CS Fallback(eRAN8.1_03).pdf
-
Upload
sarimsomaly -
Category
Documents
-
view
301 -
download
0
Transcript of CS Fallback(eRAN8.1_03).pdf
-
7/25/2019 CS Fallback(eRAN8.1_03).pdf
1/344
eRAN
CS Fallback Feature Parameter
Description
Issue 03
Date 2015-08-31
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD.
-
7/25/2019 CS Fallback(eRAN8.1_03).pdf
2/344
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 2015. All rights reserved.
No part of this document may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means without prior written
consent of Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Trademarks and Permissions
and other Huawei trademarks are trademarks of Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
All other trademarks and trade names mentioned in this document are the property of their respective
holders.
Notice
The purchased products, services and features are stipulated by the contract made between Huawei and the
customer. All or part of the products, services and features described in this document may not be within thepurchase scope or the usage scope. Unless otherwise specified in the contract, all statements, information,
and recommendations in this document are provided "AS IS" without warranties, guarantees or
representations of any kind, either express or implied.
The information in this document is subject to change without notice. Every effort has been made in the
preparation of this document to ensure accuracy of the contents, but all statements, information, and
recommendations in this document do not constitute a warranty of any kind, express or implied.
Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Address: Huawei Industrial Base
Bantian, Longgang
Shenzhen 518129
People's Republic of China
Website: http://www.huawei.com
Email: [email protected]
Issue 03 (2015-08-31) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
i
http://www.huawei.com/ -
7/25/2019 CS Fallback(eRAN8.1_03).pdf
3/344
Contents
1 About This Document.................................................................................................................. 1
1.1 Scope.............................................................................................................................................................................. 1
1.2 Intended Audience..........................................................................................................................................................2
1.3 Change History...............................................................................................................................................................2
1.4 Differences Between eNodeB Types..............................................................................................................................5
2 Overview......................................................................................................................................... 6
2.1 Overview........................................................................................................................................................................ 7
2.2 Benefits...........................................................................................................................................................................7
2.3 Architecture.................................................................................................................................................................... 7
2.4 CSFB Mechanisms....................................................................................................................................................... 10
2.4.1 CSFB toUTRAN.......................................................................................................................................................10
2.4.2 CSFB toGERAN.......................................................................................................................................................11
3 CSFB to UTRAN.......................................................................................................................... 143.1 Overview...................................................................................................................................................................... 15
3.2 Feature Classification................................................................................................................................................... 16
3.2.1 Basic CSFB to UTRAN.............................................................................................................................................16
3.2.2 Flash CSFB to UTRAN.............................................................................................................................................16
3.2.3 Ultra-Flash CSFB to UTRAN................................................................................................................................... 16
3.2.4 CS Fallback with LAI to UTRAN.............................................................................................................................17
3.2.5 E-UTRAN to UTRAN CS Steering...........................................................................................................................18
3.2.6 CS Fallback Steering to UTRAN.............................................................................................................................. 19
3.2.7 Load-based CSFB to UTRAN...................................................................................................................................21
3.3 TriggeringEvents......................................................................................................................................................... 21
3.4 Target Cell/Frequency Selection...................................................................................................................................22
3.5 Handover Decision....................................................................................................................................................... 27
3.5.1 Basic Handover Decision.......................................................................................................................................... 27
3.5.2 Flash Redirection Decision........................................................................................................................................28
3.6 Handover Execution..................................................................................................................................................... 29
3.6.1 Handover Policy Selection........................................................................................................................................ 29
3.6.2 Ultra-Flash CSFB to UTRAN................................................................................................................................... 31
3.6.3 Redirection-based CSFB Optimization for UEs in Idle Mode..................................................................................33
3.6.4 CSFB Admission Optimization for UEs in Idle Mode..............................................................................................33
eRAN
CS Fallback Feature Parameter Description Contents
Issue 03 (2015-08-31) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
ii
-
7/25/2019 CS Fallback(eRAN8.1_03).pdf
4/344
3.7 RIM Procedure Between E-UTRAN and UTRAN...................................................................................................... 34
3.7.1 RIM Procedure Through the Core Network..............................................................................................................35
3.7.2 RIM Procedure Through the eCoordinator................................................................................................................36
4 CSFB to GERAN.......................................................................................................................... 384.1 Overview...................................................................................................................................................................... 39
4.2 Feature Classification................................................................................................................................................... 39
4.2.1 Basic CSFB to GERAN.............................................................................................................................................39
4.2.2 Flash CSFB to GERAN.............................................................................................................................................40
4.2.3 CS Fallback with LAI to GERAN.............................................................................................................................40
4.2.4 CS Fallback Steering to GERAN.............................................................................................................................. 40
4.2.5 Ultra-Flash CSFB to GERAN................................................................................................................................... 41
4.3 TriggeringEvents......................................................................................................................................................... 42
4.4 Target Cell/Frequency Selection...................................................................................................................................42
4.5 Handover Decision....................................................................................................................................................... 43
4.6 Handover Execution..................................................................................................................................................... 43
4.7 RIM Procedure Between E-UTRAN and GERAN...................................................................................................... 45
5 Related Features...........................................................................................................................47
5.1 Features Related to LOFD-001033 CS Fallback to UTRAN.......................................................................................47
5.2 Features Related to LOFD-001052 Flash CS Fallback to UTRAN............................................................................. 47
5.3 Features Related to LOFD-070202 Ultra-Flash CSFB to UTRAN..............................................................................48
5.4 Features Related to LOFD-001068 CS Fallback with LAI to UTRAN....................................................................... 48
5.5 Features Related to LOFD-001088 CS Fallback Steering to UTRAN.........................................................................49
5.6 Features Related to LOFD-001078 E-UTRAN to UTRAN CS/PS Steering............................................................... 49
5.7 Features Related to LOFD-001034 CS Fallback to GERAN.......................................................................................50
5.8 Features Related to LOFD-001053 Flash CS Fallback to GERAN............................................................................. 50
5.9 Feature Related to LOFD-081283 Ultra-Flash CSFB to GERAN............................................................................... 51
5.10 Features Related to LOFD-001069 CS Fallback with LAI to GERAN..................................................................... 51
5.11 Features Related to LOFD-001089 CS Fallback Steering to GERAN.......................................................................51
6 NetworkImpact........................................................................................................................... 53
6.1 LOFD-001033 CS Fallback to UTRAN.......................................................................................................................53
6.2 LOFD-001052 Flash CS Fallback to UTRAN............................................................................................................. 54
6.3 LOFD-070202 Ultra-Flash CSFB to UTRAN..............................................................................................................54
6.4 LOFD-001068 CS Fallback with LAI to UTRAN....................................................................................................... 55
6.5 LOFD-001088 CS Fallback Steering to UTRAN.........................................................................................................55
6.6 LOFD-001078 E-UTRAN to UTRAN CS/PS Steering............................................................................................... 55
6.7 LOFD-001034 CS Fallback to GERAN.......................................................................................................................56
6.8 LOFD-001053 Flash CS Fallback to GERAN............................................................................................................. 56
6.9 LOFD-081283 Ultra-Flash CSFB to GERAN..............................................................................................................57
6.10 LOFD-001069 CS Fallback with LAI to GERAN..................................................................................................... 57
6.11 LOFD-001089 CS Fallback Steering to GERAN.......................................................................................................57
