Computational Methods for Protein Structure...
Transcript of Computational Methods for Protein Structure...

Computational Methods for Computational Methods for ppProtein Structure PredictionProtein Structure Prediction
Ying XuYing Xugg
2010/1/192010/1/19 11

OutlineOutlineOutlineOutlinei t d ti t t i t ti t d ti t t i t t introduction to protein structuresintroduction to protein structures
the problem of protein structure predictionthe problem of protein structure prediction the problem of protein structure predictionthe problem of protein structure prediction
protein secondary structure predictionprotein secondary structure prediction protein secondary structure predictionprotein secondary structure prediction
protein tertiary structure predictionprotein tertiary structure prediction protein tertiary structure predictionprotein tertiary structure prediction Ab initioAb initio foldingfolding homology modelinghomology modeling
protein threadingprotein threading
2010/1/192010/1/19 22

Protein Protein Sequence, Structure and FunctionSequence, Structure and Function
>1MBN:_ MYOGLOBIN (154 AA)
Protein sequence_
MVLSEGEWQLVLHVWAKVEADVAGHGQDILIRLFKSHPETLEKFDRFKHLKTEAEMKASEDLKKAGVTVLTALGAILKKKGHHEAELKPLAQSHATKHKIPIKYLEFISEAIIHVLHSRHPGNFGADAQGAMNKALELFRKDIAAKYKELGYQG
Protein structure
Protein function
Oxygen storage
function
2010/1/192010/1/19 33

Protein StructureProtein StructureProtein StructureProtein Structure protein sequence folds into a “unique” shape (“structure”) thatprotein sequence folds into a “unique” shape (“structure”) that protein sequence folds into a unique shape ( structure ) that protein sequence folds into a unique shape ( structure ) that
minimizes its free potential energyminimizes its free potential energy
2010/1/192010/1/19 44

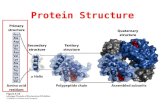
Protein StructuresProtein StructuresProtein StructuresProtein Structures Primary sequence Primary sequence
MTYKLILNGKTKGETTTEAVDAATAEKVFQYANDNGVDGEWTYTE
Secondary structureSecondary structure
-helix
-sheet
anti-parallel
ll l
2010/1/192010/1/19 55
parallel

Protein StructuresProtein StructuresProtein StructuresProtein Structures Tertiary structureTertiary structure Tertiary structureTertiary structure
Quaternary structureQuaternary structure Quaternary structureQuaternary structure
2010/1/192010/1/19 66

Protein StructuresProtein StructuresProtein StructuresProtein Structures
Backbone Backbone versusversus allall--atom structuresatom structures
Backbone + sidechain = all-atom structure
2010/1/192010/1/19 77Backbone structure == structural fold

Protein StructuresProtein StructuresProtein StructuresProtein Structures
Protein structureProtein structure generally compactgenerally compact
Soluble protein structureSoluble protein structure individual domains are generally globularindividual domains are generally globularg y gg y g they share various common characteristics, e.g. hydrophobic they share various common characteristics, e.g. hydrophobic
moment profilemoment profile
Membrane protein structureMembrane protein structure
most of the amino acid sidechains of transmembrane segments are non-polar
polar groups of the polypeptide backbone of transmembrane segments generally participate in hydrogen bonds
2010/1/192010/1/19 88
segments generally participate in hydrogen bonds

Protein Structure PredictionProtein Structure PredictionProtein Structure PredictionProtein Structure PredictionProblem: Given the amino acid sequence of a protein, computationally predict its 3-dimensional shape?
MVLSEGEWQLVLHVWAKVEADVAGHGQDILIRLFKSHPETLEKFDRFKHLKTEAEMKASEDLKKAGVTVLTALGAILKKKGHHEAELKPLAQSHATKHKIPIKYLEFISEAIIHVLHSRHPGNFGADAQGAMNKALELFRKDIAAKYKELGYQG
? ……..2010/1/192010/1/19 99

Secondary Structure PredictionSecondary Structure PredictionSecondary Structure PredictionSecondary Structure Prediction
Eight Secondary Structure Types
H: -helix (i, i+4 form hydrogen bond)G: 310 helix (i, i+3 form hydrogen bond)I: -helix (i i+5 form hydrogen bond)
HI: helix (i, i+5 form hydrogen bond)E: -strandB: bridgeT: turn
E
T: -turnS: bendC: coil
C
Rough categories: H, E, C
2010/1/192010/1/19 1010

