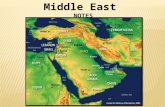
Core Case Study: Water Conflicts in the Middle East - A Preview of the Future Many countries in the...
-
Upload
augusta-claire-simon -
Category
Documents
-
view
224 -
download
0
Transcript of Core Case Study: Water Conflicts in the Middle East - A Preview of the Future Many countries in the...

Core Case Study: Water Conflicts in Core Case Study: Water Conflicts in the Middle East - A Preview the Middle East - A Preview
of the Futureof the Future Many countries in Many countries in
the Middle East, the Middle East, which has one of which has one of the world’s highest the world’s highest population growth population growth rates, face water rates, face water shortages.shortages.
Figure 14-1Figure 14-1

Water Conflicts in the Middle East: A Water Conflicts in the Middle East: A Preview of the FuturePreview of the Future
Most water in this dry region comes from the Most water in this dry region comes from the Nile, Jordan or Tigris rivers.Nile, Jordan or Tigris rivers.
Countries are in disagreement as to who has Countries are in disagreement as to who has water rights.water rights.
Currently, there are no cooperative Currently, there are no cooperative agreements for use of 158 of the world’s 263 agreements for use of 158 of the world’s 263 water basins that are shared by two or more water basins that are shared by two or more countries.countries.

WATER’S IMPORTANCE, WATER’S IMPORTANCE, AVAILABILITY, AND RENEWALAVAILABILITY, AND RENEWAL
Water Water keeps us alivekeeps us alive moderates climatemoderates climate sculpts the landsculpts the land removes and dilutes wastes and pollutantsremoves and dilutes wastes and pollutants moves continually through the hydrologic cycle.moves continually through the hydrologic cycle.
Only about 0.02% of the earth’s water supply Only about 0.02% of the earth’s water supply is available to us as liquid freshwater.is available to us as liquid freshwater.

WATER’S IMPORTANCE, WATER’S IMPORTANCE, AVAILABILITY, AND RENEWALAVAILABILITY, AND RENEWAL
ComparisoComparison of n of population population sizes and sizes and shares of shares of the world’s the world’s freshwater freshwater among the among the continents.continents.
Figure 14-2Figure 14-2

WATER’S IMPORTANCE, WATER’S IMPORTANCE, AVAILABILITY, AND RENEWALAVAILABILITY, AND RENEWAL
precipitation precipitation infiltrates the ground and is stored in soil and infiltrates the ground and is stored in soil and
rock (groundwater)rock (groundwater) EvaporatesEvaporates runs off (surface runoff) into bodies of waterruns off (surface runoff) into bodies of water
• The land from which the surface water drains into a The land from which the surface water drains into a body of water is called its body of water is called its watershedwatershed or or drainage drainage basinbasin..

Fig. 14-3, p. 308
Unconfined Aquifer Recharge Area
Precipitation Evaporation and transpiration Evaporation
Confined Recharge Area
Runoff
Flowing artesian well
Recharge Recharge Unconfined Unconfined AquiferAquifer
Stream Well requiring a pumpInfiltration Water
table LakeInfiltration
Unconfined aquifer
Confined aquiferConfining impermeable rock layer Confining impermeable rock layer
Less permeable Less permeable material such as claymaterial such as clay

WATER’S IMPORTANCE, WATER’S IMPORTANCE, AVAILABILITY, AND RENEWALAVAILABILITY, AND RENEWAL
We currently use more than half of the We currently use more than half of the world’s reliable runoff of surface water and world’s reliable runoff of surface water and could be using 70-90% by 2025.could be using 70-90% by 2025.
About 70% of the water we withdraw from About 70% of the water we withdraw from rivers, lakes, and aquifers is not returned to rivers, lakes, and aquifers is not returned to these sources.these sources.
Irrigation is the biggest user of water (70%), Irrigation is the biggest user of water (70%), followed by industries (20%) and cities and followed by industries (20%) and cities and residences (10%).residences (10%).

