Data Communication. What is data communication? Data communications deals with the transmission of...
-
Upload
jacey-kerr -
Category
Documents
-
view
219 -
download
0
Transcript of Data Communication. What is data communication? Data communications deals with the transmission of...

Data Communication

What is data communication?
• Data communications deals with the transmission of signals in a reliable and efficient manner
• Ultimately, it’s about transmitting data (i.e., bits) across some physical transmission medium:– Electricity - copper wire, twisted pair, undersea cable– Light - infra-red through air, laser through fibre-optic
cable– Electromagnetic radiation - radio, microwave, satellite

What is understood by the term ‘communication’?
• The term communication is defined as the act of disseminating information.
• It presupposes that:1. there is information to disseminate
2. the desire or requirement to disseminate exists
3. there is an agency to send/transmit information
4. there is a means of encoding information
5. there is a medium to carry the information
6. there is a recipient to receive the information
7. the recipient is capable of understanding the information received

Communication • Let us generalize
the process just described
• In any communication between two entities the following properties are required:1. Modulation:2. Signal compatibility3. Signal strength4. Data rate5. Protocol6. Demodulation
• In a face-to-face conversation between two individuals following takes place:
1. Conversion of brain waves into speech.2. Agreement of both individuals on which
vocabulary to use.3. Agreement of both individuals on volume
level at which both can be heard comfortably.
4. Agreement of both individuals on the rate of talking at which each can understand the other’s speech.
5. Agreement of both individuals on the rules used to decide when to speak and when to listen, i.e. how the flow of information is managed.
6. Conversion of the audio signals into brain waves.

Communication Model
• Source– generates data to be transmitted
• Transmitter– Converts data into transmittable signals
• Transmission System– Carries data
• Receiver– Converts received signal into data
• Destination– Takes incoming data

Diagram of Simplified Communication Model

Key Communications Tasks
– Transmission System Utilization– Interfacing– Signal Generation– Synchronization– Exchange Management– Error detection and correction– Addressing and routing– Recovery– Message formatting– Security– Network Management

Simplified Data Communications Model

Basic Elements of a Communication System
• In any communication between two entities the following 10 elements can be identified:
1. A Sender.2. A Receiver.3. Addressing, to identify where the Receiver is.4. Protocol – a set of co-operation rules to achieve
communication.5. Transmission code - an agreed “language” to be used.6. Transmission rate - the speed at which “what is being
communicated” is being sent.7. Transmission synchronisation - how to recognise what is
being communicated.8. Transmission medium.9. Error detection and correction.10.Transmission efficiency - how much overhead must be
added to manage the transmission.

Transmission Media • Two wire -“telegraph wires” seen in old films.
• Simplest arrangement, with two wires, separated by air.• Can pick up interference, and suffer “crosstalk”.• Only reliable for low data rates.
• Twisted Pair - currently used for domestic phones
• Two insulated wires twisted together.– Any interference affects both wires equally.– May also have an additional protective screen of metallic foil –
“shielded twisted pair”.– Suitable for short distance medium speed links.– Suffers from “skin effect”, leading to higher resistance at higher
data rates.» “Skin effect” – HF signals carried only on skin of wire, in effect reducing
the area of the wire from a solid wire to a tube of the same diameter.

Transmission Media • Coaxial cable - commonly seen on TV aerial leads
– Single central wire, separated from woven outer conductor by plastic insulation.
– Not prone to interference.– Can support medium to high data rates.
• Optical Fibre– Similar to coaxial cable in appearance:
» Uses single strand of glass as core, with light shield around it.
– Immune to electrical interference , and difficult to eavesdrop
» Often used in industrial or other electrically “noisy” environments.
– Capable of high data rates– Mechanically weaker than electrical wires, and difficult
to join.

