sharp image results, as seen in stained nervous tissue (top), where nerve cells are green, support cells are red, and regions of overlap are yellow. A standard fluorescence micrograph (bottom) of this relatively thick tissue is blurry.
50 µm
50 µm
(d)
(e)
(f)

Micrograph of a neuron
and dendrites using
antibodies, fluorescent
proteins, and confocal
microscope
Micrograph of a neuron
and dendrites using
antibodies, fluorescent
proteins, and confocal
microscope

Research Method: Electron Microscopy
Research Method: Electron Microscopy
TECHNIQUE RESULTS
Scanning electron micro-scopy (SEM). Micrographs takenwith a scanning electron micro-scope show a 3D image of the surface of a specimen. This SEM shows the surface of a cell from a rabbit trachea (windpipe) covered with motile organelles called cilia. Beating of the cilia helps moveinhaled debris upward toward the throat.
(a)
Transmission electron micro-scopy (TEM). A transmission electron microscope profiles a thin section of a specimen. Here we see a section through a tracheal cell, revealing its ultrastructure. In preparing the TEM, some cilia were cut along their lengths, creating longitudinal sections, while other cilia were cut straight across, creating cross sections.
(b)
Cilia 1 µm
Longitudinalsection ofcilium
Cross sectionof cilium
1 µm

Light Microscopes vs. Electron MicroscopeLight Microscopes vs. Electron Microscope
Light Microscope Electron Microscope
Weak Magnification—up to 1000x
Strong Magnification—500,000x
Cheap Expensive
Can look at living organism Can only look at dead organism

Everything that lives is made of cells.
Everything that lives is made of cells.

C.Two Basic Cell Types:
C.Two Basic Cell Types:1.1. Prokaryotes:Prokaryotes:
- no nucleus nor organelles- simple internal structure- very small, primitive,
unicellular- bacteria

ProkaryoProkaryoteteProkaryoProkaryotete
Bacteria Cell

2.Eukaryotes:2.Eukaryotes:- have a nucleus and
membrane-bound organelles- complex internal structure- animals, plants, fungi,
protists

EukaryotEukaryotee
EukaryotEukaryotee
Animal Cell

EukaryotEukaryotee
EukaryotEukaryotee
Plant Cell

Prokaryotes vs EukaryotesProkaryotes vs EukaryotesProkaryotes Eukaryotes
Plasma membrane Plasma membrane
Cytoplasm Cytoplasm
Ribosomes (makes proteins) Ribosomes(makes proteins)
DNA DNA
Prokaryotes Eukaryotes
No nucleus nucleus
No membrane bound organelles
Membrane bound organelles
DNA is not associated with proteins
DNA is associated with protiens (histones)
DNA not in nucleus DNA is in nucleus

3. Cytoplasm
II. Cell StructureII. Cell Structure- 3 main parts of cells:1. Plasma membrane
2. Nucleus

1.Composition- bilayer of phospholipids embedded with proteins- “fluid mosaic” theory
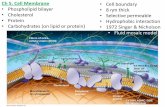
A.Plasma membrane: A.Plasma membrane:

Plasma membranePlasma membrane
lipid bilayerprotein
s

Plasma membranePlasma membrane
Glycoprotein
Carbohydrate
Microfilamentsof cytoskeletonCholesterol Peripheral
proteinIntegralprotein
CYTOPLASMIC SIDEOF MEMBRANE
EXTRACELLULARSIDE OF MEMBRANE
Glycolipid
Fibers of extracellularmatrix (ECM)

- holds cell together- regulates movement of
molecules into or out of the cell
2.Function:2.Function:

3.Cell Wall3.Cell Wall- Prokaryotes (bacteria), fungi
and plants have a cell wall- Animal cells do NOT have a cell wall.- rigid, layered structure on the
outside of cells that protects and supports cell
- found on cells of plants, fungi, and bacteria
- plant cell walls made of cellulose

Cell Wall Cell Wall

Membrane ProteinsMembrane Proteins
Look at the oligosaccharideHelps with cell to cell recognition

Peripheral proteinsPeripheral proteinsAdhere
temporarily to the plasma membrane
Regulate cell signaling

GlycoproteinGlycoproteinCell ReceptorStructureHormonesCell attachmentEnzyme

CholesterolCholesterolMaintains fluidity
-In the heat keeps phospholipids together
- In the cold prevents phospholipids from being to close to each other. **prevents rigidity.

GlycolipidGlycolipidProvides energyServe as markers
for cell to cell recognition

Nucleus
B.Nucleus:
B.Nucleus:- control center of the cell- contains chromatin (DNA
“blueprint” for cell’s proteins)

End of 7.1 and 7.2 Notes
End of 7.1 and 7.2 Notes
Stop studying here.

