Derivatives of the epidermis (skin...
Transcript of Derivatives of the epidermis (skin...

Objectives
The Skin
1. Name the tissue types composing the epidermis and dermis. List the major layers of each and describe the functions of each layer.
2. Describe the factors that normally contribute to skin color. Briefly describe how changes in skin color may be used as clinical signs of certain disease states.
Appendages of the Skin
3. List the parts of a hair follicle and explain the function of each part. Also describe the functional relationship of arrector pili muscles to the hair follicles.
4. Name the regions of a hair and explain the basis of hair color. Describe the distribution, growth, replacement, and changing nature of hair during the life span.
5. Describe the structure of nails.
6. Compare the structure and locations of sweat and oil glands. Also compare the composition and functions of their secretions.
7. Compare and contrast eccrine and apocrine glands.
Functions of the Integumentary System
8. Describe how the skin accomplishes at least five different functions.
Homeostatic Imbalances of Skin
9. Summarize the characteristics of the three major types of skin cancers.
10. Explain why serious burns are life threatening. Describe how to determine the extent of a burn and differentiate first-, second-, and third-degree burns.
Developmental Aspects of the Integumentary System
11. Describe and attempt to explain the causes of changes that occur in the skin from birth to old age.
1

The Integumentary System (p. 150)
The integumentary system is made up of:
_______________________________________________
_______________________________________________
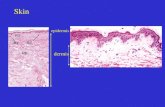
The Skin (pp. 150–157; Figs. 5.1–5.4)
The skin is composed of two distinct regions:
Epidermis
2

Dermis
Hypodermis
Epidermis
Four or five distinct layers:
o
o
o
o
o
3

Four types of cells:
o Keratinocytes
o Melanocytes
4

o Dendritic (Langerhans) cells
o Tactile (Merkel) cells
Layers of the Epidermis: Stratum Basale (Basal Layer)
Layers of the Epidermis: Stratum Spinosum (Prickly Layer)
Layers of the Epidermis: Stratum Granulosum (Granular Layer)
5

Layers of the Epidermis: Stratum Lucidum (Clear Layer)
Layers of the Epidermis: Stratum Corneum (Horny Layer)
Dermis
6

Cells are typically those found in any connective tissue proper:
Fibers in _______________________ bind body together.
Contains _________________________ fibers; ___________________ vessels and ________________________ vessels.
The major potions of ______________________________, as well as oil and swear glands, derive from epidermal tissue but reside in the _______________________________.
Two layers of the dermis:
__________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________
7

Layers of the Dermis: Papillary Layer
• __________________________ connective tissue with collagen and elastic fibers and blood vessels
• Loose tissue:
–
• Dermal papillae:
–
• Most contain ____________________________ loops
• Some contain Meissner's corpuscles (touch receptors)
• Some contain free nerve endings (pain receptors)
8

• In thick skin lie atop dermal ridges that cause epidermal ridges
– Collectively ridges called friction ridges:
• _____________________________________________
• _____________________________________________
• _____________________________________________
Layers of the Dermis: Reticular Layer
• Approximately ____________% of dermal thickness
• Dense fibrous connective tissue
• Elastic fibers provide stretch-recoil properties
Collagen fibers
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
Cleavage lines because most collagen fibers parallel to skin surface
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
Flexure Lines
– Dermal folds at or near ___________________________________
– Dermis tightly secured to deeper structure.
– Skin cannot slide easily for joint movement causing deep ______________________________.
– Visible on hands, wrists, fingers, soles, toes
9

Other Skin Markings
• Striae
– Silvery-white scars
– "_______________________________________"
– Extreme stretching causes dermal tears
• Blister
– From acute, short-term trauma
– Fluid-filled pocket that separates ________________________and ____________________________ layers
10

Skin Color
Three pigments contribute to skin color:
1. _________________________________________________________________
2. _________________________________________________________________
3. _________________________________________________________________
Melanin:
• Two forms
– __________________________________________ to _________________________________________
• Color differences due to _________________________________and __________________________________
• Produced in melanocytes
– Same relative number in all people
• Migrates to keratinocytes to form "________________________________________" for nuclei
• Freckles and pigmented moles
– Local _______________________________ of melanin
• Sun exposure stimulates melanin production
• Sunspots (________________________________________) are fungal infection; not related to melanin
Carotene:
– ___________________________ to _________________________ pigment
• Most obvious in palms and soles
– Accumulates in stratum corneum and hypodermis
– Can be converted to __________________________ for vision and epidermal health
• Yellowish-tinge of some asians – carotene and melanin variation.
11