Secondary Structure PredictionSecondary Structure PredictionSecondary Structure PredictionSecondary Structure Prediction
Given a protein sequence (primary structure), predict its Given a protein sequence (primary structure), predict its secondary structure categoriessecondary structure categoriesy gy g
GGHWIATHWIATRGQRGQLIREALIREAYEDYEDYRHFSSYRHFSSECPFIPECPFIP E: -strandH: -helix
CEEEEEEEEEECCCCCEEEEEEEEEECCCCCCHHHHHHHHHHHHCCCCCC
C: coil
Assumption: short stretches of residues have propensity to adopt certainstructural conformation
2010/1/192010/1/19 1111

Secondary Structure PredictionSecondary Structure PredictionSecondary Structure PredictionSecondary Structure PredictionSecondary structure propensitiesSecondary structure propensities::Calculate the propensity for a given amino acid to adopt a certain ssCalculate the propensity for a given amino acid to adopt a certain ss--typetype
( | ) ( , )( ) ( ) ( )
i i iP aa p aaPp p p aa
i, amino acid, secondary structure
type( ) ( ) ( )ip p p aa
Example: a data set with 300 proteins containing #residues=20 000
type
Example: a data set with 300 proteins containing #residues 20,000, #Ala=2,000, #helix=4,000, #Ala in helix=500
p(,aa) = 500/20,000, p() = 4,000/20,000, p(aa) = 2,000/20,000P = 500 / (4,000/10) = 1.25
2010/1/192010/1/19 1212

Secondary Structure PredictionSecondary Structure PredictionSecondary Structure PredictionSecondary Structure Prediction
2010/1/192010/1/19 1313

Secondary Structure PredictionSecondary Structure PredictionSecondary Structure PredictionSecondary Structure PredictionP di t h li ( d di t t d)P di t h li ( d di t t d)Predict helix (and predict strand)Predict helix (and predict strand)
1. Scan each window of 6 residues; if score > 4 predict 1. Scan each window of 6 residues; if score > 4 predict helixhelix ( if score > 3 ( if score > 3 predict predict strand)strand)
2. Propagate in both directions until 4 residue window with mean 2. Propagate in both directions until 4 residue window with mean propensity < 1propensity < 1
3. Move forward and repeat3. Move forward and repeat
Resolving ConflictsResolving ConflictsFor overlapping regions, decide according to propensity parametersFor overlapping regions, decide according to propensity parameters
2010/1/192010/1/19 1414Chou-Fasman designed the first prediction program

Secondary Structure PredictionSecondary Structure PredictionSecondary Structure PredictionSecondary Structure PredictionThi i l l ith h d 60% di ti dThi i l l ith h d 60% di ti d This simple algorithm had ~60% prediction accuracy and This simple algorithm had ~60% prediction accuracy and was the best prediction for a long whilewas the best prediction for a long while
The next breakthrough came in 1999 when PSIThe next breakthrough came in 1999 when PSI--PRED PRED program was developedprogram was developedp g pp g p
Key ideasKey ideas using sequence profiles, generated by psiusing sequence profiles, generated by psi--blast, rather than blast, rather than
individual sequence for secondary structureindividual sequence for secondary structure combining multiple predictors using a neural networkcombining multiple predictors using a neural networkg p p gg p p g accuracy reaches ~76%accuracy reaches ~76%
2010/1/192010/1/19 1515

Secondary Structure PredictionSecondary Structure PredictionSecondary Structure PredictionSecondary Structure PredictionU i l i i h di i hU i l i i h di i h Using larger training sets, the prediction accuracy can reach Using larger training sets, the prediction accuracy can reach ~80%; So how far can we further push this~80%; So how far can we further push this
NonNon--locality. Secondary structure is influenced by longlocality. Secondary structure is influenced by long--range range interactionsinteractions
S t h lti l t t tS t h lti l t t t Some segments can have multiple structure typesSome segments can have multiple structure types((chameleon sequenceschameleon sequences))
There is some room for improvement but not much
2010/1/192010/1/19 1616Long Piccolo C2A Short Piccolo C2A