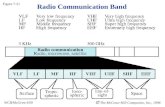
Transmission Media • Microwaves -ultra high frequency radio waves
– Line of sight from sender to receiver.– No need for wires, so good across rivers, or main roads– Extremely high data rates
– Satellite microwaves:– Mainly through space so long lines of sight.– Little human interference, but affected by extreme solar
activity.
– Terrestrial microwaves:– Need repeater stations if lines of sight short
» Curvature of earth, or mountains, or buildings

Data Transmission Terminology
• Transmission may be simplex, half-duplex or duplex.
– Simplex – in one direction only.– Half-duplex – in both directions, but only in one direction
at any time.– Full-duplex – in both directions simultaneously, if
required.
• Transmission media may be guided or unguided. – Guided – the medium is bounded and the transmission
contained within it (e.g. fibre-optic or electrical cable)– Unguided – the medium is unbounded (e.g. radio waves
in the air, or in space).

Data Transmission Terminology
• In a direct link, (or data link), a transmission path:
– Propagates signals directly from transmitter (sender) to receiver
– With no intermediate devices.» except amplifiers (or repeaters) to increase signal
strength.
• In guided transmission media– A configuration is point-to-point if it provides a direct link
between two devices, and those are the only two devices sharing the medium.
– A configuration is multipoint, if more than two devices share the same medium.

Data Transmission Terminology
Medium
(a) Point-to-point
Connection with amplifier
(b) Multipoint
Guided transmission configurations
AmplifierTransmitter / Receiver A
Transmitter / Receiver B
Medium Medium
Transmitter / Receiver A
Transmitter / Receiver B
Transmitter / Receiver C
Transmitter / Receiver D

Data Encoding • Encoding means changing how data are
represented.– This can be for convenience:– Morse code alphabet used in early radio transmissions.– Encoding to hide the meaning of data is “encryption”.
• Computer data are represented in an encoded form for storage or transmission within and between computers.
– The most common codes used to store digital data are:» ASCII (American Standards Committee for Information
Interchange)
» EBCDIC (Extended Binary Coded Decimal Interchange Code)

Data Encoding • Data are transmitted using electromagnetic
signals.• Data exists in analogue or digital forms.• Analogue or digital data can be encoded using
either analogue or digital signals.– For example digital data can be transmitted using analogue
signals.– The telephone network traditionally used analogue signals to
represent voices.– The telephone network was well-established when transmission of
digital computer data became necessary.
• The latter allows normal computer communications using widely available telephone lines.
– This is achieved using Modems.

18
Analog vs. Digital Signal

Data Encoding
0110010analogue signals
Transmission direction
Computer Modem PrinterModem0110010
digital signals
Modulation is the conversion of the digital signal into an analogue signal, and demodulation converts the analogue signal back into a digital signal. These processes are carried out by a Modem.
Another device used is a Codec (coder-decoder).
All transmissions occur within a range of frequencies called the Bandwidth.

Signalling Technologies
• Baseband is the transmission of digital signals without modulation.
• In a baseband communication network, digital signals (0s and 1s) are put onto the medium as voltage pulses.
• The entire bandwidth is consumed by the signal.
• Broadband uses coaxial cable to provide data transfer by means of analogue signals.
• The bandwidth is divided in different frequency bands or channels.
• In a broadband communication network involving computers, digital signals are passed onto the medium through a modem and transmitted over one of the channels. So, several different communication networks can be implemented over the same medium.

Signalling Technologies
• Analogue transmission is used to mean the transmission of analogue signals without regard to their content.
• Digital transmission, on the other hand, is used to mean the content of the signal.

Data Transmission : Data and Signals
SignalData Analogue Signal Digital Signal
Analogue Data
Two alternatives:1) Signal occupies the samespectrum as the analogue data;2) Analogue data are encoded tooccupy a different portion ofspectrum
Analogue data are encodedusing a codec to produce adigital bit stream
Digital Data
Digital data are encoded using amodem to produce analoguesignals
Two alternatives:1) Signal consists of two
voltage levels to representthe two binary values
2) Digital data are encodedto produce a digital signalwith desired properties

23
Data vs. Signal

Data Transmission: Treatment of Signals
TransmissionSignal Analogue Transmission Digital Transmission
Analogue SignalIs propagated throughamplifiers. Same treatmentwhether signal carriesanalogue or digital data
Assumes that theanalogue signal carriesdigital data. Signal ispropagated throughrepeaters
Digital Signal Not usedDigital signals representa stream of 0s and 1s.Signal is propagatedthrough repeaters