1. Nucleolus:1. Nucleolus:- makes ribosomes
2.2. Chromatin:Chromatin:- active form of chromosomes- long threads of DNA and protein

Cytoplasm
- liquid interior of the cell- mostly water with dissolved
substances (O2,CO2, sugar, etc.)
C. CytoplasmC. Cytoplasm

OrganellesCytoplasm
- contains Organelles:tiny structures that carry out specialized functions
C. CytoplasmC. Cytoplasm

D. Assembly, Storage,and Transport
D. Assembly, Storage,and Transport

1. Ribosomes:1. Ribosomes:- where proteins are made in a
cell- found in both prokaryotes and
eukaryotes

2. Endoplasmic Reticulum:
2. Endoplasmic Reticulum:
- produces and transports molecules

3. Golgi Body:3. Golgi Body:- store, modify, and package
proteins, hormones, etc.

- stores food, waste, sugar, water, etc.
4.Vacuole:4.Vacuole:
Vacuole
Stored food or waste

5. Lysosome:5. Lysosome:- digest food molecules or
worn-out cells

6. Leucoplasts:6. Leucoplasts: - store starch (plants only)
7.7. Chromoplasts:Chromoplasts:- contain colorful
pigments (plants only)
E.E. Energy Energy TransformationsTransformations

- "power house" of cells1.Mitochondrion:1.Mitochondrion:1.Mitochondrion:1.Mitochondrion:

- site of cellular respiration
Glucose + Oxygen Energy + CO2 +
H2O
C6H12O6 + O2
1.Mitochondrion:1.Mitochondrion:1.Mitochondrion:1.Mitochondrion:

- site of photosynthesis in plant cells
2.2. Chloroplasts:Chloroplasts:2.2. Chloroplasts:Chloroplasts:

Sunlight + H2O + CO2 C6H12O6 +
O2
2.2.Chloroplasts:Chloroplasts:2.2.Chloroplasts:Chloroplasts:

F. Support and Locomotion
F. Support and Locomotion
1.Cytoskeleton- internal framework of cell
a. Microtubulesb. Microfilaments
- contractile proteins- enable cells to move

2. Centrioles2. Centrioles- aid in the division of animal
cells

3. Cell Locomotion3. Cell Locomotiona.Cilia:
- short fibers, usually in large number
b.Flagella:- long fibers, usually single or pairs

III. Cellular TransportIII. Cellular Transport- molecules constantly
enter and leave the cell

A. DiffusionA. Diffusion- movement of molecules from
high concentration to low conc.
- until dynamic equilibrium reached
- requires no cell energy (passive)

B.B. Osmosis:Osmosis:B.B. Osmosis:Osmosis:- diffusion of water through a
selectively permeable membrane

C. Effects of OsmosisC. Effects of Osmosis1.1. Isotonic SolutionIsotonic Solution
- concentration of solutes the same on inside and
outside of cell

2. Hypotonic Solution2. Hypotonic Solution- solution outside of cell
contains a lower conc. of solutes than the cell (more water)

a)a) Turgor pressure:Turgor pressure:a)a) Turgor pressure:Turgor pressure:- pressure inside plant cells

Leaves and Onion Epidermis
Leaves and Onion Epidermis
a)a) Turgor pressure:Turgor pressure:a)a) Turgor pressure:Turgor pressure:

Plant Movements from Osmosis
Plant Movements from Osmosis
a)a) Turgor pressure:Turgor pressure:a)a) Turgor pressure:Turgor pressure:

b) Cytolysis:b) Cytolysis:b) Cytolysis:b) Cytolysis:- bursting of cells due to
increased osmotic pressure

c) Contractile Vacuoles:
c) Contractile Vacuoles:
- “pump” water out of cells of paramecium, ameba, etc. living in a hypotonic
solution
ParameciumParamecium

3.Hypertonic Solution
3.Hypertonic Solution- solution outside of cell
contains a higher conc. of solutes than the cell (less water)

a) Plasmolysis:a) Plasmolysis:a) Plasmolysis:a) Plasmolysis:- loss of cytoplasm
(shrinking of the cell)

b) Wilting:b) Wilting:b) Wilting:b) Wilting:- loss of turgor in plant cells

D.Passive vs. Active Transport
D.Passive vs. Active Transport
1.Passive Transport:- requires no energya) Diffusion and Osmosis

b) Facilitated b) Facilitated Diffusion:Diffusion:
b) Facilitated b) Facilitated Diffusion:Diffusion:- transport proteins in
membrane move sugar, amino acids, etc.
- follows concentration gradient

b) Facilitated b) Facilitated Diffusion:Diffusion:
b) Facilitated b) Facilitated Diffusion:Diffusion:

2.2.Active Transport:Active Transport:2.2.Active Transport:Active Transport:- requires cell energy
a)a)Carrier proteinsCarrier proteins transport molecules from low. conc. to high conc. using cell energy

Active Active Transport:Transport:
Active Active Transport:Transport:

b)b) Endocytosis:Endocytosis:b)b) Endocytosis:Endocytosis:

b)b) Endocytosis:Endocytosis:b)b) Endocytosis:Endocytosis:- movement of large amounts of
material into a cell by engulfing and enclosing within a membrane
- forms a vacuole within cell

b)b)Endocytosis:Endocytosis:b)b)Endocytosis:Endocytosis:
AmebaAmeba

c)c) Exocytosis:Exocytosis:c)c) Exocytosis:Exocytosis:

c)c) Exocytosis:Exocytosis:c)c) Exocytosis:Exocytosis:- expelling large amounts of
material from the cell

c)c) Exocytosis:Exocytosis:c)c) Exocytosis:Exocytosis:
Paramecium
Paramecium

The
End
The
End

Elodea Leaf CellsElodea Leaf Cells

Tomato CellsTomato Cells

Potato CellsPotato Cells

Human Epithelial Cells
Human Epithelial Cells

Onion Cells- Unstained (40x)
Onion Cells- Unstained (40x)

Onion Cells- Stained (40x)Onion Cells- Stained (40x)

Bacteria CellsBacteria Cells
CoccuCoccuss
BacilluBacilluss
SpirilluSpirillumm

Von Leeuwenhoek (1675)- first to see live cells
Von Leeuwenhoek (1675)- first to see live cells