Methods for Tertiary Structure Methods for Tertiary Structure PredictionPrediction
b i iti ab initio use first principles to fold proteins does not require templates does not require templates high computational complexity
homology modeling similar sequence similar structures practically very useful need homologues practically very useful, need homologues
protein threading many proteins share the same structural fold a folding problem becomes a fold recognition problem
2010/1/192010/1/19 1717

Ab initioAb initio Structure PredictionStructure PredictionAb initioAb initio Structure PredictionStructure PredictionA f ti t d ib th t iA f ti t d ib th t iAn energy function to describe the proteinAn energy function to describe the protein
oo bond energybond energyoo bond angle energybond angle energyoo dihedral angel energydihedral angel energyoo van der Waalsvan der Waals energyenergyoo electrostatic energyelectrostatic energy
Need an algorithm to search the conformational space to find structural Need an algorithm to search the conformational space to find structural conformation that minimizes the function.conformation that minimizes the function.
Not practical in generalNot practical in generalcomputationally too expensivecomputationally too expensiveoo computationally too expensivecomputationally too expensive
oo accuracy is pooraccuracy is poor
2010/1/192010/1/19 1818

Homology ModelingHomology ModelingHomology ModelingHomology ModelingObservation: proteins with similar sequences tend to fold into
similar structures.
1. Target sequence is aligned with the sequence of a known structure (typically requiring they share sequence identity 30% or higher)
2. Superimpose target sequence onto the template, replacing equivalent side-chain atoms where necessary
3. Refine the model by minimizing an energy function.
PPrograms: Modeller http://salilab.org/modeller/Swiss-Model http://swissmodel expasy org//SWISS MODEL html
2010/1/192010/1/19 1919
Swiss-Model http://swissmodel.expasy.org//SWISS-MODEL.html

Protein ThreadingProtein ThreadingProtein ThreadingProtein Threading Basic premiseBasic premise Basic premiseBasic premise
The number of unique structural (domain) folds in nature
Statistics from Protein Data Bank (~61 000 structures)Statistics from Protein Data Bank (~61 000 structures)
is fairly small (possibly a few thousand)
Statistics from Protein Data Bank ( 61,000 structures)Statistics from Protein Data Bank ( 61,000 structures)
90% of new structures submitted to PDB in the past
Chances for a protein to have a nativeChances for a protein to have a native like structural fold inlike structural fold in
90% of new structures submitted to PDB in the past three years have similar structural folds in PDB
Chances for a protein to have a nativeChances for a protein to have a native--like structural fold in like structural fold in PDB are quite goodPDB are quite good (estimated to be 60(estimated to be 60--70%)70%)
Proteins with similar structural folds could be Proteins with similar structural folds could be homologueshomologues or or analoguesanalogues
2010/1/192010/1/19 2020

Protein ThreadingProtein ThreadingProtein ThreadingProtein Threading
The goalThe goal: find the “correct” sequence: find the “correct” sequence--structure alignment structure alignment between a target sequence and its nativebetween a target sequence and its native--like fold in PDBlike fold in PDB
Energy functionEnergy function –– knowledge (or statistics) based rather than knowledge (or statistics) based rather than
MTYKLILN …. NGVDGEWTYTE
physics based physics based Should be able to distinguish correct structural folds from incorrect Should be able to distinguish correct structural folds from incorrect
structural foldsstructural folds Should be able to distinguish correct sequenceShould be able to distinguish correct sequence--fold alignment from fold alignment from
incorrect sequenceincorrect sequence--fold alignmentsfold alignments
2010/1/192010/1/19 2121

Protein ThreadingProtein Threading four basic componentsfour basic componentsProtein Threading Protein Threading –– four basic componentsfour basic components
Structure databaseStructure database
Energy functionEnergy function
SequenceSequence--structure alignment algorithmstructure alignment algorithm
Prediction reliability assessmentPrediction reliability assessment
2010/1/192010/1/19 2222

Protein ThreadingProtein Threading t t d t bt t d t bProtein Threading Protein Threading –– structure databasestructure database
Build a template databaseBuild a template database
2010/1/192010/1/19 2323