Hemoglobin:
– ________________________ hue of fair skin
Skin Color in Diagnosis
• Cyanosis
– ________________________________________________________________________________
• Erythema (redness)
– ________________________________________________________________________________
• Pallor (blanching)
– ________________________________________________________________________________
• Jaundice (yellow cast)
– ________________________________________________________________________________
• Bronzing
– ________________________________________________________________________________
• Bruises
– ________________________________________________________________________________
12

Appendages of the Skin (pp. 157–162; Figs. 5.5–5.7)
Derivatives of the epidermis (skin appendages:
– ____________________________________________________
– ____________________________________________________
– ____________________________________________________
– ____________________________________________________
Hairs and Hair Follicles
• Functions include:
– _________________________________________________
– _________________________________________________
– _________________________________________________
– _________________________________________________
Structure of a hair
Hair, or pili are flexible strands produced by hair follicles and consist largely of dead ____________________________cells of hard keratin.
Not in ________________________, _______________________, ________________________,
____________________, portions of _________________________________________.
13

The hard keratin that dominates the hairs and nails has two advantages over the soft keratin found in typical epidermal cells:
1.
2.
• The main regions of a hair are the ________________________, which projects from the
skin, and the ______________________, which embeds in the skin.
• Hair has three layers of keratinized cells: the inner core is the
____________________________, the middle layer is the ________________________, and the outer
layer is the _________________________.
• Hair pigments (melanins of different colors) are made by ______________________________
at the base of the hair follicle.
• _______________________________ (yellow, rust, brown, black); ________________________ in red hair.
• Gray/white hair: ____________________________melanin production, increased air bubbles in shaft.
14

Structure of a Hair Follicle
Hair follicles fold down from the ________________________into the ___________________ and occasionally into the ___________________________.
The deep end of a hair follicle is expanded, forming a ____________________________, which is surrounded by sensory nerve endings called a ____________________ receptor, or root hair_____________________________.
A hair _____________________, a nipple-like bit of dermal tissue, protrudes into the hair bulb. This ______________________ contains a knot of capillaries that supplies nutrients to growing hair and signals it to grow.
The wall of a hair follicle is composed of an outer ___________________________________ sheath, a thickened basement membrane, and an inner epithelial root sheath.
The hair ____________________________ within the hair bulb is a group of actively dividing cells that produce the hair.
Associated with each hair follicle is a bundle of smooth muscle cells called an _______________________________________muscle which, when contraction occurs, causes the hair to stand upright.
Types and Growth of Hair
Hairs can be classified as pale, fine ___________________ hairs, or longer, more coarse ___________________________hairs.
• Vellus hair:– Pale, fine body hair of ____________________________ and adult _____________________.
15

• Terminal hair– Coarse, long hair of eyebrows, scalp– At puberty:
• Appear in ________________________and _____________________ regions of both sexes• Face and neck of males
• Nutrition and hormones affect hair growth• Follicles cycle between active and regressive phases• Average ____. ________ mm growth per week• Lose __________ scalp hairs daily
Hair growth and density are influenced by many factors, such as nutrition and hormones.
The rate of hair growth varies from one body region to another and with sex and age.
Hair Thinning and Baldness• Alopecia:– Hair thinning in ________________________ after age 40
• True (frank) baldness: – Genetically determined and sex-influenced condition – Male pattern baldness caused by follicular response to DHT (___________________________________)– Treatments• Minoxidil (rogaine) and finasteride (propecia)
Nails A nail is a scalelike modification of the epidermis that forms a protective covering on the dorsal side of the distal finger or toe.
Nails are made up of ____________ keratin and have a free edge, a nail __________ attached to the skin, and a root embedded in the skin.
16

The nail __________________, located within the proximal part of the nail bed, is responsible for nail growth.
Sweat (Sudiforeous) Glands_______________________, or ___________________, sweat glands produce true sweat and are abundant on the palms of the hands, soles of the feet, and forehead.
Secretion of eccrine glands is regulated by the sympathetic nervous system and is used to prevent the body from overheating.
Apocrine sweat glands are confined to the ______________ and ____________________ areas and produce a fat and protein-rich true sweat.
___________________ glands are modified apocrine glands found lining the ear canal that secrete earwax, or cerumen.
________________________glands are modified sweat glands that secrete milk.
Sebaceous (Oil) Glands Sebaceous glands secrete _________________________, an oily secretion, and are found all over the body, except the palms of the hands and soles of the feet.
The sebaceous glands function as ___________________________ glands, secreting their product into a hair follicle or to a pore on the surface of the skin.
Secretion by sebaceous glands is stimulated by _________________________.
17

