Cysts by Dr. Syed Alam Zeb
-
Upload
syed-alam-zeb -
Category
Health & Medicine
-
view
3.529 -
download
2
description
Transcript of Cysts by Dr. Syed Alam Zeb

CYSTSBY DR.SYED ALAM ZEB, SURG B KTH
DEFINITION
CLASSIFICATION

Definition
• Pathological fluid filled sac bounded by a wall.

TRUE CYST
• Sac is lined by cells of epithelial origin. Examples are thyroglossal cyst, Sebaceous cyst, Branchial cysts.

FALSE CYSTS
• They are walled-off fluid collections not lined by epithelium. Examples are: Dental or radicular cysts, encysted pleural effusions, pancreatic pseudocysts.

CLASSIFICATION OF CYSTS
• CONGENITAL: 1. Persistence of normal vestigial remnants like Thyroglossal, Branchial, urachal & hydatid of morgagni.
• 2. Ectopia of various tissues like dermoid, epidermoid & enterogenous.
• 3. Failure of connection of tubular elements like polycystic kidneys.
• 4.Hamartomas like cystic hygromas.

Classification cont:
• Acquired Cysts: 1. Retention like mucous cyst of mouth. 2. Implantation like Epidermoid. 3. Parasitic like Hydatid. 4. Hyperplasic like mammary dysplasia. 5. Degenerative like uterine leiomyoma 6. Traumatic e.g. Haematogenous. 7. Neoplastic e.g. Cyst adenoma, cystic teratoma.

CLINICAL FEATURES
• Depends on the type of cyst, site and size.
• Pain: due to increase in size, haemorrhage, infection, rupture or torsion.
• Pressure effect: Haemorrhage in Thyroglossal cyst causes dyspnoea. Pseudocyst of pancreas may compress the CBD, or stomach.

CLINICAL FEATURES
• Fluctuation.
• Transillumination.
• Special features like a punctum on sebaceous cyst, typical location of Thyroglossal cyst.

INVESTIGATIONS
• Ultrasound
• CT scan
• MRI
• Lab tests.

COMPLICATIONS
• Infection
• Haemorrhage
• Torsion
• Obstruction
• Calcification.

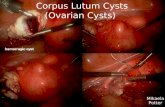
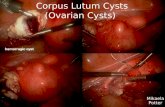
HYDATID CYST
• Mostly found in the liver but can reach to any organ in the body.

AETIOLOGY
• Echinococcus Granulosus: microscopic cestode parasites.

LIFE CYCLE
• Dogs infected by adult worms.
• Man and cattle infected with eggs passed in dogs faeces.
• Eggs hatch in to larva in the organs…the cysts.

HYDATID CYST
• Ecto-cyst or false capsule
• Endo-cyst.
• Laminated membrane.
• Germinal membrane.
• Brood capsule.
• Scolices.
• Cyst fluid.
• Hydatid sand.

CLINCAL FEATURES
• Depends on the site:
• 52-77%----liver 8.5-44%----lungs up to 8.0%----abdomen up to 7.0% ---kidneys 0.2-2.0%----CNS 1-2.0%-----bones

HYDATID LIVER DIEASE
• Patient presents with pain abdomen, mass abdomen, jaundice or fever. On exam. Liver may be enlarged, mass is palpable. Signs of liver failure may be present.

OTHER SITES
• HYDATID LUNG DISEASE: Patient presents with respiratory symptoms like breathlessness, cough etc. There may be signs of consolidation.
• HYDATID IN THE BRAIN: Patient will present with headache, vomiting or hemiplegia. Signs of focal cerebral defects may be present.

DIAGNOSIS
• Ultrasonography: Investigation of choice for suspected hydatid cysts in the solid organs of the abdomen.

CT SCAN
• Where diagnosis is in doubt, CT scan along with ultrasound is used.
• Investigation of choice in diagnosing pulmonary, brain, spleen hydatid.

CT Scan
• Hydatid of the spleen –a rare site. One of the indication for splenectomy.

CT Scan
• Ct brain and CT Chest showing hydatid cysts.

BLOOD TESTS
• FBC: There is a rise in the Esinophil count.
• Agglutination Serological tests: Has high sensitivity and specificity in diagnosing active hydatid disease.
• Casoni Test: Rarely used these days, was not a reliable test.

COMPLICATIONS
• RUPTURE: Rupture may cause anaphylacsis and dissemination.
• INFECTION:
• PRESSURE SYMPTOMS.

PROPHYLAXIS
• Eat clean food and salads.
• BEWARE your pets can give you hydatid disease.

TREATMENT
• No treatment is required if cyst is calcified and asymptomatic.
• Anti-helminthes drugs for small cysts.
• Injection therapyPAIR---puncture, aspiration, injection and reaspiration.
• Surgical procedures.

SURGICAL PROCEDURES
• Ultrasound guided or CT guided PAIR.
• Laparoscopic cystotomy, deroofing, and omentoplasty with helical fasteners
• Partial resection.
• Marsupialisation and tube drainage or omentoplasty.
• Radical surgical resection.

SCOLICIDAL AGENTS
• 20% hypertonic saline.
• 0.5% silver nitrate.
• 95% sterile ethanol.
• Absolute alcohol.
• Mebendazole
• There is no place for the use of formaldehyde.

Indications for PAIR
• Refusal of surgery.
• Inoperable cases.
• Cysts >5cm in diameter.
• Multiple cysts.
• Relapse after surgery.
• Lack of response to chemotherapy.

Complications of PAIR
• Urticaria.
• Anaphylaxis.
• Sub capsular haematoma.
• Fever.
• Biliary fistula.
• Infection.
• Hypotensive shock.

Indications for hepatic surgery
• Large cysts with suspected multiple daughter cysts.
• Superficial cysts with risk of rupture.
• Infected cysts.
• Cystobiliary communication.
• Pressure effect on vital organs.