Cytology_Membrane Structure and Function. Overview: Life at the Edge Overview: Life at the Edge The...
-
Upload
lora-charles -
Category
Documents
-
view
216 -
download
1
Transcript of Cytology_Membrane Structure and Function. Overview: Life at the Edge Overview: Life at the Edge The...

Cytology_Membrane Cytology_Membrane Structure and FunctionStructure and Function

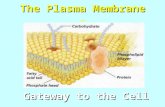
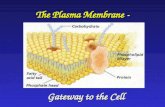
Overview: Life at the EdgeOverview: Life at the EdgeThe plasma membraneThe plasma membrane
Is the boundary that separates the living cell Is the boundary that separates the living cell from its nonliving surroundings from its nonliving surroundings

The plasma membrane exhibits The plasma membrane exhibits selective selective permeability permeability It allows some substances to cross it more It allows some substances to cross it more
easily than otherseasily than others

Membranes have certain properties:Membranes have certain properties:
They act as a barrier between the cell and its environment, allowing a complex organized system to exist inside the cell.
They permit the passage of selected substances into and out of the cell.
They flex, bend and flow to allow the cell to change shape.

Membranes have certain propertiesMembranes have certain properties
They act as a barrier between the cell and its environment, allowing a complex organized system to exist inside the cell.
They permit the passage of selected substances into and out of the cell —selective permeability.
They flex, bend and flow to allow the cell to change shape.
About 7.5 nm thick Appeared to have a “trilaminar structure” under EM

Membrane Models: Membrane Models: Scientific InquiryScientific Inquiry
Membranes have been chemically Membranes have been chemically analyzedanalyzedAnd found to be composed of proteins and And found to be composed of proteins and
lipidslipids

PhospholipidsPhospholipidsAre the most abundant lipid in the plasma Are the most abundant lipid in the plasma
membranemembranecontain both hydrophobic and hydrophilic regionscontain both hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions

Scientists studying the plasma membraneScientists studying the plasma membraneReasoned that it must be a Reasoned that it must be a phospholipid
bilayer
Figure 7.2
HydrophilicheadHydrophobictail
WATER
WATER

Different Different modelsmodels of membrane structure were of membrane structure were proposed:proposed:

In 1972, Singer and NicolsonIn 1972, Singer and NicolsonProposed that membrane proteins are Proposed that membrane proteins are
dispersed and individually inserted (in a and individually inserted (in a mosaic pattern) into the phospholipid bilayermosaic pattern) into the phospholipid bilayer
Figure 7.3
Phospholipidbilayer
Hydrophobic region of protein
Hydrophobic region of protein

The The fluid mosaic modelfluid mosaic model of membrane of membrane structurestructureStates that a membrane is a States that a membrane is a fluidfluid structure structure
with a “with a “mosaicmosaic” of various proteins embedded ” of various proteins embedded in itin it

Freeze-fracture studies of the plasma Freeze-fracture studies of the plasma membranemembraneSupported the fluid mosaic model of membrane Supported the fluid mosaic model of membrane
structurestructure


112/04/19
Freeze-fractureing show Freeze-fractureing show particles particles
embeddedembedded in Membrane in Membrane
http://www.hillstrath.on.ca/moffatt/bio3a/cellbio/phase1.htm
Further reading:

The Fluidity of MembranesThe Fluidity of Membranes
Phospholipids in the plasma membranePhospholipids in the plasma membraneCan move within the bilayerCan move within the bilayer
Figure 7.5 A
Lateral movement(~107 times per second)
Flip-flop(~ once per month)
(a) Movement of phospholipids

Proteins in the plasma membraneProteins in the plasma membraneCan drift within the bilayerCan drift within the bilayer
EXPERIMENT Researchers labeled the plasma membrane proteins of a mouse cell and a human cell with two different markers and fused the cells. Using a microscope, they observed the markers on the hybrid cell.
Membrane proteins
Mouse cell
Human cellHybrid cell
Mixedproteinsafter1 hour
RESULTS
CONCLUSION The mixing of the mouse and human membrane proteins indicates that at least some membrane proteins move sideways within the plane of the plasma membrane.Figure 7.6
+

Membrane Proteins and Their FunctionsMembrane Proteins and Their Functions
A membraneA membrane Is a collage of different proteins embedded in Is a collage of different proteins embedded in
the fluid matrix of the lipid bilayerthe fluid matrix of the lipid bilayer

112/04/19
Myelin sheath membrane Myelin sheath membrane (metabolically inactive) shows little particles (protein) embedded(metabolically inactive) shows little particles (protein) embedded

