Development Of Vertebral Column
-
Upload
anan -
Category
Health & Medicine
-
view
26.057 -
download
9
Transcript of Development Of Vertebral Column

DEVELOPMENT OF VERTEBRAL COLUMN
GROUP TUTOR: DR. NISREEN
By: NURUL AIMAN BT FAISAL
RUQAYYAH SYAKIRAH MAZWAR

CONTENTS..
• 1. STAGES OF DEVELOPMENT OF VC- FORMATION OF MESENCHYMAL VC- FORMATION OF CARTILAGINOUS VC- OSSIFICATION OF VC• 2. FATE OF NOTOCHORD• 3. FATE OF COSTAL PROCESSES• 4. ANOMALIES OF VC




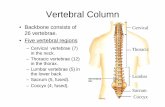
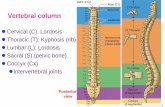
Stages in development of the vertebral
column

Stage 1
Stage of formation of mesenchymal
vertebral columnTime of development: 4th week

1.Migration of sclerotomes

2. Differentiation of sclerotomic segments
• Each segments differentiated into –Cephalic part (less condensed)–Caudal part (more condensed)

3. Development of intervertebral discs
• Densely packed cell move cranially to the middle part of each segments
• Form peripheral part – annulus fibrosus
• Enclosed notochord expands and undergo mucoid degeneration
• Form central part –nucleus pulposus



4. Development of the body of vertebrae
• Caudal remained part fuse with cephalic part adjacent to it to form mesenchymal centrum
• Notochord degenerates and disappears when surrounded by vertebral body


5. Development of neural arch• Sclerotomic tissue migrate backward from
both side of centrum and surround neural tube.
• Neural spine forms at meeting point of neural arch
• Sclerotomic tissue also extends laterally from both sides of centrum form 2 processes– Costal (ventral)– Transverse (dorsal)


Stage 2
Stage of formation of cartilaginous
vertebral columnTime of formation: 6th week

• Process of chondrification– 2 centers of chondrification in each centrum
appear– Fuse together at the end of embryonic period
(8th week) form cartilaginous centrum– Centers of chondrification appear in neural
arhes and fuse with each other and centrum– Chondrification spreads until a cartilaginous
vertebral column formed

Stages of ossification of vertebral column
• Comprises of 2 stages:• 1. primary ossification center• 2. secondary ossification center

Primary ossification center
• Time of development: at the end of 8th week• Number:• 1. 3 ossification centers are present by the end
of embryonic period• 2. one in the centrum• 3. one in the neural arch

• Process:• 1. bony halves of the vertebral arch fuse
together during the first 3 to 5 years• 2. the arches articulate with the centrum at
cartilaginous neurocentral joints• 3. these joints dissapear when vertebral
arches fuses with the centrum during the 3rd to 6th years

Secondary ossification center
• Time of development: after puberty• Number: the 5 secondary ossification center
appears at,• 1. tip of spinous process• 2. tip of each transverse process• 3. superior rim of the vertebral body• 4. inferior rim of the vertebral body


Fate of notochord
• Cranial part: merged with basilar part of occipital bone & posterior part of body of sphenoid
• Notochord located in the vertebra undergo degeneration and disappear
• The ones located in between undergo mucoid degeneration to form nucleus pulposus

Fate of the costal process
• Costal process results from ventrolateral outgrowth of the caudal, denser half of a sclerotome.
• In the cervical region: form anterior and lateral boundary of the foramen transversum
• In the thoracic region: form the ribs• In the lumbar region: fuse with the transverse
process• In the upper sacral region: they unite to form the
anterior portion of the ala of sacrum

Anomalies of the vertebral column

Spina bifida
Cause: incomplete fusion of halves of the vertebral arches resulting in midline defect usually in lumbosacral regionFeature: It varies, but generally the small bones (vertebrae) that make up the spine don’t form fully and may have gaps between them.

Hemivertebra
Cause: failure of one of the chondrofication center to appear and subsequent failure of half of vertebra to form
Feature: defective vertebra produce scoliosis ( lateral curvature)
Most likely to cause neurologic problems

Sacralization of 5th lumbar vertebraCause: 5th lumbar is fused with the sacrum
Feature: number of lumbar vertebra is 4 and the sacrum is formed of 6 vertebra

Lumbrization of first piece of sacrum to form separate vertebra
Cause: separation of first piece of sacrum to form separate vertebra
Feature: number of lumbar vertebra is 6 and the sacrum is only formed of 4 sacral vertebra

Congenital kyphosis

Congenital scoliosis

THE END…