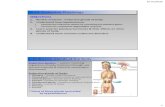
The Endocrine System /biology/the-human- body/endocrine-system
Control Of Body Processes Through The Endocrine System
-
date post
19-Oct-2014 -
Category
Education
-
view
3.649 -
download
0
description
Transcript of Control Of Body Processes Through The Endocrine System

GOOD GOOD
MORINIG
MORINIG
!!

ATTENTION ATTENTION
ATTENTION ATTENTION
ATTENTION ATTENTION
ATTENTION ATTENTION
ATTENTION ATTENTION
ATTENTION ATTENTION
ATTENTION ATTENTION
ATTENTION ATTENTION
ATTENTION ATTENTION
ATTENTION ATTENTION
ATTENTION ATTENTION
ATTENTION ATTENTION
ATTENTION ATTENTION
ATTENTION ATTENTION
ATTENTION ATTENTION
ATTENTION ATTENTION
ATTENTION ATTENTION
ATTENTION ATTENTION
ATTENTION ATTENTION
ATTENTION ATTENTION

CONTROL OF BODY PROCESSES
THROUGH THE ENDOCRINE
SYSTEM

DUCT GLAND-fine tubes present in all glands through -fine tubes present in all glands through
which their secretion pass.which their secretion pass.DUCTLESS GLANDSDUCTLESS GLANDS
- another group of glands in the body are - another group of glands in the body are which don’t have which don’t have ducts.ducts.
- they go directly into the blood streams- they go directly into the blood streams
- the secretions diffuse from the secreting - the secretions diffuse from the secreting cells through the walls of the blood vessels into cells through the walls of the blood vessels into the blood.the blood.

THYROXINTHYROXIN®® A hormone produced by the thyroid gland to regulate the A hormone produced by the thyroid gland to regulate the
growth of the body and oxidation in the cells.growth of the body and oxidation in the cells. It produces a very important component in the body which is It produces a very important component in the body which is
iodine.iodine.
HypothyroidismHypothyroidism – a disease caused by the lacking of – a disease caused by the lacking of production of thyroxin in the body. This disorder is production of thyroxin in the body. This disorder is characterized b slow beating of the heart and low metabolic characterized b slow beating of the heart and low metabolic rate.rate.
– – the prefix the prefix hypo- hypo- means means abnormal abnormal deficiency.deficiency.

HyperthyroidismHyperthyroidism – it is caused by the overproduction – it is caused by the overproduction of thyroxin or overactivity of the thyroid gland.of thyroxin or overactivity of the thyroid gland.
– – the prefix the prefix hyper- hyper- means abnormal means abnormal excess.excess.
Effects of HyperthyroidismEffects of Hyperthyroidism High metabolic rateHigh metabolic rate Oxygen is used up at a fast rate to cope with the high Oxygen is used up at a fast rate to cope with the high
rate of chemical reaction in the cells.rate of chemical reaction in the cells. The heart beat fastThe heart beat fast Highly nervous and irritableHighly nervous and irritable Bulging of the eye balls (a case of Bulging of the eye balls (a case of exophthalmic exophthalmic
goiter)goiter)

SENSITIVE SENSITIVE IMAGES IMAGES
CAUTION:CAUTION:




PARATHORMONEPARATHORMONE®®
A hormone produced by the A hormone produced by the parathyroid glands which parathyroid glands which regulates the amount of regulates the amount of calcium calcium and and phosphorus phosphorus in the blood.in the blood.
It controls the deposition of It controls the deposition of calcium salts in the bones and calcium salts in the bones and teeth.teeth.

