comprehensive management of a cleft lip and palate patient by a pedodontist
-
Upload
drsavithaks -
Category
Health & Medicine
-
view
6.280 -
download
1
description
Transcript of comprehensive management of a cleft lip and palate patient by a pedodontist

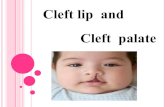
COMPREHENSIVE MANAGEMENT OF CLEFT LIP AND PALATE PATIENT BY A PEDODONTIST



EXPERTS INVOLVEDBASIC
CONFUSION



Heredity- defect seems to run in familiesEnvironmental factors- teratogens like rubella virus, thalidomide

Syndromes associated with cleft lip and palateSyndromes associated with cleft lip and palate
Treacher Collins syndromeTreacher Collins syndrome
Pierre Robbin anomalyPierre Robbin anomaly More than 300 syndromes associated According to Bixier 1 % of CL±P and 8% of CP
cases are syndromic

Inactivation or Inactivation or deletion of deletion of MSX1 MSX1 genegene
mutation of mutation of Interferon Interferon Regulatory Regulatory Factor-6 Factor-6 gene(IRF6) gene(IRF6)
Defect in Poliovirus Defect in Poliovirus receptor related-1 receptor related-1 ((PVRL1PVRL1) gene is being ) gene is being responsible for responsible for syndromes associated syndromes associated with cleftingwith clefting. .

Van der Woudes Van der Woudes syndromesyndrome
Oro-facio digital Oro-facio digital syndromesyndrome
Apert syndromeApert syndrome

DiagnosisDiagnosis

Parental Counseling At Birth

The photos of the treated patients can be used for parents counseling

Feeding Advise

Feeding problems often associated with cleft anomalies, make it difficult for the infant to maintain adequate nutrition.
These problems include insufficient suction to pull milk from the nipple, excessive air intake during feeding, choking, nasal discharge, and excessive time required to take nourishment.

Feeding by nasogastric tube

Feeding of cleft lip Feeding of cleft lip and palate patientsand palate patients
Pigeon feeder
Haberman feeder
Squeeze bottle

Feeding teats
Feeding Spoon

Cleft Babies Should Be Kept In Upright Position For Feeding To Make Gravity Aid In Milk Feeding
Fruit drinks, baby fruit juices and squashes have an erosive potential.

The feeding obturator is a prosthetic aid that is designed to obturate the cleft and restore the seperation between the oral and nasal .
The obturator prevents the tongue from entering the defect and interfering with spontaneous growth of the palatal shelves
Provides maxillary orthopedic molding of the cleft segments ino approximation before primary alveolar cleft bone grafting
Reduces nasal regurgitation,
Also helps in the development of the jaws and speech
OBTURATOROBTURATOROBTURATORSOBTURATORS

Method I To create a preliminary
impression tray, cut a piece of light-polymerizing acrylic resin to the approximate size of the hard palate.
Use a finger to insert it into the baby’s mouth and press the material over the hard palate and into the buccal and labial vestibules. Remove the material and light-polymerize it extraorally.
Technique of fabrication of Obturators:

Load the tray with a thick mix of tissue conditioning material and insert it intraorally, while the baby is held face toward the floor, in order to prevent aspiration in the event of vomiting and asphyxia due to airway obstruction.

Paint vinyl polysiloxane Paint vinyl polysiloxane adhesive over the intaglio adhesive over the intaglio surface, and load it with surface, and load it with viscous vinyl polysiloxane viscous vinyl polysiloxane impression material impression material
Monitor the baby’s oxygen Monitor the baby’s oxygen level throughout . level throughout .
Ensure that the baby is Ensure that the baby is making suckling motions, making suckling motions, for this will create the for this will create the desired border molding, desired border molding, and ensure the baby’s and ensure the baby’s ability to perform nasal ability to perform nasal breathing.breathing.
Definitive impression.

– the primary
softened green stick compound is placed in the infants mouth and molded and allowed to set which will serve as the special tray.A handle is also molded at 450
Putty consistency addition silicone impression material
Obtaining wash impression with

Method 3
A wax sheet of approximate size and shape is adapted intraorally using the thumb and index finger.