Water in the Water in the United StatesUnited States
Average Average precipitation (top) precipitation (top) in relation to in relation to water-deficit water-deficit regions and their regions and their proximity to proximity to metropolitan areas metropolitan areas (bottom).(bottom).
Figure 14-4Figure 14-4

Fig. 14-4a, p. 309
Average annual precipitation (centimeters)
More than 122
Less than 41 81–122
41–81

Fig. 14-4b, p. 309
Acute shortage
Metropolitan regions with population greater than 1 million
Shortage
Adequate supply

Case Study: Freshwater Resources in Case Study: Freshwater Resources in the United Statesthe United States
17 western states 17 western states by 2025 could face by 2025 could face intense conflict over intense conflict over scarce water scarce water needed for urban needed for urban growth, irrigation, growth, irrigation, recreation and recreation and wildlife.wildlife.
Figure 14-5Figure 14-5

TOO LITTLE FRESHWATERTOO LITTLE FRESHWATER
About 41% of the world’s population lives in About 41% of the world’s population lives in river basins that do not have enough river basins that do not have enough freshwater.freshwater.
Many parts of the world are experiencing:Many parts of the world are experiencing: Rivers running dry.Rivers running dry. Lakes and seas shrinking.Lakes and seas shrinking. Falling water tables from overpumped aquifers.Falling water tables from overpumped aquifers.

Stress on the World’s River BasinsStress on the World’s River Basins
Comparison of the amount of water available Comparison of the amount of water available with the amount used by humans.with the amount used by humans. Figure 14-6Figure 14-6

Case Study: Who Should Own and Case Study: Who Should Own and Manage Freshwater ResourcesManage Freshwater Resources
There is controversy over whether water There is controversy over whether water supplies should be owned and managed by supplies should be owned and managed by governments or by private corporations.governments or by private corporations.
European-based water companies aim to European-based water companies aim to control 70% of the U.S. water supply by control 70% of the U.S. water supply by buying up water companies and entering into buying up water companies and entering into agreements with cities to manage water agreements with cities to manage water supplies.supplies.

TOO LITTLE FRESHWATERTOO LITTLE FRESHWATER
Cities are outbidding farmers for water Cities are outbidding farmers for water supplies from rivers and aquifers.supplies from rivers and aquifers.
Countries are importing grain as a way to Countries are importing grain as a way to reduce their water use.reduce their water use.
More crops are being used to produce More crops are being used to produce biofuels.biofuels.
Our water options are:Our water options are: Get more water from aquifers and riversGet more water from aquifers and rivers desalinate ocean waterdesalinate ocean water waste less waterwaste less water

WITHDRAWING GROUNDWATER WITHDRAWING GROUNDWATER TO INCREASE SUPPLIESTO INCREASE SUPPLIES
Most aquifers are renewable resources Most aquifers are renewable resources unless water is removed faster than it is unless water is removed faster than it is replenished or if they are contaminated.replenished or if they are contaminated.
Groundwater depletion is a growing problem Groundwater depletion is a growing problem mostly from irrigation.mostly from irrigation. At least one-fourth of the farms in India are being At least one-fourth of the farms in India are being
irrigated from overpumped aquifers.irrigated from overpumped aquifers.

Fig. 14-7, p. 313
Trade-Offs
Withdrawing Groundwater
Advantages Disadvantages
Useful for drinking and irrigation
Aquifer depletion from overpumping
Available year-round
Sinking of land (subsidence) from overpumping
Exists almost everywhere
Polluted aquifers for decades or centuries
Renewable if not overpumped or contaminated
Saltwater intrusion into drinking water supplies near coastal areas
Reduced water flows into surface waters
No evaporation losses
Cheaper to extract than most surface waters
Increased cost and contamination from deeper wells