Protein ThreadingProtein Threading t t d t bt t d t bProtein Threading Protein Threading –– structure databasestructure database
• Non-redundant representatives through structure-structure and/or sequence sequence comparisonand/or sequence-sequence comparison
FSSP (http://www.bioinfo.biocenter.helsinki.fi:8080/dali/index.html)( p )(Families of Structurally Similar Proteins)
SCOP (http://scop.mrc-lmb.cam.ac.uk/scop/)
PDB-Select (http://www.sander.embl-heidelberg.de/pdbsel/)
Pisces (http://www.fccc.edu/research/labs/dunbrack/pisces/)
2010/1/192010/1/19 2424

Protein ThreadingProtein Threading f tif tiProtein Threading Protein Threading –– energy functionenergy function
MTYKLILNGKTKGETTTEAVDAATAEKVFQYANDNGVDGEWTYTE
f
how well a residue fitst t l
how preferable to put two particular residues nearby: E_p
a structural environment: E_s
alignment gap penalty: E_g
total energy: E p + E s + E gtotal energy: E_p + E_s + E_g
find a sequence-structure alignment t i i i th f ti
2010/1/192010/1/19 2525
to minimize the energy function

Protein ThreadingProtein Threading f tif tiProtein Threading Protein Threading –– energy functionenergy function
A singleton energy measures each residue’s preference in a specific A singleton energy measures each residue’s preference in a specific structural environmentsstructural environments secondary structuresecondary structure secondary structuresecondary structure solvent accessibilitysolvent accessibility
Compare actual occurrence against its “expected value” by chanceCompare actual occurrence against its “expected value” by chance
where
2010/1/192010/1/19 2626

Protein ThreadingProtein Threading f tif tiProtein Threading Protein Threading –– energy functionenergy function
A simple definition of structural environmentA simple definition of structural environment secondary structure: alphasecondary structure: alpha--helix, betahelix, beta--strand, loopstrand, loop
solvent accessibility: 0 10 20 100% of accessibilitysolvent accessibility: 0 10 20 100% of accessibility solvent accessibility: 0, 10, 20, …, 100% of accessibilitysolvent accessibility: 0, 10, 20, …, 100% of accessibility each combination of secondary structure and solvent each combination of secondary structure and solvent
accessibility level defines a structural environmentaccessibility level defines a structural environment•• E.g., (alphaE.g., (alpha--helix, 30%), (loop, 80%), …helix, 30%), (loop, 80%), …
E_s: a scoring matrix of 30 structural environments by 20 amino E_s: a scoring matrix of 30 structural environments by 20 amino acidsacidsacidsacids E.g., E_s ((loop, 30%), A)E.g., E_s ((loop, 30%), A)
i l t t
2010/1/192010/1/19 2727
singleton energy term

Protein ThreadingProtein Threading f tif tiProtein Threading Protein Threading –– energy functionenergy function
Helix Sheet LoopBuried Inter Exposed Buried Inter Exposed Buried Inter Exposed
ALA -0.578 -0.119 -0.160 0.010 0.583 0.921 0.023 0.218 0.368ARG 0 997 0 507 0 488 1 267 0 345 0 580 0 930 0 005 0 032ARG 0.997 -0.507 -0.488 1.267 -0.345 -0.580 0.930 -0.005 -0.032ASN 0.819 0.090 -0.007 0.844 0.221 0.046 0.030 -0.322 -0.487ASP 1.050 0.172 -0.426 1.145 0.322 0.061 0.308 -0.224 -0.541CYS -0.360 0.333 1.831 -0.671 0.003 1.216 -0.690 -0.225 1.216GLN 1.047 -0.294 -0.939 1.452 0.139 -0.555 1.326 0.486 -0.244GLU 0.670 -0.313 -0.721 0.999 0.031 -0.494 0.845 0.248 -0.144GLY 0.414 0.932 0.969 0.177 0.565 0.989 -0.562 -0.299 -0.601HIS 0.479 -0.223 0.136 0.306 -0.343 -0.014 0.019 -0.285 0.051ILE -0.551 0.087 1.248 -0.875 -0.182 0.500 -0.166 0.384 1.336LEU -0.744 -0.218 0.940 -0.411 0.179 0.900 -0.205 0.169 1.217LEU 0.744 0.218 0.940 0.411 0.179 0.900 0.205 0.169 1.217LYS 1.863 -0.045 -0.865 2.109 -0.017 -0.901 1.925 0.474 -0.498MET -0.641 -0.183 0.779 -0.269 0.197 0.658 -0.228 0.113 0.714PHE -0.491 0.057 1.364 -0.649 -0.200 0.776 -0.375 -0.001 1.251PRO 1.090 0.705 0.236 1.249 0.695 0.145 -0.412 -0.491 -0.641SER 0 350 0 260 0 020 0 303 0 058 0 075 0 173 0 210 0 228SER 0.350 0.260 -0.020 0.303 0.058 -0.075 -0.173 -0.210 -0.228THR 0.291 0.215 0.304 0.156 -0.382 -0.584 -0.012 -0.103 -0.125TRP -0.379 -0.363 1.178 -0.270 -0.477 0.682 -0.220 -0.099 1.267TYR -0.111 -0.292 0.942 -0.267 -0.691 0.292 -0.015 -0.176 0.946VAL -0.374 0.236 1.144 -0.912 -0.334 0.089 -0.030 0.309 0.998
2010/1/192010/1/19 2828