7 Engineering Guidelines............................................................................................................. 59
eRAN
CS Fallback Feature Parameter Description Contents
Issue 03 (2015-08-31) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
iii
-
7/25/2019 CS Fallback(eRAN8.1_03).pdf
5/344
7.1 LOFD-001033 CS Fallback to UTRAN.......................................................................................................................59
7.1.1 When to Use CS Fallback to UTRAN.......................................................................................................................59
7.1.2 Required Information................................................................................................................................................ 59
7.1.3 Requirements.............................................................................................................................................................60
7.1.4 Precautions.................................................................................................................................................................61
7.1.5 Data Preparation and Feature Activation...................................................................................................................61
7.1.5.1 Data Preparation..................................................................................................................................................... 61
7.1.5.2 Using the CME to Perform Batch Configuration for Newly Deployed eNodeBs..................................................66
7.1.5.3 Using the CME to Perform Batch Configuration for Existing eNodeBs............................................................... 67
7.1.5.4 Using the CME to Perform Single Configuration.................................................................................................. 68
7.1.5.5 Using MML Commands.........................................................................................................................................69
7.1.6 Activation Observation..............................................................................................................................................72
7.1.7 Deactivation...............................................................................................................................................................78
7.1.8 Performance Monitoring............................................................................................................................................79
7.1.9 Parameter Optimization.............................................................................................................................................80
7.2 RIM Procedure from E-UTRAN to UTRAN............................................................................................................... 84
7.2.1 When toUse RIM Procedure from E-UTRAN to UTRAN...................................................................................... 84
7.2.2 Required Information................................................................................................................................................ 84
7.2.3 Requirements.............................................................................................................................................................84
7.2.4 Precautions.................................................................................................................................................................85
7.2.5 Data Preparation and Feature Activation...................................................................................................................85
7.2.5.1 Data Preparation..................................................................................................................................................... 85
7.2.5.2 Using the CME to Perform Batch Configuration for Newly Deployed eNodeBs..................................................867.2.5.3 Using the CME to Perform Batch Configuration for Existing eNodeBs............................................................... 86
7.2.5.4 Using the CME to Perform Single Configuration.................................................................................................. 87
7.2.5.5 Using MML Commands.........................................................................................................................................88
7.2.6 Activation Observation..............................................................................................................................................88
7.2.7 Deactivation...............................................................................................................................................................89
7.2.8 Performance Monitoring............................................................................................................................................90
7.2.9 Parameter Optimization.............................................................................................................................................90
7.3 LOFD-001052 Flash CS Fallback to UTRAN............................................................................................................. 90
7.3.1 When toUse Flash CS Fallback to UTRAN............................................................................................................. 91
7.3.2 Required Information................................................................................................................................................ 91
7.3.3 Requirements.............................................................................................................................................................92
7.3.4 Precautions.................................................................................................................................................................92
7.3.5 Data Preparation and Feature Activation...................................................................................................................92
7.3.5.1 Data Preparation..................................................................................................................................................... 92
7.3.5.2 Using the CME to Perform Batch Configuration for Newly Deployed eNodeBs..................................................96
7.3.5.3 Using the CME to Perform Batch Configuration for Existing eNodeBs............................................................... 98
7.3.5.4 Using the CME to Perform Single Configuration.................................................................................................. 99
7.3.5.5 Using MML Commands.........................................................................................................................................99
7.3.6 Activation Observation............................................................................................................................................100
eRAN
CS Fallback Feature Parameter Description Contents
Issue 03 (2015-08-31) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
iv
-
7/25/2019 CS Fallback(eRAN8.1_03).pdf
6/344
7.3.7 Deactivation.............................................................................................................................................................101
7.3.8 Performance Monitoring..........................................................................................................................................102
7.3.9 Parameter Optimization...........................................................................................................................................102
7.4 LOFD-070202 Ultra-Flash CSFB to UTRAN............................................................................................................102
7.4.1 When to Use Ultra-Flash CSFB.............................................................................................................................. 102
7.4.2 Required Information.............................................................................................................................................. 102
7.4.3 Requirements...........................................................................................................................................................102
7.4.4 Precautions...............................................................................................................................................................103
7.4.5 Data Preparation and Feature Activation.................................................................................................................103
7.4.5.1 Data Preparation................................................................................................................................................... 103
7.4.5.2 Using the CME to Perform Batch Configuration for Newly Deployed eNodeBs................................................105
7.4.5.3 Using the CME to Perform Batch Configuration for Existing eNodeBs............................................................. 106
7.4.5.4 Using the CME to Perform Single Configuration................................................................................................ 107
7.4.5.5 Using MML Commands.......................................................................................................................................108
7.4.6 Activation Observation............................................................................................................................................108
7.4.7 Deactivation.............................................................................................................................................................112
7.4.8 Performance Monitoring..........................................................................................................................................112
7.4.9 Parameter Optimization........................................................................................................................................... 113
7.5 LOFD-001068 CS Fallback with LAI to UTRAN..................................................................................................... 113
7.5.1 When toUse CS Fallback with LAI to UTRAN..................................................................................................... 113
7.5.2 Required Information...............................................................................................................................................113
7.5.3 Requirements........................................................................................................................................................... 114
7.5.4 Precautions...............................................................................................................................................................1157.5.5 Data Preparation and Feature Activation.................................................................................................................115
7.5.5.1 Data Preparation................................................................................................................................................... 115
7.5.5.2 Using the CME to Perform Batch Configuration for Newly Deployed eNodeBs................................................115
7.5.5.3 Using the CME to Perform Batch Configuration for Existing eNodeBs..............................................................115
7.5.5.4 Using the CME to Perform Single Configuration................................................................................................ 115
7.5.5.5 Using MML Commands....................................................................................................................................... 115
7.5.6 Activation Observation............................................................................................................................................ 115
7.5.7 Deactivation.............................................................................................................................................................116
7.5.8 Performance Monitoring..........................................................................................................................................116
7.5.9 Parameter Optimization........................................................................................................................................... 116
7.6 LOFD-001088 CS Fallback Steering to UTRAN.......................................................................................................116
7.6.1 When toUse CS Fallback Steering to UTRAN.......................................................................................................117
7.6.2 Required Information...............................................................................................................................................117
7.6.3 Requirements........................................................................................................................................................... 117
7.6.4 Precautions...............................................................................................................................................................118