Transmission Synchronisation
• Synchronisation is essential for transmitter and receiver to understand each other.
• In serial transmission the following types of synchronisation are required:1. Bit synchronisation - how to detect each bit.
2. Byte or character synchronisation - how to group the bits to make a character or byte.
3. Block synchronisation - how to group the characters/bytes to make a block (a frame or a packet)
• Bit synchronisation depends on how the signal is encoded

Transmission Synchronisation
• In serial transmission there are two standard ways of achieving character and block synchronisation:
• Asynchronous Transmission or Character Synchronisation– The time interval between characters is random.– Each character is synchronised by the use of a start
bit, and either one or two stop bits.– The bit rate is constant on a per character basis

Transmission Synchronisation
• Synchronous Transmission or Block Synchronisation– Each block is synchronised by the use of a number of
synchronisation characters that are transmitted first– These are followed by a start of block character,
which is followed by the data block, and transmission is finished with an end of block character.
– The bit rate is constant for the whole transmission of the block I.e. the time interval between characters is fixed.

Asynchronous vs. Synchronous Transmission
Asynchronous Transmission Synchronous Transmission
Start and Stop bits reduce efficiency More efficient use of bandwidth
A character can be transmitted atrandom times
Characters buffered into blocks fortransmission
Variable idle time between characters No idle time between characters
Constant bit rate within a character.No limit on block length
Constant bit rate over a block. Blockslimited to a maximum size
Low speed communications (19.2Kbits/s)
Higher speed communication( 10 Mbits/s)
Synchronisation errors result in lossof only a single character
Synchronisation errors result in lossof a complete block

Data Transmission: Modes
• Computer based communications always use Digital Transmission, – What is transmitted is digital data, using either an
analogue or digital signal.– Normally, the digital data are recovered and repeated
at intermediate points to reduce the effects of noise.
• Irrespective of the type of communications facility being used, in most applications data are transmitted between computers in a bit-serial mode,more commonly known as serial transmission.

Data Transmission: Modes
• Within a computer, data are transferred in a word-parallel mode, most commonly known as parallel transmission.
• In computer communications is necessary to perform a parallel-to-serial conversion, in the transmitter, serial-to-parallel conversion in the receiver.
• These conversions are done in the computer interface to the network

Transmission efficiency
• Extra bits (start and stop bits) and characters (synchronisation and block delimiters) are needed to implement asynchronous and synchronous transmission.
– These add nothing to the content of the message, but must be included in what is sent.
– They reduce the overall information capacity of the transmission
– They reduce the overall efficiency of the transmission.

Transmission efficiency
• Transmission efficiency = (useful data/total bits transmitted)*100– For example for asynchronous transmission of 8-bit
characters with 1 start and 1 stop bit, we have to send 10 bits for each character:
– Transmission efficiency = (8/10)*100 = 80%
• Effective Data Rate = (Transmission Efficiency/100)*Capacity

Transmission Codes
• Symbolic data/information must be encoded in a format suitable for transmission.
• Normally, the codes used for transmission are similar to the codes used to store the information.
• The most common code is ASCII– ASCII is a 7-bit code, permitting 128 different symbols to
be encoded.• The second most commonly used code is EBCDIC
– EBCDIC is an 8-bit code enabling 256 different symbols to be encoded.

Networking

35
Data Communication vs. Networking
• Communication: Two Nodes. Mostly EE issues.
• Networking: Two or more nodes. More issues, e.g., routing

36
Distributed Systems vs. Networks
• Distributed Systems:1. Users are unaware of underlying structure.
2. Mostly operating systems issues.
3. Nodes are generally under one organization’s control.
• Networks: 1. Users specify the location of resources.
2. Nodes are autonomous.

Networking
• Point to point communication not usually practical– Devices are too far apart– Large set of devices would need impractical number
of connections
• Solution is a communications network

What are computer networks?
Networking deals with the technology & architecture of the communications networks used to interconnect communicating devices.
Computer network is a collection of autonomous computers interconnected by a single technology.
The Internet is not a single network but a network of networks.