HyperparathyroidismHyperparathyroidism
An overactivity of the parathyroid glands resulting in An overactivity of the parathyroid glands resulting in excess production of parathyroid hormones (PTH). excess production of parathyroid hormones (PTH). The parathyroid hormone regulates calcium and The parathyroid hormone regulates calcium and phosphate levels and helps to maintain these levels. phosphate levels and helps to maintain these levels. Overactivity of one or more of the parathyroid glands Overactivity of one or more of the parathyroid glands causes high calcium levels and low levels of causes high calcium levels and low levels of phosphate in the blood. phosphate in the blood.
HypoparathyroidismHypoparathyroidismIn medicine, In medicine, hypoparathyroidismhypoparathyroidism is decreased is decreased function of the parathyroid glands, leading to function of the parathyroid glands, leading to decreased levels of parathyroid hormones (PTH). The decreased levels of parathyroid hormones (PTH). The consequence, consequence, hypocalcemiahypocalcemia, is a serious medical , is a serious medical condition. condition.

Signs and symptomsSigns and symptoms(Hypoparathyroidism(Hypoparathyroidism))
Tingling lips, fingers, and toes Tingling lips, fingers, and toes Muscle cramps Muscle cramps Pain in the face, legs, and feet Pain in the face, legs, and feet Abdominal pain Abdominal pain Dry hair Dry hair Brittle nails Brittle nails Dry, scaly skin Dry, scaly skin CataractsCataracts Weakened tooth enamel (in children) Weakened tooth enamel (in children) Muscle spasms called tetany (can lead to spasms of the larynx, causing Muscle spasms called tetany (can lead to spasms of the larynx, causing
breathing difficulties) breathing difficulties) Convulsions (seizures) Convulsions (seizures) Additional symptoms that may be associated with this disease include:Additional symptoms that may be associated with this disease include: Painful menstruation Painful menstruation Hand or foot spasms Hand or foot spasms Decreased consciousness Decreased consciousness Delayed or absent tooth formation Delayed or absent tooth formation

CAUTION:CAUTION:VERY VERY
SENSITIVE SENSITIVE IMAGESIMAGES

vv

INSULININSULIN®® A hormone secreted by a group of cells in the A hormone secreted by a group of cells in the
pancreas known as the pancreas known as the Islets of Langerhans.Islets of Langerhans.It controls the transformation of the simple It controls the transformation of the simple
sugar glucose into sugar glucose into glycogenglycogenLowers the amount of sugar in the blood.Lowers the amount of sugar in the blood.
DIABETES DIABETES
- - The condition when the body does not have The condition when the body does not have enough insulin, the blood sugar increases, enough insulin, the blood sugar increases, and glucose appears even in the urine.and glucose appears even in the urine.

GLUCAGONGLUCAGON®®
Another hormone produced by Another hormone produced by the pancreas.the pancreas.
It tends to raise the amount of It tends to raise the amount of sugar in the blood by changing sugar in the blood by changing liver glycogen into glucose that liver glycogen into glucose that is more energy is needed by the is more energy is needed by the cells.cells.


HORMONES OF MANHORMONES OF MAN
Regulates sodium, calcium and water balance of the
blood
Maintains carbohyadrates, fat and protein metabolism,
and promotes health of connective tissues.
Influence development of secondary sex characteristics.
Cortin
Cortisone
Sex hormones
Adrenal
I. CORTEX
Regulates amount of calcium in the blood.
ParathormoneParathyroid
Controls metabolic rate, physical and mental
growth.
ThyroxinThyroid
FUNCTIONHORMONEGLAND

Controls male secondary sex characteristics.
AndrogenTestis
Controls female secondary sex characteristics.
EstrogenOvary
Controls transformation of blood glucose into liver glycogen.
InsulinBeta Cells of Islets of Langerhans
Controls transformation of liver glycogen into blood glucose.
Glucagon
Pancreas
Islets of Langerhans
Hastens release of glucose into blood, increase rate of heartbeat, increases blood
pressures.
Controls blood vessels.
Adrenaline
Noradrenaline
I. MEDULLA

Controls elimination of water by the kidneys.
Controls contraction of smooth muscles of uterus.
Vasoressin
Oxytocin
II. NEURO PHYPO-
PHYSIS
Regulates growth of skeleton.
Regulates activity of thyroid.
Regulates follicle formation in ovary and sperm-formation in testis.
Stimulates mammary glands to secrete milk.
Regulates activity to adrenal cortex.
Growth hormone
Thyrotropic hormone
Follicle-Stimulating hormone (FSH)
Prolactin
Adrenocorticortropic hormone (ACTCH)
Hypophysis
I. ADENOHYPOPHYSIS