7.6.5 Data Preparation and Feature Activation.................................................................................................................118
7.6.5.1 Data Preparation................................................................................................................................................... 118
7.6.5.2 Using the CME to Perform Batch Configuration for Newly Deployed eNodeBs................................................122
7.6.5.3 Using the CME to Perform Batch Configuration for Existing eNodeBs............................................................. 123
eRAN
CS Fallback Feature Parameter Description Contents
Issue 03 (2015-08-31) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
v
-
7/25/2019 CS Fallback(eRAN8.1_03).pdf
7/344
7.6.5.4 Using the CME to Perform Single Configuration................................................................................................ 123
7.6.5.5 Using MML Commands.......................................................................................................................................124
7.6.6 Activation Observation............................................................................................................................................126
7.6.7 Deactivation.............................................................................................................................................................126
7.6.8 Performance Monitoring..........................................................................................................................................127
7.6.9 Parameter Optimization...........................................................................................................................................127
7.7 LOFD-001078 E-UTRAN to UTRAN CS/PS Steering............................................................................................. 127
7.7.1 When toUse E-UTRAN to UTRAN CS/PS Steering............................................................................................. 127
7.7.2 Required Information.............................................................................................................................................. 127
7.7.3 Requirements...........................................................................................................................................................128
7.7.4 Precautions...............................................................................................................................................................128
7.7.5 Data Preparation and Feature Activation.................................................................................................................128
7.7.5.1 Data Preparation................................................................................................................................................... 128
7.7.5.2 Using the CME to Perform Batch Configuration for Newly Deployed eNodeBs................................................130
7.7.5.3 Using the CME to Perform Batch Configuration for Existing eNodeBs............................................................. 130
7.7.5.4 Using the CME to Perform Single Configuration................................................................................................ 131
7.7.5.5 Using MML Commands.......................................................................................................................................132
7.7.6 Activation Observation............................................................................................................................................132
7.7.7 Deactivation.............................................................................................................................................................133
7.7.8 Performance Monitoring..........................................................................................................................................134
7.7.9 Parameter Optimization...........................................................................................................................................134
7.8 LOFD-001034 CS Fallback to GERAN.....................................................................................................................134
7.8.1 When toUse CS Fallback to GERAN.....................................................................................................................1347.8.2 Required Information.............................................................................................................................................. 134
7.8.3 Requirements...........................................................................................................................................................135
7.8.4 Precautions...............................................................................................................................................................136
7.8.5 Data Preparation and Feature Activation.................................................................................................................136
7.8.5.1 Data Preparation................................................................................................................................................... 136
7.8.5.2 Using the CME to Perform Batch Configuration for Newly Deployed eNodeBs................................................140
7.8.5.3 Using the CME to Perform Batch Configuration for Existing eNodeBs............................................................. 141
7.8.5.4 Using the CME to Perform Single Configuration................................................................................................ 142
7.8.5.5 Using Feature Operation and Maintenance on the CME......................................................................................143
7.8.5.6 Using MML Commands.......................................................................................................................................148
7.8.6 Activation Observation............................................................................................................................................152
7.8.7 Deactivation.............................................................................................................................................................155
7.8.8 Performance Monitoring..........................................................................................................................................156
7.8.9 Parameter Optimization...........................................................................................................................................158
7.9 RIM Procedure from E-UTRAN to GERAN............................................................................................................. 158
7.9.1 When toUse RIM Procedure Between E-UTRAN and GERAN............................................................................159
7.9.2 Required Information.............................................................................................................................................. 159
7.9.3 Requirements...........................................................................................................................................................159
7.9.4 Precautions...............................................................................................................................................................160
eRAN
CS Fallback Feature Parameter Description Contents
Issue 03 (2015-08-31) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
vi
-
7/25/2019 CS Fallback(eRAN8.1_03).pdf
8/344
7.9.5 Data Preparation and Feature Activation.................................................................................................................160
7.9.5.1 Data Preparation................................................................................................................................................... 160
7.9.5.2 Using the CME to Perform Batch Configuration for Newly Deployed eNodeBs................................................160
7.9.5.3 Using the CME to Perform Batch Configuration for Existing eNodeBs............................................................. 161
7.9.5.4 Using the CME to Perform Single Configuration................................................................................................ 162
7.9.5.5 Using MML Commands.......................................................................................................................................162
7.9.6 Activation Observation............................................................................................................................................163
7.9.7 Deactivation.............................................................................................................................................................164
7.9.8 Performance Monitoring..........................................................................................................................................165
7.9.9 Parameter Optimization...........................................................................................................................................165
7.10 LOFD-001053 Flash CS Fallback to GERAN......................................................................................................... 165
7.10.1 When to Use Flash CS Fallback to GERAN......................................................................................................... 165
7.10.2 Required Information............................................................................................................................................ 166
7.10.3 Requirements.........................................................................................................................................................166
7.10.4 Precautions.............................................................................................................................................................167
7.10.5 Data Preparation and Feature Activation...............................................................................................................167
7.10.5.1 Data Preparation................................................................................................................................................. 167
7.10.5.2 Using the CME to Perform Batch Configuration for Newly Deployed eNodeBs..............................................171
7.10.5.3 Using the CME to Perform Batch Configuration for Existing eNodeBs........................................................... 173
7.10.5.4 Using the CME to Perform Single Configuration.............................................................................................. 174
7.10.5.5 Using MML Commands.....................................................................................................................................174
7.10.6 Activation Observation..........................................................................................................................................175
7.10.7 Deactivation...........................................................................................................................................................1767.10.8 Performance Monitoring........................................................................................................................................177
7.10.9 Parameter Optimization.........................................................................................................................................177
7.11 LOFD-081283 Ultra-Flash CSFB to GERAN..........................................................................................................177
7.11.1 When to Use This Feature..................................................................................................................................... 177
7.11.2 Required Information.............................................................................................................................................177
7.11.3 Requirements......................................................................................................................................................... 178
7.11.4 Precautions.............................................................................................................................................................178
7.11.5 Data Preparation and Feature Activation...............................................................................................................178
7.11.5.1 Data Preparation................................................................................................................................................. 178
7.11.5.2 Using the CME to Perform Batch Configuration for Newly Deployed eNodeBs..............................................181
7.11.5.3 Using the CME to Perform Batch Configuration for Existing eNodeBs............................................................183
7.11.5.4 Using the CME to Perform Single Configuration.............................................................................................. 183
7.11.5.5 Using MML Commands.....................................................................................................................................184