39
Types of Networks
• Point to point vs. Broadcast• Circuit switched vs. packet switched• Local Area Networks (LAN)
vs.
Metropolitan Area Networks (MAN)
vs.
Wide Area Networks (WAN)

Communications Networks
• A Communications Network is a set of interconnected devices that provide data transmission facilities between user's end points.
User
UserUser
User on Host B
Communications Network comprising communications
links and connecting computers
User on Host A

Simplified Network Model

Objectives of Networking
• To share and exchange data between systems;• To share expensive resources;• To facilitate communication among humans and
machines;

Some terminology
• Host – a machine on the network;• End system/end point – a machine “on the
edge” of the network, rather than an “internal” (switching) node;
• Subnet – sub network, a subset of the whole network;– Also used to refer to the internal “routing” part of a
network.
• IMP – Interface Message Processor, hardware connecting host to network.

Some terminology
• Packet – we often break messages into many chunks, sent separately. The chunks are called packets.– Size of packet and how it’s treated depends on
network protocol in use.– A packet might get split up further by another
protocol.– Some protocols (e.g. IP) use varying size packets; in
others (e.g. ATM) they’re fixed. Small fixed-size packets are called cells

Some terminology
• internetworking – act of connecting multiple networks together to form a larger network;– Fun issues include how to route and address
across multiple heterogeneous networks;• internet – a network thus produced
– Also the name of a common protocol for doing this (IP);
• Internet – “the” global internet;

Network sizes
• Computer Networks can be classified by the area they cover:– PAN – Personal Area Network: very small– LAN – Local Area Network: room/building/campus– MAN – Metropolitan Area Network: city, region – WAN – Wide Area Network: country/continent.

47
Interconnection of Networks
• Networks of low capacity may be connected together via a backbone (network of high capacity)
• LANs and WANs can be interconnected via T1 or T3 digital leased lines
• According to the protocols involved, networks interconnection is achieved using one or several of the following devices: – Bridge: a computer or device that links two similar LANs based on the same protocol.
– Router: a communication computer that connects different types of networks using different protocols.
– B-router or Bridge/Router: a single device that combines both the functions of bridge and router.
– Gateway: a network device that connects two different systems, using direct and systematic translation between protocols.

Broadcast vs. Point-to-point
• Broadcast Networks:– A single communication channel shared by all
machines on a network;• Multicast: simultaneous transmission to a subset.
• Point-to-point networks:– Many connections between individual pairs of
machines;– Transmission from A to C might go via B;– Often multiple routes: a fundamental question is
which to use?

Local Area Networks
• A Local Area Network (LAN) is a computer network intended to link computers and associated devices within a small geographical area.
• The linking distances are relatively short, with cable lengths rarely exceeding 5 kilometres.
• The linked computers may include large computers, word processors, or desktop computers.
• Associated devices include computer terminals, printers, plotters, scanners, etc.

Local Area Networks
• LANs normally offer much higher data transmission rates than WANs.– This difference is apparent in the network oriented
protocols only.
• At application level, LANs provide the sharing of resources like programs, files, printers, plotters, scanners, etc.

LAN Topologies
• LAN topology is one of the issues that must be considered when selecting LAN technology.
– It defines the interconnection of stations to form the network.
• LAN topologies are classified as:– Broadcast topology– Store-and-forward topology

LAN Topologies
• Broadcast topology» This implies that all stations are connected
to a common transmission medium.
• Store-and-forward topology» A complete message or packet is received
into a buffer in the memory of an intermediate station
» It is then re-transmitted on the route to its destination.
» The stations in a store-and-forward topology network are connected by independent point-to-point transmission lines.

LAN Topologies
• The topology of a LAN is important because it influences the following features of the network:– expansion cost
• the incremental cost of adding another station to an existing network.
– reconfiguration capabilities• the ease of modifying the topology to deal with a failed node
or component.
– reliability• The extent of dependency on a single component for network
operation.

