PIN 2008-01, Defining Scope of Project and Policy for Requesting ...
Defining your Data Quality Project Scope
-
Upload
helpitsystems -
Category
Business
-
view
301 -
download
0
description
Transcript of Defining your Data Quality Project Scope

Defining Your Data Quality Project
Scope

Intro
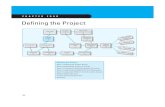
Define your data quality project scope by following these guidelines:
Consider the main product functions and processing modes
Develop your required features
Establish project parameters
Create a budget and timeframe
Establish an evaluation strategy

Define the Main Product Functions
Data Quality product suites span a broad range of functions and in varying combinations.
Develop an understanding of the features and how they apply to your business in order to establish what will work for you
The functions listed below are standard in a Data Quality package, and are listed in order of process flow

Select Main Product Functions
Standardization General ‘cleansing’ functions Fixing misspellings, inconsistencies, transpositions and the like Moving data across columns, adding state names, zip codes,
titles in places where they are missing
Address Validation (Verification) Matching contact data to standard Postal Address Files (PAF) or
USPS and NCOA Data to validate and update addresses CASS Standardization

Select Main Product Functions
Data Enrichment Expanding and enhancing your existing contact data with
additional datasets. The variety of datasets includes names data, date of birth, length
of residency, phone and fax numbers, SIC codes, geocoding data and more.
Matching/Deduplication Matching records within a file or between multiple files for
merging and purging duplicate records, identifying your best customers or a multiplicity of other reasons.
A simple count of duplicates, suppressions or records matched is essentially meaningless – it is the number of true and false matches that is significant.

Select Main Product Functions
Record – Linking/ Single Customer View ‘Link’ specific records to one another, specifically for the purpose
of creating a single master record (or golden record) Master record includes all relevant data for a specific contact
including email preferences, transactions and customer service history
Generates the elusive Single Customer View (or 360 Degree View)

Consider Main Processing ModesNot all vendors will handle all applications. Consider what processing modes are critical to your data quality
Batch (Existing Data) Often referred to as “batch data cleansing” Cleansing of data already in your database Curative measure
Batch (Load Data) Batch processing is also used to match data across files Preventative measure
Real Time (Interactive) Tools that work interactively to warn the user entering data that the
information already exists, or if the information is invalid Preventative measure
Real Time (Firewall) New records are captured without the user correcting any of the info The record is validated and corrected in the background, or logged for
manual attention by someone later Preventative Measure

Consider Main Processing ModesWith this information background, the current objective is to identify your ideal solution based on the business objectives and data quality functions you need to achieve your goals
Think ahead to your anticipated needs, granularly and globally
Consider larger data projects that may impact the needs of the tools that you invest in
Processing Needs:

Develop Your Required FeaturesHere are other items to consider when developing your list of Required Features:
• Some companies use different terminology for the same feature.
• Some data quality tools are modular and will offer features or sets of features in individual components with different price points and installations.
• Consider where a new or improved application or process would be the best direction to go in

Features WorksheetStandardization Features Nee
dWant
Correct poorly structured and non – standard recordsIdentify Foreign RecordsFlag inappropriate data in name and address Flag garbage or incomplete data Intelligent casingSalutation generation from names Address Standardization
Address Verification Capabilities Need
Want
Integration of addresses against Postal Address Files/U
Control over updates to postcode/address
Update record with mail format address
Split address completely into component parts

Features Worksheet Data Enrichment Capabilities Nee
dWant
Append geocoding data
Append consumer data
Append business data
Record – Linking Features Need
Want
Grouping/ Linking of matches
Master record identification
Retain information from duplicate records
Reassign orphaned records
Real-time view across databases for inquiry and data capture

Features WorksheetMatching and Deduplication Features Nee
dWant
Fuzzy matching
Grading of matches
Tuning of matching rules
Ability to automate matching
Manual review of matches
Multiple level of matches in one pass
Matching on non – standard data
Matching allows for missing and inconsistent data
Effective matching out – of – the – box
Customizable matching reports
Matching files in different formats

Processing Modes WorksheetBatch (Existing Data) Nee
dWant
Integrated into your database to clean up existing data
Timely and efficient single file matching
Timely and efficient address verification
Batch (Load Data) Need
Want
Load new batches of data
Easy to load data in different formats
Rapid matching of small batches of new data against a large master file Automatic scheduled operation of solution
Production of standard management and exception reports