7.11.6 Activation Observation..........................................................................................................................................185
7.11.7 Deactivation...........................................................................................................................................................186
7.11.8 Performance Monitoring........................................................................................................................................187
7.11.9 Parameter Optimization.........................................................................................................................................188
7.12 LOFD-001069 CS Fallback with LAI to GERAN................................................................................................... 188
7.12.1 When to Use CS Fallback with LAI to GERAN...................................................................................................188
eRAN
CS Fallback Feature Parameter Description Contents
Issue 03 (2015-08-31) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
vii
-
7/25/2019 CS Fallback(eRAN8.1_03).pdf
9/344
7.12.2 Required Information............................................................................................................................................ 188
7.12.3 Requirements.........................................................................................................................................................189
7.12.4 Precautions.............................................................................................................................................................190
7.12.5 Data Preparation and Feature Activation...............................................................................................................190
7.12.5.1 Data Preparation................................................................................................................................................. 190
7.12.5.2 Using the CME to Perform Batch Configuration for Newly Deployed eNodeBs..............................................190
7.12.5.3 Using the CME to Perform Batch Configuration for Existing eNodeBs........................................................... 190
7.12.5.4 Using the CME to Perform Single Configuration.............................................................................................. 190
7.12.5.5 Using MML Commands.....................................................................................................................................190
7.12.6 Activation Observation..........................................................................................................................................190
7.12.7 Deactivation...........................................................................................................................................................191
7.12.8 Performance Monitoring........................................................................................................................................191
7.12.9 Parameter Optimization.........................................................................................................................................191
7.13 LOFD-001089 CS Fallback Steering to GERAN.....................................................................................................191
7.13.1 When to Use CS Fallback Steering to GERAN.................................................................................................... 191
7.13.2 Required Information............................................................................................................................................ 192
7.13.3 Requirements.........................................................................................................................................................192
7.13.4 Precautions.............................................................................................................................................................192
7.13.5 Data Preparation and Feature Activation...............................................................................................................192
7.13.5.1 Data Preparation................................................................................................................................................. 193
7.13.5.2 Using the CME to Perform Batch Configuration for Newly Deployed eNodeBs..............................................196
7.13.5.3 Using the CME to Perform Batch Configuration for Existing eNodeBs........................................................... 197
7.13.5.4 Using the CME to Perform Single Configuration.............................................................................................. 1987.13.5.5 Using MML Commands.....................................................................................................................................198
7.13.6 Activation Observation..........................................................................................................................................199
7.13.7 Deactivation...........................................................................................................................................................199
7.13.8 Performance Monitoring........................................................................................................................................200
7.13.9 Parameter Optimization.........................................................................................................................................200
7.14 Troubleshooting........................................................................................................................................................200
7.14.1 CSFB Calling Procedure Failure........................................................................................................................... 200
7.14.2 eNodeB Receiving No Measurement Report........................................................................................................ 201
7.14.3 CSFB Blind Handover Failure.............................................................................................................................. 201
7.14.4 CSFB Handover Failure........................................................................................................................................ 202
8 Parameters...................................................................................................................................204
9 Counters...................................................................................................................................... 254
10 Glossary.....................................................................................................................................313
11 Reference Documents.............................................................................................................314
12 Appendix...................................................................................................................................315
12.1 CSFB to UTRAN......................................................................................................................................................315
12.1.1 Combined EPS/IMSI Attach Procedure................................................................................................................ 315
eRAN
CS Fallback Feature Parameter Description Contents
Issue 03 (2015-08-31) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
viii
-
7/25/2019 CS Fallback(eRAN8.1_03).pdf
10/344
12.1.2 CSFB Based on PS Handover............................................................................................................................... 316
12.1.3 Signaling procedure of redirection to CDMA2000 1xRTT...................................................................................318
12.1.4 Flash CSFB............................................................................................................................................................320
12.1.5 Ultra-Flash CSFB to UTRAN............................................................................................................................... 321
12.1.6 Redirection-based CSFB Optimization for UEs in Idle Mode..............................................................................323
12.1.7 CSFB for SMS.......................................................................................................................................................324
12.1.8 Emergency Call..................................................................................................................................................... 324
12.1.9 CSFB for LCS....................................................................................................................................................... 325
12.2 CSFB to GERAN......................................................................................................................................................325
12.2.1 Combined EPS/IMSI Attach Procedure................................................................................................................ 325
12.2.2 CSFB Based on PS Handover............................................................................................................................... 325
12.2.3 CSFB Based on CCO/NACC................................................................................................................................ 327
12.2.4 CSFB Based on Redirection..................................................................................................................................328
12.2.5 Flash CSFB............................................................................................................................................................330
12.2.6 Ultra-Flash CSFB to GERAN............................................................................................................................... 331
12.2.7 CSFB for SMS.......................................................................................................................................................334
12.2.8 Emergency Call..................................................................................................................................................... 334
12.2.9 CSFB for LCS....................................................................................................................................................... 334
eRAN
CS Fallback Feature Parameter Description Contents
Issue 03 (2015-08-31) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
ix
-
7/25/2019 CS Fallback(eRAN8.1_03).pdf
11/344
1About This Document
1.1 Scope
This document describes circuit switched fallback (CSFB), including its technical principles,
related features, network impact, and engineering guidelines.
This document covers the following features:
l LOFD-001033 CS Fallback to UTRAN
l LOFD-001052 Flash CS Fallback to UTRAN
l LOFD-070202 Ultra-Flash CSFB to UTRAN
l
LOFD-001068 CS Fallback with LAI to UTRANl LOFD-001088 CS Fallback Steering to UTRAN
l LOFD-001078 E-UTRAN to UTRAN CS/PS Steering
l LOFD-001034 CS Fallback to GERAN
l LOFD-001053 Flash CS Fallback to GERAN
l LOFD-001069 CS Fallback with LAI to GERAN
l LOFD-001089 CS Fallback Steering to GERAN
l LOFD-081283 Ultra-Flash CSFB to GERAN
If Huawei devices are used in the GERAN or UTRAN to which CS fallback is performed,
refer to the following documents to obtain details about CSFB implementation in thecorresponding network:
l GERAN: CS Fallback Feature Parameter Descriptionin GBSS Feature Documentation.
l UTRAN:Interoperability Between UMTS and LTE Feature Parameter Descriptionin
RAN Feature Documentation.
Any managed objects (MOs), parameters, alarms, or counters described herein correspond to
the software release delivered with this document. Any future updates will be described in the
product documentation delivered with future software releases.
This document applies only to LTE FDD. Any "LTE" in this document refers to LTE FDD,
and "eNodeB" refers to LTE FDD eNodeB.
This document applies to the following types of eNodeBs.
eRAN
CS Fallback Feature Parameter Description 1 About This Document
Issue 03 (2015-08-31) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
1
-
7/25/2019 CS Fallback(eRAN8.1_03).pdf
12/344
-
7/25/2019 CS Fallback(eRAN8.1_03).pdf
13/344
ChangeType
Change Description Parameter Change AffectedEntity
Feature
change
Added the measurement-specific
DRX configuration for Ultra-Flash
CSFB to GERAN. For details, see
4.2.5 Ultra-Flash CSFB to
GERAN.
None Macro,
micro, and
LampSite
eNodeBs
Added the random selection
optimization switch for CSFB. For
details, see 3.4 Target Cell/
Frequency Selectionand 7.1.5.1
Data Preparation.
Added the
RsvdSwPara1_bit23
option in the reserved
parameter
eNBRsvdPara.
RsvdSwPara1.
Macro,
micro, and
LampSite
eNodeBs
Editorial
change
None None -
eRAN8.1 01 (2015-03-23)
This issue includes the following changes.
Change Type Change Description ParameterChange
Affected Entity
Feature change Added the UE compatibility
risk optimization for ultra-flashCSFB. For details, see 7.11.5.1
Data Preparation.
Added the
UltraFlashCsfbComOptSwoption
to the
GlobalProcSwitc
h.UeCompatSwitc
hparameter.