An overview of four major functions of An overview of four major functions of membrane proteinsmembrane proteins
Figure 7.9
Transport. (left) A protein that spans the membrane may provide a hydrophilic channel across the membrane that is selective for a particular solute. (right) Other transport proteins shuttle a substance from one side to the other by changing shape. Some of these proteins hydrolyze ATP as an energy source to actively pump substances across the membrane.
Enzymatic activity. A protein built into the membranemay be an enzyme with its active site exposed tosubstances in the adjacent solution. In some cases,several enzymes in a membrane are organized asa team that carries out sequential steps of ametabolic pathway.
Signal transduction. A membrane protein may havea binding site with a specific shape that fits the shapeof a chemical messenger, such as a hormone. Theexternal messenger (signal) may cause aconformational change in the protein (receptor) thatrelays the message to the inside of the cell.
(a)
(b)
(c)
ATP
Enzymes
Signal
Receptor

Cell-cell recognition. Some glyco-proteins serve as identification tags that are specifically recognized by other cells.
(d)
Glycoprotein

Membrane carbohydratesMembrane carbohydrates Interact with the surface molecules of other Interact with the surface molecules of other
cells, facilitating cells, facilitating cell-cell recognitioncell-cell recognition

Membrane proteins and lipidsMembrane proteins and lipidsAre synthesized in the ER and Golgi Are synthesized in the ER and Golgi
apparatusapparatus
ER
Figure 7.10
Transmembraneglycoproteins
Secretoryprotein
Glycolipid
Golgiapparatus
Vesicle
Transmembraneglycoprotein
Membrane glycolipid
Plasma membrane:Cytoplasmic face
Extracellular face
Secretedprotein
4
1
2
3

Membrane structure results in selective Membrane structure results in selective permeabilitypermeability
A cell must exchange materials with its surroundings, a A cell must exchange materials with its surroundings, a process controlled by the plasma membraneprocess controlled by the plasma membrane
Body cellsBody cells
Red blood cellsRed blood cells
Blood capillaryBlood capillary

The Permeability of the Lipid BilayerThe Permeability of the Lipid Bilayer Hydrophobic moleculesHydrophobic molecules
Are lipid soluble and can pass through the membrane Are lipid soluble and can pass through the membrane rapidlyrapidly
Polar moleculesPolar molecules Do not cross the membrane rapidlyDo not cross the membrane rapidly

Transport ProteinsTransport ProteinsTransport proteins (channel or carrier)Transport proteins (channel or carrier)
Allow passage of hydrophilic substances Allow passage of hydrophilic substances across the membraneacross the membrane

Concept 7.3: Passive transport is diffusion Concept 7.3: Passive transport is diffusion of a substance across a membrane with of a substance across a membrane with NONO energy expenditure energy expenditure

DiffusionDiffusion Is the tendency for molecules of any Is the tendency for molecules of any
substance to spread out evenly into the substance to spread out evenly into the available spaceavailable space
Figure 7.11 A
Diffusion of one solute. The membrane has pores large enough for molecules of dye to pass through. Random movement of dye molecules will cause some to pass through the pores; this will happen more often on the side with more molecules. The dye diffuses from where it is more concentrated to where it is less concentrated (called diffusing down a concentration gradient). This leads to a dynamic equilibrium: The solute molecules continue to cross the membrane, but at equal rates in both directions.
Molecules of dye Membrane (cross section)
Net diffusion Net diffusion Equilibrium
(a)

Substances diffuse down their Substances diffuse down their concentration gradient, the difference in concentration gradient, the difference in concentration of a substance from one concentration of a substance from one area to anotherarea to another
Figure 7.11 B
Diffusion of two solutes. Solutions of two different dyes are separated by a membrane that is permeable to both. Each dye diffuses down its own concen-tration gradient. There will be a net diffusion of the purple dye toward the left, even though the total soluteconcentration was initially greater onthe left side.
(b)
Net diffusion
Net diffusion
Net diffusion
Net diffusion Equilibrium
Equilibrium

Osmosis is the Osmosis is the diffusiondiffusion of water through a selectively of water through a selectively permeable membrane.permeable membrane.Water tends to diffuse from Water tends to diffuse from a dilute region (higher water a dilute region (higher water potential) to a more concentrated region (lower water potential) to a more concentrated region (lower water potential).potential).