Protein ThreadingProtein Threading f tif tiProtein Threading Protein Threading –– energy functionenergy function
It measures the preference of a pair of amino acids to be It measures the preference of a pair of amino acids to be close in 3D space. close in 3D space.
Observed occurrence of a pair compared with its “expected” Observed occurrence of a pair compared with its “expected” occurrenceoccurrenceoccurrenceoccurrence
uniform state model
pair-wise interaction energy term
2010/1/192010/1/19 2929

Protein ThreadingProtein Threading f tif tiProtein Threading Protein Threading –– energy functionenergy function
ALA -140ARG 268 -18ASN 105 -85 -435ASP 217 -616 -417 17CYS 330 67 106 278 -1923GLN 27 -60 -200 67 191 -115GLU 122 -564 -136 140 122 10 68GLY 11 -80 -103 -267 88 -72 -31 -288HIS 58 -263 61 -454 190 272 -368 74 -448ILE -114 110 351 318 154 243 294 179 294 -326LEU -182 263 358 370 238 25 255 237 200 -160 -278LYS 123 310 -201 -564 246 -184 -667 95 54 194 178 122MET -74 304 314 211 50 32 141 13 -7 -12 -106 301 -494PHE -65 62 201 284 34 72 235 114 158 -96 -195 -17 -272 -206PRO 174 -33 -212 -28 105 -81 -102 -73 -65 369 218 -46 35 -21 -210SER 169 -80 -223 -299 7 -163 -212 -186 -133 206 272 -58 193 114 -162 -177THR 58 60 -231 -203 372 -151 -211 -73 -239 109 225 -16 158 283 -98 -215 -210TRP 51 -150 -18 104 52 -12 157 -69 -212 -18 81 29 -5 31 -432 129 95 -20TYR 53 -132 53 268 62 -90 269 58 34 -163 -93 -312 -173 -5 -81 104 163 -95 -6VAL -105 171 298 431 196 180 235 202 204 -232 -218 269 -50 -42 46 267 73 101 107 -324
ALA ARG ASN ASP CYS GLN GLU GLY HIS ILE LEU LYS MET PHE PRO SER THR TRP TYR VAL
2010/1/192010/1/19 3030

Protein ThreadingProtein Threading f tif tiProtein Threading Protein Threading –– energy functionenergy function
w(k) = h + gk, k ≥ 1, w(0) = 0;
h: opening gap penaltyg: extension gap penaltyg: extension gap penalty
FDSK---THRGHR:.: :: :::FESYWTCTH GHR
FDSK-T--HRGHR:.: : : :::FESYWTCTH GHRFESYWTCTH-GHR FESYWTCTH-GHR
gap penalty term
2010/1/192010/1/19 3131
gap penalty term

Threading Parameter OptimizationThreading Parameter OptimizationThreading Parameter OptimizationThreading Parameter Optimization
How to determine the weight of different energy term?How to determine the weight of different energy term?EEtotal = total = ssEEsingletonsingleton + + ppEEpairwisepairwise + + ggEEgapgap
Select the weights to give the “best” threading Select the weights to give the “best” threading g g gg g gperformance on a training setperformance on a training set (fold recognition and (fold recognition and alignment accuracy)alignment accuracy)
Different weights for different classes? (superfamily, fold)Different weights for different classes? (superfamily, fold)pairpair--wise may contribute more for fold level threadingwise may contribute more for fold level threadingy gy gmutation/profile terms dominate in superfamily level threading mutation/profile terms dominate in superfamily level threading
2010/1/192010/1/19 3232