Macro, micro,
and LampSiteeNodeBs
Editorial
change
None None -
eRAN8.1 Draft A (2015-01-15)
Compared with Issue 06 (2014-12-30) of eRAN7.0, Draft A (2015-01-15) of eRAN8.1
includes the following changes.
eRAN
CS Fallback Feature Parameter Description 1 About This Document
Issue 03 (2015-08-31) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
3
-
7/25/2019 CS Fallback(eRAN8.1_03).pdf
14/344
Change Type
Change Description ParameterChange
AffectedEntity
Feature
change
Supported the cell-level blind handling switch for
CSFB in CS Fallback to UTRAN or GERAN and
Flash CS Fallback to UTRAN or GERAN
scenarios.
l For details about the switch, see 3.2.1 Basic
CSFB to UTRANand 3.4 Target Cell/
Frequency Selection.
l For details about handover policy selection,
see 3.6.1 Handover Policy Selection.
l For details about scenario-specific parameter
preparations, see section "Data Preparation" in
engineering guidelines.
l For details about scenario-specificconfigurations, see "Using the CME to
Perform Batch Configuration for Newly
Deployed eNodeBs" and "Using MML
Commands" in section "Activation" in
engineering guidelines.
Added the
CellHoParaCf
g.HoModeSwit
chparameter.
Macro,
micro,
and
LampSite
eNodeBs
Added the feature LOFD-081283 Ultra-Flash
CSFB to GERAN.
l For details about the feature description, see
4.2.5 Ultra-Flash CSFB to GERAN.
l For details about the signaling procedure, see
12.2.6 Ultra-Flash CSFB to GERAN.
l For details about related features and network
impact, see 5.9 Feature Related to
LOFD-081283 Ultra-Flash CSFB to
GERANand 6.9 LOFD-081283 Ultra-Flash
CSFB to GERAN.
l For details about engineering guidelines, see
7.11 LOFD-081283 Ultra-Flash CSFB to
GERAN.
l Added the
GeranExte
rnalCell.Ul
traFlashCs
fbInd
parameter.l Added the
GeranUltr
aFlashCsfb
Switch
option in
the
ENodeBAl
goSwitch.
HoAlgoSwi
tch
parameter.
Macro,
micro,
and
LampSite
eNodeBs
Added the configuration of the round-robin
function for L2U blind redirections.
l For details about the switch, see 3.4 Target
Cell/Frequency Selection.
l For details about scenario-specific data
preparations, see 7.1.5.1 Data Preparation.
l For details about the function activation, see
7.1.5.5 Using MML Commands.
Added the
CSFallBackBl
indHoCfg.Utr
anCsfbBlindR
edirRrSw
parameter.
Macro,
micro,
and
LampSite
eNodeBs
eRAN
CS Fallback Feature Parameter Description 1 About This Document
Issue 03 (2015-08-31) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
4
-
7/25/2019 CS Fallback(eRAN8.1_03).pdf
15/344
Change Type
Change Description ParameterChange
AffectedEntity
Added SPID-based mobility management. For
details about the function, see 3.4 Target Cell/
Frequency Selection, 3.5.1 Basic Handover
Decision, and 3.5.2 Flash Redirection Decision.
None Macro,
micro,
and
LampSite
eNodeBs
Ultra-flash CSFB to GERAN uses the DRX-
based measurement, which is controlled by the
CellDrxPara.DrxForMeasSwitchparameter.
l For details about the parameter, see 4.2.5
Ultra-Flash CSFB to GERAN.
l For details about data preparations and MML
configurations, see related sections in 7.11
LOFD-081283 Ultra-Flash CSFB toGERAN.
Added the
CellDrxPara.
DrxForMeasS
witch
parameter.
Macro,
micro,
and
LampSite
eNodeBs
Editoria
l change
Changed "blind handling" to "blind handover".
For details, see descriptions of blind handover in
this document.
None -
1.4 Differences Between eNodeB Types
The features described in this document are implemented in the same way on macro, micro,
and LampSite eNodeBs.
eRAN
CS Fallback Feature Parameter Description 1 About This Document
Issue 03 (2015-08-31) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
5
-
7/25/2019 CS Fallback(eRAN8.1_03).pdf
16/344
2OverviewIn an early phase of EPS construction, operators who own a mature UTRAN or GERAN can
protect their investments in legacy CS networks and reduce their investments in the EPS by
using legacy CS networks to provide CS services.
Currently, CSFB and voice over IP (VoIP) over IP multimedia subsystem (IMS) are the two
standard solutions to provide voice services for E-UTRAN UEs. After the technological
maturity, industry chain, and deployment costs of the two methods are well weighed, CSFB is
chosen to serve as an interim solution for voice service access before mature commercial use
of IMS.
eRAN
CS Fallback Feature Parameter Description 2 Overview
Issue 03 (2015-08-31) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
6
-
7/25/2019 CS Fallback(eRAN8.1_03).pdf
17/344
2.1 Overview
With the CSFB solution, when a UE initiates a CS service, the mobility management entity
(MME) instructs the UE to fall back to the legacy CS network before the UE performs the
service. CSFB is a session setup procedure. UEs fall back to CS networks before CS sessions
are set up, and they always stay in the CS networks during the CS sessions. For details, see
3GPP TS 23.272 V8.5.0.
The eNodeB handles the CSFB for different types of CS services in a uniform way such as the
voice service, SMS, LCS, and emergency calls.
2.2 Benefits
CSFB brings the following benefits:
l Facilitates voice services for the LTE network.
l Helps operators reduce costs by reusing legacy CS networks and not deploying an IMS
network.
2.3 Architecture
CSFB is applicable to scenarios where the CS network of the UTRAN/GERAN has the same
or larger coverage area than that of the E-UTRAN.
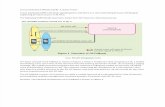
Figure 2-1shows the network architecture for CSFB to UTRAN/GERAN.
Figure 2-1Network architecture for CSFB to UTRAN/GERAN
Table 2-1describes the elements of the network architecture in Figure 2-1.
eRAN
CS Fallback Feature Parameter Description 2 Overview
Issue 03 (2015-08-31) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
7
-
7/25/2019 CS Fallback(eRAN8.1_03).pdf
18/344
Table 2-1Elements of the network architecture for CSFB to UTRAN/GERAN
NE Function
SGs interface l Is an interface between the MME and the MSC server.
l Assists mobility management and paging between the EPS and theCS network.
l Transmits mobile originated (MO) and mobile terminated (MT)
SMS messages.
l Transmits messages related to combined attach and combined TAU/
LAU.
UE l Is capable of accessing the EPS and accessing the UTRAN,
GERAN, or both.
l Supports combined EPS/IMSI (IMSI is short for international
mobile subscriber identity) attach, combined EPS/IMSI detach, and
combined TAU/LAU.
l Supports CSFB mechanisms, such as PS redirection and PS
handover.
NOTE
CSFB-capable UEs must support SMS over SGs, but UEs that support SMS over
SGs are not necessarily CSFB-capable.
MME l Supports the SGs interface to the MSC/VLR.
l Selects the VLR and location area identity (LAI) based on the
tracking area identity (TAI) of the serving cell.
l Forwards paging messages delivered by the MSC.
l Performs public land mobile network (PLMN) selection andreselection.
l Supports combined EPS/IMSI attach, combined EPS/IMSI detach,
and combined TAU/LAU.
l Routes CS signaling.
l Supports SMS over SGs.
l Supports RIM, which is required when flash CSFB or CCO with
NACC is used as the CSFB mechanism. (CCO is short for cell
change order and NACC is short for network assisted cell change.)