Water Balance of Cells Without WallsWater Balance of Cells Without Walls Tonicity /concentration strength of a solution:Tonicity /concentration strength of a solution:
Is the ability of a solution to cause a cell to Is the ability of a solution to cause a cell to gain or losegain or lose water water
Has a great impact on cells without wallsHas a great impact on cells without walls

If a solution is isotonic The concentration of solutes is the The concentration of solutes is the same as it is it is
inside the cellinside the cell There will be There will be no net movement of water of water
If a solution is hypertonic The concentration of solutes is The concentration of solutes is greater than it is
inside the cell The cell will lose water
If a solution is hypotonic The concentration of solutes is The concentration of solutes is less than it is
inside the cell The cell will gain water

Water balance in cells without wallsWater balance in cells without walls
Figure 7.13
Hypotonic solution Isotonic solution Hypertonic solution
Animal cell. Ananimal cell fares bestin an isotonic environ-ment unless it hasspecial adaptations tooffset the osmoticuptake or loss ofwater.
(a)
H2O H2O H2O H2O
Lysed/ burst Normal Shrunk / Shriveled

Animals and other organisms without rigid Animals and other organisms without rigid cell walls living in hypertonic or hypotonic cell walls living in hypertonic or hypotonic environmentsenvironmentsMust have special adaptations for Must have special adaptations for
osmoregulationosmoregulation
Paramecium has Paramecium has contractile vacuoles to contractile vacuoles to remove excess waterremove excess water

Water Balance of Cells with WallsWater Balance of Cells with Walls
Cell wallsCell wallsHelp maintain water balanceHelp maintain water balance

Water balance in cells with wallsWater balance in cells with walls
Plant cell. Plant cells are turgid (firm) and generally healthiest ina hypotonic environ-ment, where theuptake of water iseventually balancedby the elastic wallpushing back on thecell.
(b)
H2OH2OH2OH2O
Turgid (normal) Flaccid Plasmolyzed
Figure 7.13


If a plant cell is turgidIf a plant cell is turgid It is in a hypotonic environmentIt is in a hypotonic environment It is very firm, a healthy state in most plantsIt is very firm, a healthy state in most plants

If a plant cell is flaccidIf a plant cell is flaccid It is in an isotonic or hypertonic environmentIt is in an isotonic or hypertonic environment

WiltingWilting can be reversed -- can be reversed -- if water is if water is replaced fast enoughreplaced fast enough

Water is a polar molecule, In water, the negative regions on one molecule are attracted to the positive regions on another, and the molecules form hydrogen bonds. hydrogen bonds.
Hydrogen Bond between water molecules

The Process of Transpiration

When water enters the roots, hydrogen bonds link each water molecule to the next so the molecules of water are pulled up the thin xylem vessels like beads on a string. The water moves up the plant, enters the leaves, moves into air spaces in the leaf, and then evaporates (transpires) through the stomata (singular, stoma).
Movement of Water Up Xylem Vessels

Water movement in plantsWater movement in plants
The The transpiration transpiration pullpull on xylem on xylem sap isap iss transmittedtransmitted all all the waythe way from the from the leaves to the leaves to the root tips and root tips and even into the even into the soil solutionsoil solution
Is facilitated by Is facilitated by cohesion and cohesion and adhesionadhesion
Xylemsap
Outside air = –100.0 MPa
Leaf (air spaces) = –7.0 MPa
Leaf (cell walls) = –1.0 MPa
Trunk xylem = – 0.8 MPa
Wat
er p
ote
nti
al g
rad
ien
t
Root xylem = – 0.6 MPa
Soil = – 0.3 MPa
Mesophyllcells
Stoma
Watermolecule
Atmosphere
Transpiration
Xylemcells Adhesion Cell
wall
Cohesion,byhydrogenbonding
Watermolecule
Roothair
Soilparticle
Water
Cohesion and adhesionin the xylem
Water uptakefrom soil Figure 36.13

Facilitated Diffusion: Passive Facilitated Diffusion: Passive Transport Aided by ProteinsTransport Aided by Proteins
In facilitated diffusionIn facilitated diffusionTransport proteinsTransport proteins speed the movement of speed the movement of
molecules across the plasma membranemolecules across the plasma membrane

Channel proteinsChannel proteinsProvide corridors that allow a specific Provide corridors that allow a specific
molecule or ion to cross the membranemolecule or ion to cross the membrane
Figure 7.15
EXTRACELLULARFLUID
Channel proteinSolute
CYTOPLASM
A channel protein (purple) has a channel through which water molecules or a specific solute can pass.
(a)

Carrier proteinsCarrier proteinsUndergo a subtle change in shape that Undergo a subtle change in shape that
translocates the solute-binding site across the translocates the solute-binding site across the membranemembrane
Figure 7.15
Carrier proteinSolute
A carrier protein alternates between two conformations, moving a solute across the membrane as the shape of the protein changes. The protein can transport the solute in either direction, with the net movement being down the concentration gradient of the solute.
(b)