Protein Threading Protein Threading ---- algorithmalgorithm Dynamic programmingDynamic programming Heuristic algorithms for pairHeuristic algorithms for pair--wise interactionswise interactions
Frozen approximation algorithm (A. Godzik Frozen approximation algorithm (A. Godzik et alet al.).) Double dynamic programming (D. Jones Double dynamic programming (D. Jones et alet al.).) Monte carlo sampling (S.H. Bryant Monte carlo sampling (S.H. Bryant et alet al.).)p g ( yp g ( y ))
Rigorous algorithms for pairRigorous algorithms for pair--wise interactionswise interactionsB hB h dd b d (R H L th d T F S ith)b d (R H L th d T F S ith) BranchBranch--andand--bound (R.H. Lathrop and T.F. Smith)bound (R.H. Lathrop and T.F. Smith)
DivideDivide--andand--conquer (Y. Xu conquer (Y. Xu et alet al.) .) ----PROSPECTPROSPECT Linear programming (J. Xu Linear programming (J. Xu et alet al.) .) ––RAPTORRAPTOR Tree decomposition (L. Cai Tree decomposition (L. Cai et al.)et al.)
Rigorous algorithm for treating backbone and sideRigorous algorithm for treating backbone and side--chain chain simultaneously (Li et al )simultaneously (Li et al )
2010/1/192010/1/19 3333
simultaneously (Li et al.)simultaneously (Li et al.)

Fold RecognitionFold RecognitionFold RecognitionFold Recognition
MTYKLILNGKTKGETTTEAVDAATAEKVFQYANDNGVDGEWTYTE
S 1500 S 900S 1120S 720Score = -1500 Score = -900Score = -1120Score = -720
Which one is the correct structural fold for the target sequence if any?fold for the target sequence if any?
The one with the lowest score ?
2010/1/192010/1/19 3434
The one with the lowest score ?

Fold RecognitionFold RecognitionFold RecognitionFold Recognition
Query sequence: AAAA
Template #1: AATTAATACATTAATATAATAAAATTACTGA
B l ?
Template #2: CGGTAGTACGTAGTGTTTAGTAGCTATGAA
Better template?
Template #2: CGGTAGTACGTAGTGTTTAGTAGCTATGAA
Which of these two sequences will have betterWhich of these two sequences will have better chance to have a good match with the query sequence after randomly reshuffling them?
2010/1/192010/1/19 3535

Fold RecognitionFold RecognitionFold RecognitionFold Recognition
Different template structures may have different background score Different template structures may have different background score distribution making direct comparison of threading scores againstdistribution making direct comparison of threading scores againstdistribution, making direct comparison of threading scores against distribution, making direct comparison of threading scores against different templates invaliddifferent templates invalid
Comparison of threading results should be made based on howComparison of threading results should be made based on how Comparison of threading results should be made based on how Comparison of threading results should be made based on how standout the score is in its background score distribution rather than standout the score is in its background score distribution rather than the threading scores directlythe threading scores directly
2010/1/192010/1/19 3636

Fold RecognitionFold RecognitionFold RecognitionFold RecognitionThreading 100 000Threading 100,000 sequences against a template structure provides th b li i f tithe baseline information about the background scores of the template
By locating where the y gthreading score with a particular query sequence, one can decide howone can decide how significant the score, and hence the threading result, is!
2010/1/192010/1/19 3737
is!Not significant significant

Fold RecognitionFold RecognitionFold RecognitionFold Recognition
Z-score = standard deviation
score - average
--randomly shuffle the query sequence and calculate the alignment score
The goal is to pick the predicted structure with high statistical significance
2010/1/192010/1/19 3838

State of the ArtState of the ArtState of the ArtState of the Art
~60% of the proteins in encoded in any genome can ~60% of the proteins in encoded in any genome can b bl h th i t t l f ld di t db bl h th i t t l f ld di t dprobably have their structural folds predictedprobably have their structural folds predicted
~60% of these proteins can have their structures ~60% of these proteins can have their structures predicted accurate enough to be useful to guidepredicted accurate enough to be useful to guidepredicted accurate enough to be useful to guide predicted accurate enough to be useful to guide experimental designsexperimental designs
2010/1/192010/1/19 3939