LAN Topologies
• As well as:• software complexity
– the complexity of the protocols required to achieve communications.
• performance– The effectiveness of the LAN in terms of throughput, or
delays in transmission.
• broadcast capabilities– how difficult it is to broadcast in the LAN, i.e. to transmit
a single message which is received by all other stations in the network.

Bus Topology
Single medium to which all hosts are connected
Hosts
The bus is a broadcast topology – anything placed on the medium by one host is available to all hosts attached to the bus.
If the destination address is recognised by a node it copies the contents into that node.
Network connection cable between NIC on host and the network medium

Ring TopologyThe ring is a store-&-forward topology – a packet placed on the medium by one node is received by the next node along, and is then resent by that node, and so on.
If the destination address matches that of the receiver, the packet is not resent.
If the sender’s address matches that of the receiver, the packet has gone all the way round and will not be resent. It is a “lost” packet and is effectively removed from the ring.

Star Topology
The star is a store-&-forward topology – a packet placed on the medium by one node is received by central node which is forwarded to it’s destination by the central node.
Central node

Hub Topology • The “hub” is derivative of the bus and ring
topologies– It has the appearance of the star topology, with a central
hub in place of the central node.– The hub is simply the bus or ring wiring “collapsed” into a
central unit.– Unlike the central node in the star topology, the hub does
not perform any switching. The hub simply consists of a set of repeaters.
• Many modern networks are implemented using hubs for convenience.
– Care is needed when deciding what topology is being used in a real network.

Hub Topology : Network with and without hub
Bus network – long network “backbone” installed through building, with short network connection cables between host computers and backbone.
The same bus network, implemented using a hub
Hub containing network “backbone” and stubs of connection cables
Network connecting cables extending through the building to the host devices

Network topologies
• Tree• Corresponding to
an organisational hierarchy?
• Internal nodes maybe bottlenecks.

Network topologies
• Graph– Generalisation of a
tree– Cycles allowed
• Complete graph (Mesh)– Dedicated link from
every node to everyother node
– Rapidly becomes prohibitively expensive

62
Communications System

63
Communications System
• A communications system is the combination of network hardware and communications system software that supports the communications between user-oriented processes running in remote computers.
• The communications system provides the services required by the applications to communicate. These services are outlined on the next slide.

64
Communications System
• Communication System Functions– Naming and Addressing of entities.– Segmenting and reassembly of messages– Blocking of messages– Connection or session control– Error control– Congestion and flow control– Synchronisation– Priority

65
Communication System Architecture
• The user-oriented layers:• The application offers services to users through a
set of rules or steps for accessing web-sites or sending e-mails.
– Some applications operate on different types of user-interface. A means of converting alphabets and screen formats may be needed
– Some applications require a session of activity with a definite set-up and closedown of the session (e.g. logon and logoff)
• The transport layer provides an end-to-end virtual channel between the source and destination.

66
Communication System Architecture
• The system-oriented layers:– Implement the connections between nodes that make
a machine part of a communications network– The network layer is responsible for routing between
nodes– The Data link and Physical layers provide the means of
moving packages of data between pairs of nodes.

67
Communication System Architecture
1. Application
2. Presentation
3. Session
4. Transport
5. Network
6. Data Link
7. Physical
• The ISO Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model has 7 layers:– The top 3 layers are user or application
oriented.
– The bottom 3 layers are system-oriented.
– The middle layer, transport, acts as a broker between the basic services provided by the network and the needs of the users
• Each layer can be thought of as “talking” directly to its peer on another machine.– A user of a web-browser holds a
“conversation” with a remote web-site
– Only at the physical layer does direct communication take place, using signals.