MSC l Supports combined EPS/IMSI attach.
l Supports SMS over SGs.
l Forwards paging messages transmitted through the SGs interface.
eRAN
CS Fallback Feature Parameter Description 2 Overview
Issue 03 (2015-08-31) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
8
-
7/25/2019 CS Fallback(eRAN8.1_03).pdf
19/344
NE Function
E-UTRAN l Forwards paging messages related to CSFB.
l Selects target cells for CSFB for E-UTRAN UEs.
l Supports one or more of the following functions:
PS redirection to UTRAN or GERAN, if PS redirection is used
as the CSFB mechanism.
PS handover to UTRAN or GERAN, if PS handover is used as
the CSFB mechanism.
CCO without NACC to GERAN, if CCO without NACC is used
as the CSFB mechanism; RIM for acquiring the system
information of GERAN cells, if NACC is used as the CSFB
mechanism.
RIM for acquiring the system information of UTRAN or
GERAN cells, in addition to PS redirection, if flash CSFB isused as the CSFB mechanism.
UTRAN/
GERAN
Supports one or more of the following functions:
l Incoming handovers from the E-UTRAN, if PS handover is used as
the CSFB mechanism.
l RIM for delivering the system information of GERAN cells to
eNodeBs, if CCO with NACC is used as the CSFB mechanism.
l RIM for delivering the system information of UTRAN or GERAN
cells to eNodeBs, in addition to PS redirection, if flash CSFB is
used as the CSFB mechanism.
NOTEThe UTRAN and GERAN do not need to provide extra functions to support PSredirection. The GERAN does not need to provide extra functions to support
CCO without NACC.
SGSN l Supports the follow-up procedures performed for the PS handover,
including data forwarding, path switching, RAU, and encryption
and authentication.
l Supports RIM, which is required when flash CSFB or CCO with
NACC is used as the CSFB mechanism.
eCoordinator Is a network element provided by Huawei, and is optional. The
eCoordinator supports the RIM procedure.
To implement CSFB to provide CS services for UEs on the E-UTRAN, all mobile switching
centers (MSCs) that serve overlapping areas with the E-UTRAN coverage must be upgraded
to support functions involving the SGs interface. The SGs interface is between an MSC and a
mobility management entity (MME), and functions involving the SGs interface include
combined attach, combined TAU/LAU (TAU is short for tracking area update, and LAU is
short for location area update), paging, and SMS. If the live network uses an MSC pool, only
one or multiple MSCs in the MSC pool need to be upgraded to support the SGs interface.
eRAN
CS Fallback Feature Parameter Description 2 Overview
Issue 03 (2015-08-31) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
9
-
7/25/2019 CS Fallback(eRAN8.1_03).pdf
20/344
2.4 CSFB Mechanisms
2.4.1 CSFB to UTRAN
Based on the capabilities of UEs and networks, three fallback mechanisms are available for an
eNodeB to perform CSFB to UTRAN:
l R8 PS Redirection
After receiving a CS Fallback Indicator, the eNodeB sends an RRC Connection Release
message containing frequency information about the target UTRAN to the UE. Based on the
received frequency information, the UE searches for a UTRAN cell, obtains the system
information of the UTRAN cell, and initiates initial access and CS services.
l R9 PS Redirection (Flash CSFB)
After receiving a CS Fallback Indicator, the eNodeB sends an RRC Connection Release
message containing information about a target UTRAN frequency as well as system
information about multiple target cells to the UE. Based on the received frequency
information, the UE searches for a UTRAN cell. As the UE obtains system information about
the target cell, the UE initiates initial access and CS services in the target cell, thereby
reducing voice delay.
l PS Handover
The UE is handed over to the UMTS network through the PS handover procedure between the
eNodeB and the UMTSnetwork. After the handover, the UE initiates CS services in the targetcell.
Table 2-2describes the requirements of the three CSFB mechanisms on the network side and
UEs.
Table 2-2Requirements of CSFB to UTRAN on the network side and UEs
NE R8 PS Redirection R9 Redirection (FlashCSFB)
PS Handover
UE l Support combined
EPS/CS attach andcombined TA/LA
update.
l Support CSFB by R8
PS Redirection.
l Support R9 PS
Redirection with SIB.l The other
requirements are the
same as those of R8
PS Redirection.
l Support PS
Handover.l The other
requirements are
the same as those
of R8 PS
Redirection.
eNodeB Support CSFB by R8 PS
Redirection.
l Support the RIM
procedure.
l The other
requirements are the
same as those of R8
PS Redirection.
Support PS Handover.
eRAN
CS Fallback Feature Parameter Description 2 Overview
Issue 03 (2015-08-31) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
10
-
7/25/2019 CS Fallback(eRAN8.1_03).pdf
21/344
NE R8 PS Redirection R9 Redirection (FlashCSFB)
PS Handover
UTRAN N/A Support the RIM
procedure.
Support PS Handover.
MME l Support combined
EPS/CS attach and
combined TA/LA
update.
l Support the CSFB
procedure.
l Support the RIM
procedure.
l The other
requirements are the
same as those of R8
PS Redirection.
Support PS Handover.
SGSN N/A Support the RIM
procedure.
Support PS Handover.
MSC l Support combined
EPS/CS attach andcombined TA/LA
update.
l Support the CSFB
procedure.
The requirements are the
same as those of R8 PSRedirection.
The requirements are
the same as those ofR8 PS Redirection.
2.4.2 CSFB to GERAN
Based on the capabilities of UEs and networks, five fallback mechanisms are available for an
eNodeB to perform CSFB toGERAN:l R8 PS Redirection
For details, see 2.4.1 CSFB to UTRAN.
l R9 PS Redirection (Flash CSFB)
For details, see 2.4.1 CSFB to UTRAN.
l CCO
After receiving a CS Fallback Indicator, the eNodeB sends aMobilityFromEUTRACommand
message containing information about a target GERAN cell to the UE, and instructs the UE to
access the target cell. The UE needs to be synchronized to the specified cell, obtains system
information about the target cell, and accesses the cell to initiate CS services.
l CCO with NACC
When the LTE-to-GSM RIM procedure is enabled, which indicates that NACC is enabled, the
eNodeB delivers system information about the target cell when triggering CCO. The UE
directly initiates access and a CS service to the target cell and does not need to read system
information about the target cell, shortening delays.
l PS Handover
For details, see 2.4.1 CSFB to UTRAN.
Table 2-3describes the requirements of the five CSFB mechanisms on the network side andUEs.
eRAN
CS Fallback Feature Parameter Description 2 Overview
Issue 03 (2015-08-31) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
11
-
7/25/2019 CS Fallback(eRAN8.1_03).pdf
22/344
Table 2-3Requirements of CSFB to GERAN on the network side and UEs
NE R8 PSRedirection
R9 Redirection(Flash CSFB)
CCO CCO withNACC
PSHandover
UE l Supportcombined
EPS/CS
attach and
combined
TA/LA
update.
l Support
CSFB by
R8 PS
Redirection.
lSupport R9PS
Redirection
with SIB.
l The other
requirements
are the same
as those of
R8 PS
Redirection.
lSupportCCO.
l The
other
require
ments
are the
same as
those of
R8 PS
Redirect
ion.
lSupportNACC
l The
other
requirem
ents are
the same
as those
of R8 PS
Redirecti
on.
lSupportPS
handove
r.
l The
other
require
ments
are the
same as
those of
R8 PS
Redirect
ion.
eNodeB Support CSFB
by R8 PS
Redirection.
l Support the
RIM
procedure.
l The other
requirements
are the same
as those of
R8 PS
Redirection.