Stimulates secretion of pancreatic juice by pancreatic glands.
Secretin
Stimulates secretion of gastric juice by gastric glands.
GastrinStomach
Upper Intestine
Controls formation of andtibodies.
Thymus hormoneThymus

HomeostasisHomeostasis The ability or tendency of an organism or cell to maintain The ability or tendency of an organism or cell to maintain
internal equilibrium by adjusting its physiological internal equilibrium by adjusting its physiological processes.processes.
Any self-regulating process by which a biological or Any self-regulating process by which a biological or mechanical system maintains stability while adjusting to mechanical system maintains stability while adjusting to changing conditions. Systems in dynamic changing conditions. Systems in dynamic equilibrium reach a balance in which internal change continuously reach a balance in which internal change continuously compensates for external change in a feedback control compensates for external change in a feedback control process to keep conditions relatively uniform. An example process to keep conditions relatively uniform. An example is temperature regulation — mechanically in a room by a is temperature regulation — mechanically in a room by a thermostat or biologically in the body by a complex system or biologically in the body by a complex system controlled by the controlled by the hypothalamus, which adjusts breathing , which adjusts breathing and metabolic rates, blood-vessel dilation, and blood-and metabolic rates, blood-vessel dilation, and blood-sugar level in response to changes caused by factors sugar level in response to changes caused by factors including ambient temperature, hormones, and disease.including ambient temperature, hormones, and disease.

The following discussion illustrates homeostasis The following discussion illustrates homeostasis involving the sugar level in the blood. The normal level involving the sugar level in the blood. The normal level is about 90 mg glucose per 100 mL of blood.is about 90 mg glucose per 100 mL of blood.
Suppose a student plays a basketball during the Suppose a student plays a basketball during the noon break and incidentally misses his lunch. noon break and incidentally misses his lunch. What may happen inside his body as a result?What may happen inside his body as a result?
1.1. The level of his blood glucose may drop The level of his blood glucose may drop below normal.below normal.
2.2. The hypothalamus detects the situation and The hypothalamus detects the situation and sends out appropriate signals.sends out appropriate signals.
3.3. The pancreas is stimulated to release The pancreas is stimulated to release glucagon glucagon directly into the blood.directly into the blood.
4.4. The liver transforms glycogen into glucose The liver transforms glycogen into glucose and releases it into the blood.and releases it into the blood.

5.5. The blood glucose level rises to normal; the The blood glucose level rises to normal; the pancreas stops releasing glucagon.pancreas stops releasing glucagon.
Suppose a student chooses for snacks a serving Suppose a student chooses for snacks a serving of spaghetti, cake, ice cream and a bottle of of spaghetti, cake, ice cream and a bottle of softdrink. What may happen inside her a body as softdrink. What may happen inside her a body as a result?a result?
1)1) The level of her blood glucose may The level of her blood glucose may rise beyond normal.rise beyond normal.
2)2) The hypothalamus detects the situation and The hypothalamus detects the situation and sends out appropriate signals.sends out appropriate signals.
3)3) The pancreas is stimulated to release The pancreas is stimulated to release insulin insulin into into the bloodstream.the bloodstream.
4)4) The liver transforms glucose into glycogen and The liver transforms glucose into glycogen and strores it in its tissues, while the muslcdes and strores it in its tissues, while the muslcdes and

other body tissues also take up additional glucose.
5) The blood glucose level goes down to normal; the pancreas stops releasing extra insulin.
What happens when the body is not healthy? For instance, what happens when the pancreas does not produce enough insulin for one reason or another, or when the body cells do not take in glucose as efficiently or as fast as they should?

Thank You For Thank You For ListeningListening

REPORTED REPORTED BY:BY:VILLOTE, VILLOTE,
JOMAR K.JOMAR K.
The EndThe End