Control Of Gas Exchange In Humans
-
Upload
scuffruff -
Category
Health & Medicine
-
view
3.709 -
download
0
description
Transcript of Control Of Gas Exchange In Humans

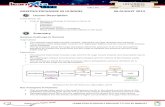
Gas Exchange in Gas Exchange in HumansHumans
The control of the rate of The control of the rate of breathing (ventilation)breathing (ventilation)

Optimum concentration of oxygen in blood

Optimum concentration of oxygen in blood
Increase in oxygen

Optimum concentration of oxygen in blood
Increase in oxygen

Optimum concentration of oxygen in blood
Increase in oxygen
Detected by chemoreceptors in aorta, carotid artery, and medulla oblongata in brain

Optimum concentration of oxygen in blood
Increase in oxygen
Detected by chemoreceptors in aorta, carotid artery, and medulla oblongata in brain

Optimum concentration of oxygen in blood
Increase in oxygen
Detected by chemoreceptors in aorta, carotid artery, and medulla oblongata in brain
Decrease in ventilation rate (and in heart rate)

Optimum concentration of oxygen in blood
Increase in oxygen
Detected by chemoreceptors in aorta, carotid artery, and medulla oblongata in brain
Decrease in ventilation rate (and in heart rate)

Optimum concentration of oxygen in blood
Increase in oxygen
Detected by chemoreceptors in aorta, carotid artery, and medulla oblongata in brain
Decrease in ventilation rate (and in heart rate)
Decrease in oxygen

Optimum concentration of oxygen in blood
Increase in oxygen
Detected by chemoreceptors in aorta, carotid artery, and medulla oblongata in brain
Decrease in ventilation rate (and in heart rate)
Decrease in oxygen
Optimum concentration of oxygen in blood

Optimum concentration of oxygen in blood
Increase in oxygen
Detected by chemoreceptors in aorta, carotid artery, and medulla oblongata in brain
Decrease in ventilation rate (and in heart rate)
Decrease in oxygen
Optimum concentration of oxygen in blood
Decrease in oxygen

Optimum concentration of oxygen in blood
Increase in oxygen
Detected by chemoreceptors in aorta, carotid artery, and medulla oblongata in brain
Decrease in ventilation rate (and in heart rate)
Decrease in oxygen
Optimum concentration of oxygen in blood
Decrease in oxygen

Optimum concentration of oxygen in blood
Increase in oxygen
Detected by chemoreceptors in aorta, carotid artery, and medulla oblongata in brain
Decrease in ventilation rate (and in heart rate)
Decrease in oxygen
Optimum concentration of oxygen in blood
Decrease in oxygen
Detected by chemoreceptors in aorta, carotid artery, and medulla oblongata in brain

Optimum concentration of oxygen in blood
Increase in oxygen
Detected by chemoreceptors in aorta, carotid artery, and medulla oblongata in brain
Decrease in ventilation rate (and in heart rate)
Decrease in oxygen
Optimum concentration of oxygen in blood
Decrease in oxygen
Detected by chemoreceptors in aorta, carotid artery, and medulla oblongata in brain

Optimum concentration of oxygen in blood
Increase in oxygen
Detected by chemoreceptors in aorta, carotid artery, and medulla oblongata in brain
Decrease in ventilation rate (and in heart rate)
Decrease in oxygen
Optimum concentration of oxygen in blood
Decrease in oxygen
Detected by chemoreceptors in aorta, carotid artery, and medulla oblongata in brain
Increase in ventilation rate (and in heart rate)

Optimum concentration of oxygen in blood
Increase in oxygen
Detected by chemoreceptors in aorta, carotid artery, and medulla oblongata in brain
Decrease in ventilation rate (and in heart rate)
Decrease in oxygen
Optimum concentration of oxygen in blood
Decrease in oxygen
Detected by chemoreceptors in aorta, carotid artery, and medulla oblongata in brain
Increase in ventilation rate (and in heart rate)
Increase in oxygen

Optimum concentration of oxygen in blood
Increase in oxygen
Detected by chemoreceptors in aorta, carotid artery, and medulla oblongata in brain
Decrease in ventilation rate (and in heart rate)
Decrease in oxygen
Optimum concentration of oxygen in blood
Decrease in oxygen
Detected by chemoreceptors in aorta, carotid artery, and medulla oblongata in brain
Increase in ventilation rate (and in heart rate)
Increase in oxygen