Support
CCO.
l Support
the RIM
procedur
e.
l The
other
requirem
ents are
the same
as those
of R8 PS
Redirecti
on.
Support PS
Handover.
GERAN N/A Support the RIM
procedure.
N/A Support the
RIM
procedure.
Support PS
Handover.
MME l Support
combined
EPS/CS
attach andcombined
TA/LA
update.
l Support the
CSFB
procedure.
l Support the
RIM
procedure.
l The other
requirements
are the same
as those of
R8 PS
Redirection.
The
requiremen
ts are the
same asthose of R8
PS
Redirection
.
l Support
the RIM
procedur
e.
l The
other
requirem
ents are
the same
as those
of R8 PS
Redirecti
on.
Support PS
Handover.
eRAN
CS Fallback Feature Parameter Description 2 Overview
Issue 03 (2015-08-31) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
12
-
7/25/2019 CS Fallback(eRAN8.1_03).pdf
23/344
NE R8 PSRedirection
R9 Redirection(Flash CSFB)
CCO CCO withNACC
PSHandover
SGSN N/A Support the RIM
procedure.
N/A Support the
RIM
procedure.
Support PS
Handover.
MSC l Support
combined
EPS/CS
attach and
combined
TA/LA
update.
l Support the
CSFB
procedure.
The
requirements are
the same as
those of R8 PS
Redirection.
The
requiremen
ts are the
same as
those of R8
PS
Redirection
.
The
requirement
s are the
same as
those of R8
PS
Redirection.
The
requiremen
ts are the
same as
those of R8
PS
Redirection
.
eRAN
CS Fallback Feature Parameter Description 2 Overview
Issue 03 (2015-08-31) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
13
-
7/25/2019 CS Fallback(eRAN8.1_03).pdf
24/344
3CSFB to UTRANThis chapter describes each CSFB to UTRAN feature, CSFB procedure, and RIM procedure
between E-UTRAN and UTRAN.
eRAN
CS Fallback Feature Parameter Description 3 CSFB to UTRAN
Issue 03 (2015-08-31) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
14
-
7/25/2019 CS Fallback(eRAN8.1_03).pdf
25/344
3.1 Overview
CSFB to UTRAN can be implemented in different ways and includes the following features/
functions:
l LOFD-001033 CS Fallback to UTRAN
l LOFD-001052 Flash CS Fallback to UTRAN
l LOFD-070202 Ultra-Flash CSFB to UTRAN
l LOFD-001068 CS Fallback with LAI to UTRAN
l LOFD-001078 E-UTRAN to UTRAN CS/PS Steering
l LOFD-001088 CS Fallback Steering to UTRAN
l Load-based CSFB to UTRAN
CSFB ProcedureFigure 3-1shows the CSFB to UTRAN procedure.
Figure 3-1CSFB to UTRAN procedure
Measurement and Blind Handover
The eNodeB determines whether to trigger UTRAN measurements or blind handling forCSFB to UTRAN based on the status of the blind handling switch first.
eRAN
CS Fallback Feature Parameter Description 3 CSFB to UTRAN
Issue 03 (2015-08-31) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
15
-
7/25/2019 CS Fallback(eRAN8.1_03).pdf
26/344
l If this option is selected, the eNodeB triggers blind handover directly.
l If this option is cleared, the eNodeB determines whether to trigger inter-RAT
measurements or blind handover based on the UE capability:
If the UE supports UTRAN measurements, the eNodeB triggers inter-RAT
measurements.
If the UE does not support UTRAN measurements, the eNodeB triggers a blind
handover.
For details about the measurement and handover, see Overview of Mobility Management in
Connected Mode Feature Parameter Description.
3.2 Feature Classification
3.2.1 Basic CSFB to UTRANThis section describes the optional feature LOFD-001033 CS Fallback to UTRAN. The
UtranCsfbSwitchoption of the ENodeBAlgoSwitch .HoAlgoSwitchparameter specifies
whether to enable this feature.
When a UE initiates a CS service in the E-UTRAN, the MME sends an S1-AP message
containing CS Fallback Indicator to the eNodeB, instructing the eNodeB to transfer the UE as
well as the CS service to a target network. For details about signaling procedures of MOC and
MTC, see 12.1 CSFB to UTRAN.
3.2.2 Flash CSFB to UTRAN
This section describes the optional feature LOFD-001052 Flash CS Fallback to UTRAN. TheUtranFlashCsfbSwitchoption of the ENodeBAlgoSwitch .HoAlgoSwitchparameter
specifies whether to enable this feature.
This feature is an enhancement to the optional feature LOFD-001033 CS Fallback to
UTRAN. When this feature is activated after enabled LOFD-001033 CS Fallback to UTRAN,
the eNodeB obtains the UTRAN cell information through the RIM procedures and then sends
the EUTRAN-to-UTRAN redirection message including the obtained UTRAN cell
information to the UE. In this case, the UE can access a UTRAN cell without obtaining
UTRAN cell information. This reduces the access delay. For details about how the UTRAN
cell information is delivered to the eNodeB through the RIM procedure, seeInteroperability
Between UMTS and LTE Feature Parameter Description.
This feature requires that the eNodeB can obtain UTRAN cell information through the RIM
procedures and the networks and UEs involved must comply with 3GPP Release 9 or later.
For details about the RIM procedure, see 3.7 RIM Procedure Between E-UTRAN and
UTRAN.
Other procedures are the same as those in CSFB to UTRAN. For details, see 3.2.1 Basic
CSFB to UTRAN.
3.2.3 Ultra-Flash CSFB to UTRAN
This section describes the optional feature LOFD-070202 Ultra-Flash CSFB to UTRAN. The
UtranUltraFlashCsfbSwitchoption of the ENodeBAlgoSwitch .HoAlgoSwitchparameterspecifies whether to enable this feature. This feature is a Huawei-proprietary feature. To
eRAN
CS Fallback Feature Parameter Description 3 CSFB to UTRAN
Issue 03 (2015-08-31) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
16
-
7/25/2019 CS Fallback(eRAN8.1_03).pdf
27/344
enable this feature, the MME, MSC, and RNC must be all provided by Huawei and support
this feature.
When a UE initiates a CS service setup request in an LTE cell that does not support VoIP, this
feature enables the eNodeB to hand over the UE to the UTRAN through the SRVCC
procedure. It prepares CS resources on the UTRAN in advance and omits unnecessarysignaling processes during UTRAN access, thereby shortening the access delay for CSFB by
1s and improving user experience significantly. Compared with the standard procedure, the
ultra-flash CSFB to UTRAN procedure for Huawei omits certain signaling processes. For
details, see 12.1.5 Ultra-Flash CSFB to UTRAN.