A stone model of the negative wax reproduction is then obtained.
Stone cast used to fabricate the acrylic tray.
• A wax spacer is adapted on the stone model on which a custom acrylic tray with a handle is prepared.
Custom acrylic tray smoothened and polished

Final Impression of the BCLP infant made with infant lying on the lap of the parent
Final Impression of BCLP infant in fast setting putty material.

The Pre Maxillary orthopedicsThe Pre Maxillary orthopedics Naso Alveolar Molding Naso Alveolar Molding
Movie.wmv

It is a modern presurgical orthopedic device that allows for a positive It is a modern presurgical orthopedic device that allows for a positive growth of alveolar ridges into a improved arch formgrowth of alveolar ridges into a improved arch form
NAM is non surgical method of reshaping alveolus, lip and nostrils before cleft lip NAM is non surgical method of reshaping alveolus, lip and nostrils before cleft lip and palate surgery, lessening the severity of cleft. and palate surgery, lessening the severity of cleft. It is the passive method of bringing the gum and lip together by redirecting the It is the passive method of bringing the gum and lip together by redirecting the forces of natural growthforces of natural growth

The modern school of The modern school of presurgical orthopaedic presurgical orthopaedic treatment in cleft lip and treatment in cleft lip and plate was started by plate was started by McNeil McNeil in 1950in 1950.. He used a series He used a series of plates to actively mould of plates to actively mould the alveolar segments into the alveolar segments into the desired position.the desired position.
Burston, an orthodontist, Burston, an orthodontist, further developed McNeil's further developed McNeil's technique and made it technique and made it popular.popular.
In 1689, Hoffmann demonstrated the use of facial binding to narrow the cleft and prevent postsurgical dehiscence.

The moulding plate is fabricated on the The moulding plate is fabricated on the dental stone model. All the undercutsdental stone model. All the undercuts
and the cleft space are blocked with and the cleft space are blocked with wax. The plate is made up of clear wax. The plate is made up of clear self-cure acrylicself-cure acrylic
The plate must be 2-3 mm in thickness to The plate must be 2-3 mm in thickness to provide structural integrity and to provide structural integrity and to permit adjustments during the process permit adjustments during the process of molding .of molding .
A small opening measuring 6-8 mm in A small opening measuring 6-8 mm in diameter is made on the palatal surface diameter is made on the palatal surface of the moulding plate to provide an of the moulding plate to provide an airway in the event that the plate drops airway in the event that the plate drops down posteriorly.down posteriorly.

Materials usedTray material
To make custom trays or for relining where stability & accuracy is required(combines the accuracy of self cure and strength & dimensional stability of light cure)
COE-SOFT Resilient,self cure relining material(no
monomers-no burning sensation,no unpleasant taste)
The initial gap is measured with a caliper and ruler and recorded in the patient`s chart

A retention button is fabricated and A retention button is fabricated and positioned anteriorly at an positioned anteriorly at an angle of angle of 404000toto the plate. the plate.
In the unilateral cleft only one retention In the unilateral cleft only one retention arm is used. arm is used. The exact location of the The exact location of the retention arm is determined at the retention arm is determined at the chair side. It is positioned so as not chair side. It is positioned so as not to interfere with bringing the cleft lips to interfere with bringing the cleft lips together. together.
The vertical position of the retention The vertical position of the retention arm should be at the junction of the arm should be at the junction of the upper and lower lip.upper and lower lip.

Appliance insertion and tapingAppliance insertion and taping The appliance is inserted in the same
fashion as a denture by sliding one side in first and then the other.
The elastics are stretched as far as possible so that the entire set is tied.
The appliance is secured extraorally to the The appliance is secured extraorally to the cheeks by surgical tapes that have cheeks by surgical tapes that have orthodontic elastic bands at one end. orthodontic elastic bands at one end.
A liquid adhesive like Masitol is painted with a cotton applicator horizontally on the cheeks
Non-soluble,non-irritating,clear
The use of skin barrier tapes on the cheeks The use of skin barrier tapes on the cheeks like like DuoDerm or TegadermDuoDerm or Tegaderm is advocated to is advocated to reduce irritation on the cheeks. reduce irritation on the cheeks.