68
Communication System Architecture
1. Application
2. Transport
3. Network
4. Data Link / Physical
• The TCP/IP model has 4 layers:– The top layers is the application.– The bottom 2 layers are system-oriented.– The middle layer, transport, acts as a broker
between the basic services provided by the network and the needs of the users.
• Although the model is simpler than OSI it recognises the same purpose and requirements.– The transport level protocols are TCP and
UDP– The network level protocol is usually IP– The data link and physical level protocols are
specific to the network

69
Communication System Architecture
1. Application
2. Transport
3. Network
4. Data Link / Physical
1. Application
2. Transport
3. Network
4. Data Link / Physical
Application-level protocol based on messages used by the application. For example, the PIN
and card details from a bank card
Transport level data packets exchanged using transport protocol
Network level data packets exchanged using network protocol
Data Link frames exchanged using data link protocol.
Frames transmitted over the physical medium using appropriate signalling techniques
Communications Network

70
Communication System Architecture
Application-level protocol1. Application
2. Transport
3. Network
4. Data Link / Physical
3. Network
4. Data Link / Physical
3. Network
4. Data Link / Physical
Transport-level protocol acting end-to-end – e.g. TCP
IP IPIP
1. Application
2. Transport
3. Network
4. Data Link / Physical
Host A Host BNetwork
Intermediate nodes inside network
DC
Node DHost A Host BNode C

Circuit Switching vs. Packet Switching
• Fundamental question: how to move bits from one host to another, via ‘n’ others?
• Two key approaches (opposed):– Circuit switching
• Establish fixed-bandwidth circuit & use it;
– Packet switching• Split messages into packets, send separately;
• Trend is very much towards packet switching.

Circuit Switching
• Resources along a path are reserved for duration of communication.– Buffers, link bandwidth, CPU time, etc.
• All nodes on path genuinely maintain connection state information;
• All data in a some communication is sent on the same circuit, through same nodes;
• Classic example: PSTN (Public Switched Telephone Network)

Circuit Switching

Circuit Switching
• Each circuit has a fixed bandwidth for its lifetime.• Channels typically split into n equal bandwidth
circuits.
• Pro: Makes QoS (Quality of Service) guarantees easy to achieve;
• Con: Wasteful during “silent” periods.– Data transmission tends to be bursty.

Circuit Switched Multiplexing
• Multiplexing – combining information channels onto a common transmission medium.
• FDM (Frequency Division Multiplexing)– Frequency spectrum of link is shared among circuits;– Typically, each of n circuits gets 1/n;– e.g. PSTN bandwidth divided in 4KHz bands;
• TDM (Time Division Multiplexing)– Time divided into fixed size chunks;– Each circuit gets a portion of the total time

Packet Switching
• No prior reservation of resources;• Each packet transmitted separately;• Nodes don’t maintain connection state
information:– Each packet dealt with individually;– Two packets might take different paths;
• Classic example: the Internet.

Packet Switching
• Con: QoS harder to do, can only really make “best effort” promises;– IPv6 addresses this somewhat – complex;
• Pros: more efficient use of bandwidth, no hard limit to number of comms.– Ideally: “graceful degradation” curves;– What happens when queues fill? Delays and,
ultimately, packet loss.
• Store-and-forward (on routers):– Read entire packet in, then send it out

Packet switching

Delay & Loss in Packet Switching
• Processing delay– Time to examine packet & decide where to send it;
maybe also some error checking;
• Queuing delay– Delay while packet is queued; depends on size of
queue, ie traffic levels;
• Transmission delay– Time taken for node to “push out” packet;– Depends on size of packet & speed of outbound link.

Delay & Loss in Packet Switching
• Propagation delay– Time taken for packet to propagate across link to next
node;– Depends on speed of physical medium and distance
to next node;
• Packet loss– Happens when things get too busy, queues overflow,
nodes can’t keep up;
• End-to-end delay– Total delay on transmission between two end points.

Frame Relay
• Packet switching systems have large overheads to compensate for errors
• Modern systems are more reliable• Errors can be caught in the end system• Most overhead for error control is stripped out

Asynchronous Transfer Mode
• ATM• Evolution of frame relay• Little overhead for error control• Fixed packet (called cell) length• Anything from 10Mbps to Gbps• Constant data rate using packet switching
technique

Virtual circuits vs. datagram networks
• We can, in fact, simulate circuit switching on packet switched networks:– Virtual Circuits being the result;
• Otherwise, it’s a datagram network:– Datagram: another word for packet;
• Choice has huge impact on routing;– At IP level, Internet is a datagram network

Virtual Circuit Networks
• Packets carry VC identifier;• Hosts have table mapping VCIDs to outbound
connections;• Setting up involves both ends and every host in
between;• Every packet follows the same path;• Requires complex state maintenance protocols.