The measurement procedure and blind handover procedure for this feature are the same as
those in CSFB to UTRAN. For details, see 3.2.1 Basic CSFB to UTRAN.
NOTE
The following table describes the parameters that must be set in the GLOBALPROCSWITCHMO to
turn on the UE compatibility switch when UEs do not support Ultra-Flash CSFB, resulting in UE
compatibility problems.
3.2.4 CS Fallback with LAI to UTRAN
This section describes the optional feature LOFD-001068 CS Fallback with LAI to UTRAN.
This feature is under license control and is not controlled by a switch.
This feature mainly applies to the following scenarios:
l In a multi-PLMN or national roaming scenario
An LAI consists of a PLMN ID and a LAC. In the CSFB with LAI function, the PLMN
ID identifies the CS network that the UE has registered with and will fall back to after
fallback.
If the serving E-UTRAN cell has multiple neighboring UTRAN or GERAN cells with
different PLMN IDs or the serving PLMN differs from the target PLMN, the operator
can use CSFB with LAI to achieve CSFB to a PLMN of the LAI preferentially.
l In a tracking area (TA) that overlaps multiple location areas (LAs)
The eNodeB selects a CSFB target cell with the same LAC as that mapped to the
network to which the UE has attached. An LAU is not required after CSFB, and
therefore the CSFB delay does not include the LAU time.
The eNodeB obtains the value of the LAI from the MME using an Initial Context Setup Req
or UE Context Mod Req message.
This feature is an enhancement to the optional feature LOFD-001033 CS Fallback to
UTRAN. With this feature, the eNodeB selects a target frequency or cell for measurement or
blind handover based on the LAI sent by the MME.
l In a measurement procedure, the eNodeB selects only an inter-RAT frequency on which
the PLMN ID of a neighboring cell is the same as that in the LAI received. The follow-
up measurement procedure is similar to that in CS Fallback to UTRAN. For details, see
3.4 Target Cell/Frequency Selection.
The difference is that the eNodeB sorts neighboring cells in the following order after
receiving measurement reports from a UE:
a. Neighboring cells with PLMN IDs and LACs the same as those in the LAI
b. Neighboring cells with PLMN IDs the same as that in the LAI but LACs different
from that in the LAI
eRAN
CS Fallback Feature Parameter Description 3 CSFB to UTRAN
Issue 03 (2015-08-31) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
17
-
7/25/2019 CS Fallback(eRAN8.1_03).pdf
28/344
If no frequency or neighboring cell can be selected based on the LAI, the processing is
the same as that when no LAI is received.
l In a blind handover procedure, the eNodeB first selects a target cell for blind handover.
If no neighboring UTRAN cell is configured, the eNodeB preferentially selects the
UTRAN frequencies whose PLMN ID is the same as that in the LAI. The follow-upprocedure is the same as that described in 3.4 Target Cell/Frequency Selection.
If neighboring UTRAN cells are configured, the eNodeB preferentially selects the
operating UTRAN frequencies of the neighboring UTRAN cells whose PLMN ID is the
same as that in the LAI. The eNodeB then sorts thefrequencies based on the blind
handover priorities of the neighboring cells and frequency priorities for connected mode.
For details, see 3.4 Target Cell/Frequency Selection.
The eNodeB selects a target cell in the following order of preference:
a. Neighboring cell whose PLMN ID and LAC are the same as those in the LAI
b. If no neighboring cells described in aexist, the eNodeB selects the neighboring
cells with PLMN IDs the same as that in the LAI but LACs different from that inthe LAI.
c. If no neighboring cells described in aand bexist, the eNodeB selects the
neighboring cells with PLMN IDs the same as the serving PLMN ID of the UE.
If the InterPlmnHoSwitchoption of the ENodeBAlgoSwitch .HoAlgoSwitch
parameter is selected, the eNodeB also selects cells whose PLMN IDs are in the
target PLMN list.
3.2.5 E-UTRAN to UTRAN CS Steering
This section describes the CS steering function in the optional feature LOFD-001078 E-
UTRAN to UTRAN CS/PS Steering. For details about the PS steering function in this feature,seeInter-RAT Mobility Management in Connected Mode Feature Parameter Description.
This feature applies to a scenario where service steering is required in a UTRAN with
multiple UTRA frequencies. By setting CS service priorities for UTRA frequencies, the
operator can achieve CSFB from E-UTRAN only to the UTRA frequency that has a high CS
service priority.
CS Steering in CSFB
This function is an enhancement to the CS Fallback to UTRAN feature. The enhancements
are as follows:
l During inter-RAT measurement on the UTRAN, frequencieswith a high CS service
priority are preferentially measured.
The UtranFreqLayerMeasSwitch option of the ENodeBAlgoSwitch .FreqLayerSwtich
parameter specifies whether to enable this function.
If the option is selected, the eNodeB preferentially selects frequencies with a high CS
service priority specified by the UtranNFreq. CsPriorityparameter as the measurement
targets. A larger value of this parameter indicates a higher priority. If this parameter is set
to Priority_0(Priority 0)fora frequency, the eNodeB does not select this frequency as
the measurement target. The follow-up measurement procedure is similar to that in CS
Fallback to UTRAN. For details, see 3.4 Target Cell/Frequency Selection.
l
During blind handover, cells working on frequencies with a high CS service priority arepreferentially selected.
eRAN
CS Fallback Feature Parameter Description 3 CSFB to UTRAN
Issue 03 (2015-08-31) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
18
-
7/25/2019 CS Fallback(eRAN8.1_03).pdf
29/344
The UtranFreqLayerBlindSwitch option of the ENodeBAlgoSwitch.FreqLayerSwtich
parameter specifies whether to enable this function.
If the option is selected, the eNodeB preferentially selects cells working on frequencies
with a high CS service priority specified by the UtranNFreq.CsPriorityparameter. A
larger value of this parameter indicates a higher priority. If this parameter is set toPriority_0(Priority 0)for a frequency, the eNodeB does not select cells working on this
frequency. The follow-up blind handover procedure is the same as that in CS Fallback to
UTRAN. For details, see 3.4 Target Cell/Frequency Selection.
LAI-based CS Steering in CSFB
This function is an enhancement to the CS Fallback with LAI to UTRAN feature. The
enhancements ar


![LIBOR Fallback - and Quantitative Finance · muRisQ Advisory LIBOR Fallback { Quantitative Finance 1 From basics to fallback [Pay-o ] 2 Fallback implementation { Adjusted RFR [Measurability]](https://static.fdocuments.net/doc/165x107/5f524239becc8538b630391f/libor-fallback-and-quantitative-finance-murisq-advisory-libor-fallback-quantitative.jpg)




![Rémi Forax - lrde.epita.fr · PDF fileRémi Forax Université Paris ... Object fallback(CallSite cs, Object[] args) { ... } The BSM installs a fallback method creates. ... ASM –](https://static.fdocuments.net/doc/165x107/5a710de67f8b9aac538c7ebd/rmi-forax-lrdeepitafr-nbsppdf-filermi-forax-universit.jpg)