The horizontal surgical The horizontal surgical tapes are a quarter tapes are a quarter inch in width and about inch in width and about 3-4 inches in length.3-4 inches in length.
The elastic on the The elastic on the surgical tape is looped surgical tape is looped on the retention arm of on the retention arm of the moulding plate and the moulding plate and the tape is secured to the tape is secured to the cheeks.the cheeks.
The elastics (inner The elastics (inner diameter 0.25 inch, diameter 0.25 inch, wall thickness heavywall thickness heavy) ) should be stretched should be stretched approximately two approximately two times their resting times their resting diameter for proper diameter for proper activation force of activation force of about 100 gramsabout 100 grams. .

Additional tapes may be Additional tapes may be necessary to secure the horizontal necessary to secure the horizontal tape to the cheeks. tape to the cheeks.
It is worn 24 hours a day and is removed only for feeding. The desired movement can usually be accomplished within 6 to 8 weeks
The infant may require time to The infant may require time to adjust to feeding with the NAM adjust to feeding with the NAM appliance in the first few days.appliance in the first few days.

Appliance AdjustmentsAppliance Adjustments
The baby is seen weekly for adjustments to the molding plate to bring the alveolar The baby is seen weekly for adjustments to the molding plate to bring the alveolar segments together .segments together . moulding plate is adjusted by removing about 1mm soft acrylic along the medial surface of distorted major segment.
The labial flange and palate adjacent to the cleft are areas of adjustments.. They are made by selectively removing the hard acrylic and adding the soft They are made by selectively removing the hard acrylic and adding the soft
denture base material(Coe soft) to the molding plate. denture base material(Coe soft) to the molding plate. No more than 1 mm of modification of the molding plate should be made at one visit. No more than 1 mm of modification of the molding plate should be made at one visit. Weekly adjustments are required for maximum effectiveness of the presurgical
appliance. On each visit, a anew impression is taken and poured with plaster of paris The alveolar cleft is measured with a gauge and approximated by 1mm
If the appliance is lost or not worn the cleft gap that been closed early during the moulding therapy may widen again as the infant places his or her tongue into the cleft.

Nostril horizontally oriented.
Cleft lip nasal deformity is characterised by a flattened nasal alar cartilage on the side of the cleft that is splayed out by the alveolar gap
Clinical features


The nasal stent is delayed until the cleft of the alveolus is reduced to about 5-6 mm in width.
Incorporation of the nasal stent Incorporation of the nasal stent

Extreme care should be taken while Extreme care should be taken while removing the cheek tape to avoid removing the cheek tape to avoid any irritation to the skin. Skin any irritation to the skin. Skin barrier tapes like Tegaderm TM are barrier tapes like Tegaderm TM are recommended. recommended.
Slight relocation of the position of Slight relocation of the position of the tape during treatment is also the tape during treatment is also recommended to provide rest to the recommended to provide rest to the tissues in case they become tissues in case they become irritated. irritated.
It is also recommended that an aloe It is also recommended that an aloe vera gel be applied to the cheeks vera gel be applied to the cheeks when changing tapes. when changing tapes.

Advantages of performing NAMAdvantages of performing NAM provides a more coalescent cleft and an
ideally shaped alveolar arch form. It diminishes tension during primary
surgery,making scar formation more diificult
Alignment of alveolar segment creates the foundation for good lip symmetry
More favourable bone formation by reducing the cleft gap
Allows the surgeon to definitely correct the nose, without extensive dissection
Diminished need for bone grafting during the mixed dentition stage,


To achieve non-surgical To achieve non-surgical lengthening of the lengthening of the columella, a horizontal columella, a horizontal band of the denture band of the denture material is added to join material is added to join the left and right lower the left and right lower lobes of the nasal stent, lobes of the nasal stent, spanning the base of the spanning the base of the columella.columella.
This band sits at the naso This band sits at the naso labial junction and defines labial junction and defines this angle as the nasal tip this angle as the nasal tip continues to be lifted and continues to be lifted and projected forward. projected forward.
Non-surgical columella lengthening in bilateral cleft lip and Non-surgical columella lengthening in bilateral cleft lip and palatepalate

Premaxillary Retraction.In cases of bilateral cleft lip and palate, premaxillary segment may be positioned severely anterior to the maxillary arch if lip surgery is undertaken with the premaxilla in such an abnormal position, the chances of lip dehiscence by increased pressure at the suture lines are increased.