Groundwater Depletion: Groundwater Depletion: A Growing ProblemA Growing Problem
The Ogallala, the world’s largest aquifer, is The Ogallala, the world’s largest aquifer, is most of the red area in the center (Midwest).most of the red area in the center (Midwest).
Areas of Areas of greatest greatest aquifer aquifer depletion depletion from from groundwater groundwater overdraft in overdraft in the the continental continental U.S.U.S.
Figure 14-8Figure 14-8

Other Effects of Groundwater Other Effects of Groundwater OverpumpingOverpumping Groundwater Groundwater
overpumping overpumping can cause can cause land to sink, land to sink, and and contaminate contaminate freshwater freshwater aquifers near aquifers near coastal areas coastal areas with saltwater.with saltwater.
Figure 14-11Figure 14-11

Other Effects of Groundwater Other Effects of Groundwater OverpumpingOverpumping
Sinkholes Sinkholes form when form when the roof of an the roof of an underground underground cavern cavern collapses collapses after being after being drained of drained of groundwater.groundwater.
Figure 14-10Figure 14-10

Groundwater Pumping in Saudi Groundwater Pumping in Saudi Arabia (1986 – 2004)Arabia (1986 – 2004)
Irrigation systems from the nonrenewable aquifer appear as Irrigation systems from the nonrenewable aquifer appear as green dots. Brown dots are wells that have gone dry.green dots. Brown dots are wells that have gone dry. Figure 14-9Figure 14-9

Fig. 14-12, p. 316
Solutions
Groundwater Depletion
Prevention Control
Waste less water Raise price of water to discourage waste
Subsidize water conservation
Ban new wells in aquifers near surface waters
Tax water pumped from wells near surface waters
Buy and retire groundwater withdrawal rights in critical areas
Do not grow water-intensive crops in dry areas
Set and enforce minimum stream flow levels

USING DAMS AND RESERVOIRS USING DAMS AND RESERVOIRS TO SUPPLY MORE WATERTO SUPPLY MORE WATER
Large dams and reservoirs Large dams and reservoirs produce cheap electricityproduce cheap electricity reduce downstream floodingreduce downstream flooding provide year-round water for irrigating cropland provide year-round water for irrigating cropland
displace peopledisplace people disrupt aquatic systemsdisrupt aquatic systems

Figure 14-13Figure 14-13

Case Study: The Colorado Basin – an Case Study: The Colorado Basin – an Overtapped ResourceOvertapped Resource
The Colorado River has so many dams and The Colorado River has so many dams and withdrawals that it often does not reach the withdrawals that it often does not reach the ocean.ocean. 14 major dams and reservoirs, and canals.14 major dams and reservoirs, and canals. Water is mostly used in desert area of the U.S.Water is mostly used in desert area of the U.S. Provides electricity from hydroelectric plants for Provides electricity from hydroelectric plants for
30 million people (1/1030 million people (1/10thth of the U.S. population). of the U.S. population).

The Colorado River BasinThe Colorado River Basin
The area The area drained by this drained by this basin is equal to basin is equal to more than one-more than one-twelfth of the twelfth of the land area of the land area of the lower 48 states.lower 48 states.
Figure 14-14Figure 14-14

Dam RemovalDam Removal
Some dams are being removed for ecological Some dams are being removed for ecological reasons and because they have outlived their reasons and because they have outlived their usefulness.usefulness. In 1998 the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers In 1998 the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers
announced that it would no longer build large announced that it would no longer build large dams and diversion projects in the U.S.dams and diversion projects in the U.S.
The Federal Energy Regulatory Commission has The Federal Energy Regulatory Commission has approved the removal of nearly 500 dams.approved the removal of nearly 500 dams.
Removing dams can reestablish ecosystems, but Removing dams can reestablish ecosystems, but can also re-release toxicants into the can also re-release toxicants into the environment.environment.