Functions of the Integumentary System (pp. 162–164)
Functions of the Integumentary System:
1. ____________________________________________________________
2. ____________________________________________________________
3. ____________________________________________________________
4. ____________________________________________________________
5. ____________________________________________________________
6. ____________________________________________________________
Protection
Skin constitutes three types of barriers:1. ____________________________________________________________
2. ____________________________________________________________
3. ____________________________________________________________
Chemical Barriers include ___________________ secretions and _________________.
Skin secretions:
o ________________________________________________________________________________
o ________________________________________________________________________________
Melanin:
o ________________________________________________________________________________
18

Physical Barriers
• Flat, dead cells of ______________________________________surrounded by lipids
• Keratin and ________________________block most water and water- soluble substances
• Limited penetration of skin; Substances that do penetrate the skin in limited amounts include:
– ______________________________________
– ______________________________________
– ______________________________________
– ______________________________________
– ______________________________________
– ______________________________________
Biological Barriers
Dendritic cells of epidermis
o Present foreign ___________________________ to white blood cells
Macrophages of dermis
o Present foreign _____________________________to white blood cells
DNA
o Its electrons absorb _______________ radiation
o Radiation converted to _______________________
19

Body Temperature Regulation
If body temperature normal ~500 ml/day of routine _______________________________________.
o (if environmental temperature below ________-_________° C)
If body temperature rises, dilation of dermal vessels and increased sweat gland activity (_______________________________________________) cool the body.
Cold external environment
o Dermal blood vessels _____________________________________.
o Skin temperature drops to slow passive heat loss
Cutaneous Sensations
Cutaneous __________________________receptors – part of nervous system – detect temperature, touch, and pain
Metabolic Functions
• Synthesis of vitamin ________ precursor and _________________________.
• Chemical conversion of carcinogens and activate some hormones
Blood Reservoir
• Up to __________% of body's blood volume
Excretion
• _____________________________ wastes and salt in sweat
20

Homeostatic Imbalances of Skin (pp. 164–167; Figs. 5.8–5.10)
Skin Cancer
• Most skin tumors are ____________________________ (not cancerous) and do not
_____________________________________ (spread)
• Risk factors– Overexposure to UV radiation– Frequent irritation of skin
Three major types of skin cancer:
1. ___________________________________________
2. ___________________________________________
3. ___________________________________________
_____________________________ cell carcinoma results from invasive proliferation of cells of the stratum basale and is the least malignant and the most common skin cancer.
_____________________________cell carcinoma derives from the keratinocytes of the stratum spinosum and tends to grow rapidly and metastasize if not removed.
______________________________is a cancer of the melanocytes and is the most dangerous of the skin cancers because it is highly metastatic and resistant to chemotherapy.
21

The ABCD rule is used to evaluate moles or pigmented spots for cancer and corresponds to Asymmetry, Border irregularity, Color, and Diameter.
A:
B:
C:
D:
Burns
• Tissue damage caused by heat, electricity, radiation, certain chemicals– Denatures __________________________________– Kills cells
• Immediate threat:– ________________________ and __________________________ imbalance
• Leads to ____________________ shutdown and circulatory shock.
• To evaluate burns:– Rule of nines– Used to estimate volume of fluid loss
22

Figure 5.9 Estimating the extent and severity of burns using the rule of nines.
23

Burns are classified according to their severity:
24

________________________________burns involve damage only to the epidermis.
_______________________________burns injure the epidermis and the upper region of the dermis.
______________________________ burns involve the entire thickness of the skin.
Partial-thickness burns:• First degree:
– ___________________________________________________________
– ___________________________________________________________
• Second degree:– ___________________________________________________________
– ___________________________________________________________
Full-thickness burns:• Third degree:
– ___________________________________________________________
– ___________________________________________________________
– ___________________________________________________________
– ___________________________________________________________
Figure 5.10 Partial thickness and full thickness burns.
25

• Critical if:– >____________% of body has second-degree burns
– >____________% of body has third-degree burns
– Face, hands, or feet bear ________________-degree burns
• Treatment includes:– ______________________________________
– ______________________________________
– ______________________________________
– ______________________________________
26