Segments may be deviated laterally to one side of the cleft defect. In such cases a straight extra oral force would not place the pre maxilla in the facial midline, it must be positioned before pre maxillary retraction. By the application of sequential differential force to the premaxilla with elastic straps attached to the bulb prosthesis.

An impression is made of the infant's premaxilla for construction of an external acrylic "bulb" prosthesis.
This appliance is fitted over the protruding and laterally displaced premaxilla and anchored to the infant's head with a bonnet appliance.

The premaxillary segment are retracted in a simpler manner than with the bonnet retraction system.

LATHAM S APPLIANCE FOR PRESURGICAL REPOSITIONING OF THE PROTRUDED PREMAXILLA IN BILATERAL CLEFT LIP AND PALATE
The appliance is designed so that it could be secured to the palatal segments with stainless steel pins(pinning principle as described by Georgiade in 1970

Turning the screw expands the gap between the anterior borders of the lateral segments.
The appliance is available commercially and individually adapted to a plaster cast with the help of an acrylic plate.
Journal of Cranio-Maxillo-Facial Surgery 1992:20,99-110

This treatment is expensive,
may inhibits maxillary growth (Pruzansky.,1964)
Increases the incidence of dental caries (Bokhoutet al.,1996)
Emmy M Konst et al Cleft Palate-Craniofacial Journal,Jan 2004,41(1);71-77
CONTROVERSIES OF INFANT ORTHOPAEDICS


SURGICAL REPAIR OF CLEFT LIP & PALATE

Palatoplasty

As soon as the alveolar gap distance reaches a gap of 2mm or less,primary surgical repair of the nose and the lip can be carried out
the repair of palate between 1- 11/2 year of age gives the best balanced resultEarly repair leads to better speech development but severe midfacial growth retardation and dental malocclusion
If palatal repair is done after full growth of the maxilla, midfacial growth retardation and dental malocclusion problems will be less, but speech problem will be very severe.

Timing of cleft palate repair

surgeon must obtain tissue to bridge the cleft area. techniques involved is raising mucoperiosteal flaps from the palate and relocating them medially and posteriorly, leaving a denuded area of bone adjacent to the alveolar process.

DENUDED BONE
The filling in of the denuded area produces scar tissue, which exerts an initial contracting force onadjacent tissues resulting in midfacial growth retardationand skeletal malocclusionhemorrhage, and hematoma formation, or contraction during healing, tends to pull the flaps away from the vault. The lowered, irregular vault impinges on the space available for the tongue and interferes with tongue posture and function.
Effect of palate reconstruction on maxillary complex

The scarred palatal mucosa resists further growth to some extent, and tension on the periodontal fibers during tooth eruption causes a posterior and medial deflection of the teeth . Thus, the satisfactory relationship of the primary teeth progressively worsens by the time of full permanent dentition.
Non
cleftcleft
14 yrs
4 yrs

HEARING•More middle ear disease mainly due to failure of ventilatory function of eustachian tube i.e it is short,•Tensor veli palatine muscle is abnormally inserted into tube, These dysfunctions causes otitis media with effusion commonly known as glue ear. Early palatine surgery improves eustachian tube functions and any hearing problem should be hearing problem should be repaired before the child learns to repaired before the child learns to speak.speak.

Speech disorders are due to multi causes.
1. Abnormal oronasal structure
eg. Velopharyngeal insufficiencyIt occurs when velopharyngeal spincher does not close adequately,.
ENT problems(hearing), nasal deviation oronasal fistula etc.
2. Abnormal growth of oronasal structures
eg. Malocclusion
3. Neurological deficit
eg. Learning disorders and psychological level.

