Ddst r Ppihe July 2010
-
Upload
iibhidayat -
Category
Documents
-
view
213 -
download
0
description
Transcript of Ddst r Ppihe July 2010
-
Developmental Screening and Surveillance
DENVER IIPaola Carugno, MD7/27/2010
-
Why me? MDs have access to young children and families.Familiarity with social, familial factors.Professional guidelines: AAP Committee on Children with Disabilities, Bright Futures.
-
Development in WCCSurveillanceScreeningDDST II
-
Surveillance
a flexible, continuous process in which a knowledgeable professional performs skilled observations of children during child health care
USE IT AS A GROWTH CHART
-
Screening
Process of testing whole populations of children at various set ages to detect those at high risk for significant, unexpected deviations from normal.
-
ScreeningProcess of identifying children with an atypical development.About 16% of children have disabilities.Early identification will improve outcome.
-
How to screen?Variety of techniques currently in use: Reviewing developmental milestones. Informal collection of age-appropriate tasks.Clinical judgment based on history, exam.Formal screening with standardized testing.
-
ScreeningASQPEDSPEDS:DMDDST
-
SurveillanceComponents:Eliciting/attending to parents concernsObtaining a relevant developmental historySkillfully observing childrens development (not estimating)
-
When to screen?At least 3 times before age 3:9 month18 month24-30 monthScreening tests should be done when suspicions of delay arise
-
DDST-RRevised, re-standardized in 1988Sensitive, but with limited specificity and predictive value (high referral rate)Use it to aid monitoringUse in second stage screening (following a parents questionnaire)Interpret the results in context of childs functioning and circumstance.
-
Denver II
0 to 6 yearsNot an IQ test, not predictor of outcomeCannot generate a diagnosisNot a substitute for testingJust compares children of the same age
-
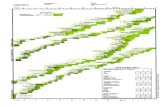
Denver II4 Areas of function: Personal-Social, Fine Motor-Adaptive, Language, Gross motor.
-
Calculating ageDate of testyear month dayDate of birthyearmonth dayIf needed, borrow: 12 30Adjusting for prematurity (if born more than 2 weeks early, and younger than 24 months)Age of the child, - weeks early (in months and days)
-
IntroductionReassure caregiverTest is not an IQ testThe child is not expected to pass all itemsDetermine developmental status
-
AdministrationFlexibleScore what you seeFollow a certain order: First do items (R), less active participation, easier tasks, same materials on the table.
-
Administration3 items to the left andEvery item crossed, OREvery item until 3 failures are recorded (Ceiling).If the child fails, then continue testing items to the left until 3 items are passed (Basal).
-
AdministrationUp to 3 trialsTest behaviorItem scoring: P (Passing), F (Fail), N.O. (no opportunity), R (refusal)
-
InterpretationAdvanced items: Child passes an item to the right of the age lineNormal items: Child can pass, fail or refuse an item between the 25th and 75th%Caution: refuses or fails an item between 75th and 90th %Delayed: refuses or fails an item completely to the left of the age line.
-
Follow upNormal: no delays and a maximum of 1 caution. Routine follow up.Questionable: 1 delay and/or 2 or more cautions. Offer stimulation suggestions and repeat in 3 monthsAbnormal: 2 or more delays, or fails twice 3 months apart. Refer to EI.