Concept 7.4: Active transport uses energy Concept 7.4: Active transport uses energy to move solutes against their gradientsto move solutes against their gradients

The Need for Energy in Active The Need for Energy in Active TransportTransport
Active transportActive transportMoves substances against their concentration Moves substances against their concentration
gradientgradientRequires Requires energyenergy, usually in the form of ATP, usually in the form of ATP

The sodium-potassium pumpThe sodium-potassium pump Is one type of active transport systemIs one type of active transport system

Review: Passive and active transport comparedReview: Passive and active transport compared
Figure 7.17
Passive transport. Substances diffuse spontaneously down their concentration gradients, crossing a membrane with no expenditure of energy by the cell. The rate of diffusion can be greatly increased by transport proteins in the membrane.
Active transport. Some transport proteins act as pumps, moving substances across a membrane against their concentration gradients. Energy for this work is usually supplied by ATP.
Diffusion. Hydrophobicmolecules and (at a slow rate) very small uncharged polar molecules can diffuse through the lipid bilayer.
Facilitated diffusion. Many hydrophilic substances diffuse through membranes with the assistance of transport proteins,either channel or carrier proteins.
ATP

Maintenance of Membrane Maintenance of Membrane Potential by Ion PumpsPotential by Ion Pumps
Membrane potentialMembrane potential Is the voltage difference across a membraneIs the voltage difference across a membrane

An ion pump that can generate An ion pump that can generate a electrical a electrical potentialpotential Is a transport protein that generates the Is a transport protein that generates the
voltage across a membranevoltage across a membrane
Figure 7.18
EXTRACELLULARFLUID
+
H+
H+
H+
H+
H+
H+Proton pump
ATP
CYTOPLASM
+
+
+
+–
–
–
–
–
+

Cotransport: Coupled Transport by Cotransport: Coupled Transport by a Membrane Proteina Membrane Protein
CotransportCotransportOccurs when active transport of a specific Occurs when active transport of a specific
solute indirectly drives the active transport of solute indirectly drives the active transport of another solute another solute

Cotransport: active transport driven by a Cotransport: active transport driven by a concentration gradientconcentration gradient
Figure 7.19
Proton pump
Sucrose-H+
cotransporter
Diffusionof H+
Sucrose
ATP H+
H+
H+
H+
H+
H+
H+
+
+
+
+
+
+–
–
–
–
–
–

Concept 7.5: Bulk transport across the Concept 7.5: Bulk transport across the plasma membrane occurs by exocytosis plasma membrane occurs by exocytosis and endocytosisand endocytosis
Large proteinsLarge proteinsCross the membrane by different mechanismsCross the membrane by different mechanisms

Bulk transport : Bulk transport : Large proteinsLarge proteins Cross the membrane by ‘membrane fusion’ Cross the membrane by ‘membrane fusion’

ExocytosisExocytosis
In exocytosisIn exocytosisTransport vesicles migrate to the plasma Transport vesicles migrate to the plasma
membrane, fuse with it, and release their membrane, fuse with it, and release their contentscontents

EndocytosisEndocytosis
In endocytosisIn endocytosisThe cell takes in macromolecules by forming The cell takes in macromolecules by forming
new vesicles from the plasma membranenew vesicles from the plasma membrane

In exocytosisIn exocytosisTransport vesicles migrate to the plasma membrane, fuse Transport vesicles migrate to the plasma membrane, fuse with it, and release their contentswith it, and release their contents
• In endocytosis
The cell takes in macromolecules by forming new vesicles from the plasma membrane

EXTRACELLULARFLUID
PseudopodiumCYTOPLASM
“Food” or other particle
Foodvacuole
1 µm
Pseudopodiumof amoeba
Bacterium
Food vacuole
An amoeba engulfing a bacterium viaphagocytosis (TEM).
PINOCYTOSIS
Pinocytosis vesiclesforming (arrows) ina cell lining a smallblood vessel (TEM).
0.5 µm
In pinocytosis, the cell “gulps” droplets of extracellular fluid into tinyvesicles. It is not the fluiditself that is needed by the cell, but the molecules dissolved in the droplet. Because any and all included solutes are taken into the cell, pinocytosisis nonspecific in the substances it transports.
Plasmamembrane
Vesicle
In phagocytosis, a cellengulfs a particle by Wrapping pseudopodia around it and packaging it within a membrane-enclosed sac large enough to be classified as a vacuole. The particle is digested after the vacuole fuses with a lysosome containing hydrolytic enzymes.
Types of endocytosisTypes of endocytosis
Figure 7.20
PHAGOCYTOSIS