TRANSFERRING WATER FROM TRANSFERRING WATER FROM ONE PLACE TO ANOTHERONE PLACE TO ANOTHER
Transferring water can: Transferring water can: make unproductive areas more productivemake unproductive areas more productive
• Promotes:Promotes: InvestmentInvestment JobsJobs Strong economyStrong economy
cause environmental harmcause environmental harm• encourages unsustainable use of waterencourages unsustainable use of water

Case Study: The Aral Sea DisasterCase Study: The Aral Sea Disaster
Aral Sea Aral Sea once the world’s 4once the world’s 4thth largest freshwater lake largest freshwater lake Figure 14-17Figure 14-17

Case Study: The Aral Sea DisasterCase Study: The Aral Sea Disaster
Diversion of water from the Aral Sea and its Diversion of water from the Aral Sea and its two feeder rivers two feeder rivers Used for irrigationUsed for irrigation
created a major ecological, economic, and health created a major ecological, economic, and health disasterdisaster• About 85% of the wetlands have been eliminatedAbout 85% of the wetlands have been eliminated• roughly 50% of the local bird and mammal species roughly 50% of the local bird and mammal species
have disappearedhave disappeared• the sea’s salinity has tripled the sea’s salinity has tripled • water has dropped by 22 meters water has dropped by 22 meters
causing 20 of the 24 native fish species to go extinctcausing 20 of the 24 native fish species to go extinct

DESALTING SEAWATER, SEEDING DESALTING SEAWATER, SEEDING CLOUDS, AND TOWING ICEBERGS CLOUDS, AND TOWING ICEBERGS
AND GIANT BAGGIESAND GIANT BAGGIES Removing salt from seawater by current Removing salt from seawater by current
methods is methods is expensiveexpensive and produces large and produces large amounts of salty amounts of salty wastewaterwastewater that must be that must be disposed of safelydisposed of safely DistillationDistillation: :
• heating saltwater until it evaporates, leaves behind heating saltwater until it evaporates, leaves behind waste in solid form.waste in solid form.
Reverse osmosisReverse osmosis::• uses high pressure to force saltwater through a uses high pressure to force saltwater through a
membrane filter.membrane filter.

INCREASING WATER SUPPLIES BY INCREASING WATER SUPPLIES BY WASTING LESS WATERWASTING LESS WATER
We waste about two-thirds of the water we We waste about two-thirds of the water we use, but we could cut this waste to 15%use, but we could cut this waste to 15% 65-70% of the water people use throughout the 65-70% of the water people use throughout the
world is lost through evaporation, leaks, and world is lost through evaporation, leaks, and other lossesother losses
Water is underpriced through government Water is underpriced through government subsidiessubsidies
The lack of government subsidies for improving The lack of government subsidies for improving the efficiency of water use contributes to water the efficiency of water use contributes to water wastewaste

INCREASING WATER SUPPLIES BY INCREASING WATER SUPPLIES BY WASTING LESS WATERWASTING LESS WATER
60% of the world’s irrigation water is currently 60% of the world’s irrigation water is currently wastedwasted improved irrigation techniques could cut this improved irrigation techniques could cut this
waste to 5-20%waste to 5-20% Center-pivot, low pressure sprinklers sprays Center-pivot, low pressure sprinklers sprays
water directly onto cropwater directly onto crop It allows 80% of water to reach cropIt allows 80% of water to reach crop Has reduced depletion of Ogallala aquifer in Has reduced depletion of Ogallala aquifer in
Texas High Plains by 30%.Texas High Plains by 30%.

Fig. 14-18, p. 325
Center pivotCenter pivot
Drip irrigationDrip irrigation
Gravity flowGravity flow(efficiency 60% and
80% with surge valves)
Above- or below-ground pipes or tubes deliver water to individual plant roots.
Water usually comes from an aqueduct system or a nearby river.
(efficiency 90–95%)
(efficiency 80%–95%)
Water usually pumped from underground and sprayed from mobile boom with sprinklers.

TOO MUCH WATERTOO MUCH WATER
Human activities have contributed to flood Human activities have contributed to flood deaths and damages.deaths and damages. Figure 14-23Figure 14-23