Processing Modes WorksheetReal – Time (Interactive) Nee
dWant
Integrated into your database at point of capture
Real time feedback on data errors
Rapid address entry using Postcode
Intelligent inquiry to find exact matches
Real – Time (Firewall) Need
Want
Run on individual records entering the database
Additional Notes:

Establish Project Parameters
Don’t ignore the need for strategies and guidelines to keep both your vendors and your organization on track
Be flexible as you go through the evaluation process, especially when it comes to moving parts such as budget and timeframe
Having a plan and some goal parameters in place will be priceless and may mean the difference between getting the project off the ground or letting inertia win out

Anticipated Budget (Potential Savings)
Ballpark the potential cost savings of improving your data
Vendors can help with data analysis
Typically there are as many as 10% duplicates in a database. Assume you have 5% duplicates in your system, start from there
Try to calculate money wasted on advertising, resources needed to handle customer shipping complaints, or how much more money you would make if you had more control over marketing
Take a look at the high and low end of vendors you have created on your shortlist
Rather than call a data quality company and ask for a price, develop your list and create your price range based on the functions and features you need

Timeframe
At the beginning stages this will be more of an awareness technique rather than a goal, and will evolve over the course of your evaluation
Seek input from vendors and your internal team to keep a realistic approach
If there is an internal goal that you have set, plan your time by working backwards from that date
Budget time for all key steps including:
Internal Planning
Searching for vendors
Initial review
Demoing the short list
Internal Decision making
Negotiation
Implementation and Training

Review and Approval Team
Be aware of all of the necessary influencers, decision-makers and budget approvers that need to be a part of this process
By making the vendor aware of these key departments early on, they will be able to work with you through the approval process by:
Requesting presentations to all influencers on the team
Making demo software available to all potential users
Helping you with documentation to make the case for a C – level executive

Establish Your Evaluation Strategy
Evaluate the applications selected.
Knowing your strategy in advance will help you communicate expectations and guidelines to your vendors, and inform your internal staff and approvals team so that the process stays on track
Some considerations for this strategy are below

To RFP or Not to RFP
Distribute a Request for Proposals (RFP/RFQ) to a list of vendors, to help with your evaluation
Submitting a formal bid obligates you to perform a completely fair, balanced and unbiased evaluation that follows a set of rules and guidelines set out in the bid
Referrals, the unexpected and sheer gut instinct do not get to play a part, which ultimately may mean that you may not get to choose your preferred vendor

Demo Data or Real Data
This will likely be the first question asked of you when making contact with vendors
Evaluate a solution on your own data.
Sometimes this is not possible right away, or even necessary. You may have such basic needs that preparing your own data is not necessary
Prepare your sample data accordingly to do a thorough and efficient test of the software

Who is Driving the Ship
Determine whether the project will be spearheaded by the business or technology department before starting your evaluation
E.g. If you are from a business department but, after identifying your requirements, decide that the organization is likely to take an integrated approach, it may be best to hand off the lead role to a technology representative (or vice versa)

Gather the Appropriate Documentation and Files
Documents that you should gather before and during this process:
Request for Proposal (if appropriate) using the functional and feature requirements outlined here
Required Features List (with columns outlined for your individual shortlist vendors)
Demo data
Review/Approval forms for the members of your team
Budget Spreadsheet

Keep These Things In Mind
Review the list of main product features and processing modes in order to interpret what functions you need for your data
Establish a timeframe and budget for your project, with input from vendors and the internal team
Remember to keep vendors and your internal team on the same track in order to help the process run smoothly

Contact helpITUS HEADQUARTERS(The Americas, Australia, New Zealand)
helpIT systems inc.51 Bedford Rd.Suite 9Katonah, NY 10536United States
US Toll Free: 866.332.7132US Local: 914.600.7240Australia: +61 280363191Fax: 914.232.1429Email: [email protected] TECHNICAL SUPPORTSupport: 866.matchITEmail: [email protected]
EUROPEAN HEADQUARTERS(UK, Europe, Asia)
helpIT systems ltd.15-17 The Crescent.LEATHERHEADSurreyKT22 8DY
United KingdomTel: +44 (0) 1372 360070Fax: +44 (0) 1372 360081Email: [email protected]
TECHNICAL SUPPORTSupport: +44 (0) 1372 225904Email: [email protected] Registered in EnglandRegistered Office: as aboveCompany No. 02007292VAT No. 564228340