Datagram Networks
• Packets carry destination address;• Host has (more complex) table to help it decide
where to send next.– Table at a given host can change over lifetime of a
communication;
• Packets really can take different paths;• No connection state information maintained
(except maybe at ends);• Almost all of the Internet.

Connection-oriented vs. Connectionless Services
• Characterises end-to-end communication services available to end users.
• Connection-oriented:– Application must establish connection to other end
before sending any actual data;– Each packet then sent via that connection.
• Allows delivery guarantees.
• Connectionless:– Application just sends each packet individually;– Thus, must know destination address every time you
send a packet.• No guarantee of delivery, generally.

Caution: don’t get confused…
• Circuit-switched vs. packet switched:• Concerns how packets are routed;• Distinction made in “core” of network;• Mainly at Network layer (see later).
• Connection-oriented vs. connectionless:• Concerns how packets are sent/received;• Distinction made at “edge” of network;• Mainly at Transport layer (see later).

88
Basic Types of Networks
Yet another way to classify…

89
Basic Types• Peer-to-peer
– Does not require dedicated resource (dedicated server) – Any host can share its resources – Typically less expensive, easier to work with – Less secure, support fewer users (10 or fewer), experience more
problems with file system management
• Server-based – Configuration of nodes, certain of which are dedicated to
providing resources (servers) – Offer (better) user security – Dedicated servers can be expensive, may require a full-time
network administrator
• Enterprise network (which combines the two) – Provide connectivity among all nodes in an organization – Include (connect) both peer-to-peer and server-based
networks – May consist of multiple protocol stacks and network
architectures

Client/Server Networks
• Client/Server is a networking model mainly applicable at the Application layer;
• Concerns the roles of end systems:• Client – system requesting some service;• Server – system providing some service.
• Ubiquitous example: HTTP• Client is your web browser• Server is www.isy.vcu.edu (or whatever)

Peer Networks
• Not all applications use Client/Server model;• Often, all parties have equal status:
– In some sense they’re all clients and servers.– Although sometimes have distinguished nodes
providing certain services.

Protocols
• Used for communications between entities in a system
• Must speak the same language• Entities
– User applications– e-mail facilities– terminals
• Systems– Computer– Terminal– Remote sensor

Key Elements of a Protocol
• Syntax– Data formats– Signal levels
• Semantics– Control information– Error handling
• Timing– Speed matching– Sequencing
Protocols define format, order of messages sent and received among network entities, and actions taken on message’s transmission, receipt

In Summary, a protocol is ....
• An agreement about communication between two or more entities
• It specifies– Format of messages
– Meaning of messages
– Rules for exchange
– Procedures for handling problems

Protocol Architecture
• Task of communication broken up into modules• For example file transfer could use three
modules• File transfer application• Communication service module• Network access module

Simplified File Transfer Architecture

A Three Layer Model
• At the Top: – User Oriented layer-Application Layer
• In the Middle: – Transport Layer
• At the Bottom: – System Oriented Layer - Network Access Layer

Network Access Layer
• Exchange of data between the computer and the network
• Sending computer provides address of destination
• May invoke levels of service• Dependent on type of network used (LAN,
packet switched etc.)

Transport Layer
• Reliable data exchange• Independent of network being used• Independent of application

Application Layer
• Support for different user applications
• e.g. e-mail, file transfer

Addressing Requirements
• Two levels of addressing required• Each computer needs unique network address• Each application on a (multi-tasking) computer
needs a unique address within the computer• The service access point or SAP• The port on TCP/IP stacks

102
Addressing• Different levels of entity use different addresses.
• MAC address: Identifies the NIC and set by manufacturer.
– Used by Physical and Data Link layer
• IP address: Identifies a computer in a network.– Used by the Network layer
• Socket: Identifies a process (running program).– Used by the Transport layer
– Application level addresses vary:• One example is the Uniform Resource Locator
(URL) used by WWW applications

103
IP Addresses • IP = Internet Protocol
• Each IP address is 32 bits long
• An IP address has a network part and host part• The former identifies a specific network and the latter a
specific computer, or host, on that network.
• IP addresses may be in one of five network classes:
– Class A: Used for a small number of networks, each with many hosts.
– Class B: Used for a larger number of networks, each with a medium number of hosts
– Class C: Used for a large number of networks, each with only a few hosts
– Classes D and E are for special purposes.

