Detailed Study of Representative Proteins. MOLECULAR CHAPERONES Specialized Function.
-
Upload
nelson-clark -
Category
Documents
-
view
217 -
download
0
Transcript of Detailed Study of Representative Proteins. MOLECULAR CHAPERONES Specialized Function.

Detailed Study of Representative Proteins

MOLECULAR CHAPERONES
Specialized Function

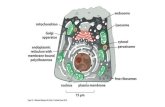
Molecular ChaperonesA large group of unrelated
protein families whose role is to stabilize unfolded proteins, unfold them for translocation across membranes or for degradation, and/ or to assist in their correct folding and assembly

Properties Molecular chaperones interact with unfolded or partially folded
protein subunits, e.g. nascent chains emerging from the ribosome, or extended chains being translocated across subcellular membranes.
They stabilize non-native conformation and facilitate correct folding of protein subunits.
They do not interact with native proteins, nor do they form part of the final folded structures.
Some chaperones are non-specific, and interact with a wide variety of polypeptide chains, but others are restricted to specific targets.
They often couple ATP binding/hydrolysis to the folding process.
Essential for viability, their expression is often increased by cellular stress.

GroEL-GroES

STRUCTURAL PROTEINS

Cytoskeletal Proteins

Microfilament
Hollow cylindrical filaments with a diameter of 25 nm
radiates from the cell nucleus. are organized by the microtubule organizing centers
(centrioles and basal bodies). Capable of growing and shrinking to generate force.
They can be used by motor proteins that support the movement of organelles and other cellular factors along the microtubules.

Intermediate Filament
Have an average diameter of 10 nm, and they are mostly cytoplasmic (except the nuclear filaments known as lamins).
These filaments are deformable proteins that can be stretched to several times their initial length due to their hierarchical structure
More stable than actin filaments Like actin filaments, they help maintain the cell-shape by
resisting tensional forces. Organize the internal structure of the cell and anchor the
organelles.

Microtubules
Rigid, hollow cylinders approximately 25 nm in diameter, and are polymers of the protein tubulin.
Exhibit a highly dynamic behavior as they polymerize and depolymerize. Are commonly organized by the centrosome, play role in the intracellular
transport of organelles and vesicles, and construct the cilia, flagella, and mitotic spindles.
They resist compression, and thus, in tensegrity models they are considered rigid bars (rods).
These rigid microtubules are interconnected by prestressed, extensible microfilaments (cables)


Collagen Important component of
connective tissue and has tremendous tensile strength
Contains repeating units of Gly-Pro-Hyp in a narrow left-handed helix
Three polypeptide chains wind around each other in a right-handed helix with Gly at the center
The triple helix is stabilized by hydrogen bonding
Cross links between the side chains are covalent bonds (not disulfide) by modified residues (post-translational modification)◦ Crosslinks increase with age

MOTOR PROTEINS

Kinesin Microtubule-associated protein



Myosin


TRANSPORT PROTEINS

Hemoglobin



Myoglobin and other globins


IMMUNOGLOBULINS

Structure



PROTEASES: CHYMOTRYPSIN

Chymotrypsin