104
IP Addressing Example
• All hosts on a network have the same network prefix

105
User Oriented Names and DNS
• Human users prefer names to numbers.• The communications system translates these
names into IP addresses, and vice versa.• The translation is done using the Domain Name
System (DNS) application.– This is a “directory” service.– It uses multiple levels of server to resolve
queries as close to the point of issue as possible.
– All servers cache query results to reduce need for repeat queries in the near future.

106
Name Resolution in DNS
• Each computer has a name resolver routine– ‘gethostbyname’ in UNIX
• Each resolver knows the name of a local DNS server
• Resolver sends a DNS request to the server• DNS server either gives the answer, forwards
the request to another server, or gives a referral– Referral = Next server to whom request should be
sent

107
How the DNS works
Requesting Host
Root Name Server
Local Name Server
Intermediate Name Server
Authoritative Name Server
A “requesting host” issues a query to its local name server to translate from a host name to an IP address. This request is routed to a server which can supply the IP address.
The root server may not know the IP address, but may “know the address of someone who does”. This can result in queries being forwarded to an “authoritative name server, via an intermediate name server, if necessary.
All name servers employ caches which store the results of recent queries. This can speed up later requests for the same IP address.
Name embedded in query IP address, or error
message, embedded in reply

Protocol Architectures and Networks

Protocols in Simplified Architecture

Protocol Data Units (PDU)
• At each layer, protocols are used to communicate
• Control information is added to user data at each layer
• Transport layer may fragment user data• Each fragment has a transport header added
– Destination SAP– Sequence number– Error detection code
• This gives a transport protocol data unit

Protocol Data Units

Network PDU
• Adds network header• network address for destination computer• Facilities requests

Operation of a Protocol Architecture

114
Standards
• Required to allow for interoperability between equipment
• Advantages• Ensures a large market for equipment and
software• Allows products from different vendors to
communicate
• Disadvantages• Freeze technology• May be multiple standards for the same thing

Standardized Protocol Architectures
• Required for devices to communicate• Vendors have more marketable products• Customers can insist on standards based
equipment• Two standards:
• OSI Reference model– Never lived up to early promises
• TCP/IP protocol suite– Most widely used

OSI
• Open Systems Interconnection• Developed by the International Organization for
Standardization (ISO)• Seven layers• A theoretical system delivered too late!• TCP/IP is the de facto standard

OSI - The Model
• A layer model• Each layer performs a subset of the required
communication functions• Each layer relies on the next lower layer to
perform more primitive functions• Each layer provides services to the next higher
layer• Changes in one layer should not require
changes in other layers

OSI Layers

The OSI Environment

TCP/IP Protocol Architecture
• Developed by the US Defense Advanced Research Project Agency (DARPA) for its packet switched network (ARPANET)
• Used by the global Internet• Not official model but a working one.
– Application layer– Host to host or transport layer– Internet layer– Network access layer– Physical layer

TCP/IP Protocol Architecture: Physical Layer
• Physical interface between data transmission device (e.g. computer) and transmission medium or network
• Characteristics of transmission medium• Signal levels• Data rates
• etc.

TCP/IP Protocol Architecture:Network Access Layer
• Exchange of data between end system and network
• Destination address provision• Invoking services like priority

TCP/IP Protocol Architecture: Internet Layer (IP)
• Systems may be attached to different networks• Routing functions across multiple networks• Implemented in end systems and routers

TCP/IP Protocol Architecture: Transport Layer (TCP)
• Reliable delivery of data• Ordering of delivery

TCP/IP Protocol Architecture: Application Layer
• Support for user applications• e.g. http

TCP/IP Protocol Architecture Model

Protocol Data Units in TCP/IP

OSI vs. TCP/IP