In hyponasality there is insufficient air in the nose during speech. Hypernasal speech is the common speech defect occurs due to incomplete closure Hypernasal speech is the common speech defect occurs due to incomplete closure
between soft palate and pharyngeal wall.due to velopharyngeal between soft palate and pharyngeal wall.due to velopharyngeal insufficiency It should be corrected by pharyngoplasty and speech therapy.It should be corrected by pharyngoplasty and speech therapy.

A rehabilitative procedure employing a A rehabilitative procedure employing a palatal lift prosthesis (PLP) to recover palatal lift prosthesis (PLP) to recover diminished speech function.diminished speech function.

A lateral cephalogram showing A: a low-draped soft palate and a wide opening in the velopharyngeal port, and B: elevation of the soft palate by the palatal lift prosthesis.

Clinical Examination
Use of small dental mirrors No.2.18mm diameter. (Busch and Co Engelskirchen, Germany.)
Lap to lap examination with head of the child gently lowered on to the dentist lap.

Tooth brushingAfter lip repair parents
should be told to lift the lip with the aid of index finger along the labial gingiva without damaging the scar.

Access to the teeth in the cleft region is often Access to the teeth in the cleft region is often difficult and a baby-sized toothbrush is still useful difficult and a baby-sized toothbrush is still useful even at this age, especially where the upper lip is even at this age, especially where the upper lip is tight. tight.
This can be supplemented with an interspace This can be supplemented with an interspace brush. brush.

Tooth paste containing no more than 600ppm fluoride is recommended for children under 6 yrs of age.
BDJ 2000

Current treatment protocols of cleft lip and palate patients involve the combined use of Orthodontic treatment Alveolar bone grafting Implant rehabilitation lefort1Maxilarry advancementosteogenisis distractionMandibular osteotomy after growth completion
MIXED DENTITIONMIXED DENTITION(6th year to 11nth year.)(6th year to 11nth year.)

Orthodontic treatment The midfacial deformities in cleft lip
and palate due to limitation of growth include
Transverse maxillary deficiency with of crossbite
Midfacial retrusion Reduced antero-posterior
development Mandibular prognathism A concave soft tissue profile
Katsuhiro Minami et al J Cleft palate craniofacial anomalies

Collapsed maxillary buccal segments bilaterally. Surgical procedures of the palate result in scar tissue adjacent to the alveolus which undergo contraction during healing.

Palatal expansion Objectives of treatment
Achievement of proper anterior and lateral overjet correction
Correction of the antero-posterior discrepancy.
Various expansion appliances used are Fan shaped maxillary expander Butter fly expander Rapid maxillary expander Nickel titanium expander Quad helix expansion appliance The banded hyrax appliance, and Bonded rapid palatal expander
Quad helix appliance
Rapid palatal expansion appliance

Expansion Screws
Bonded Type
Banded Type
An acrylic splint with full occlusal coverage bonded to expand (0.2mm/day) for one month has shown approximately 4.2mm expansion.

Below the transition point of 94 0F, the metal is flexible enough for bending.After insertion as the patients mouth warms wire it tends to return to its original shape.
The action of the appliance is a consequence of nickel titanium’s shape memory and transition temperature effects.
permitting the patients to mitigate the pressure , if necessary, by drinking a cold liquid.
. uses force level b/w 230gms and 300gms.

The children should be instructed to wear the facemask a minimum of 12-14 hrs/day.Though the skeletal changes are limited, they produce marked improvements in the soft tissue profile
Orthopedic expansion and protraction of maxilla in cleft palate patients-a new treatment rationale.
Protraction using a Petit’s face mask orthopedically Moving the maxillary segments after expansion of the maxilla with an expander appliance, 450 grams per side attached to the canines for 1.2 years.

3 months of maxillary expansion increased arch width between first deciduous molars by 8 mm and was followed by protraction using the facial mask for 6 months.Post treatment retention period was for 1 year.
Changes in 3months of expansion8 months of protraction
Changes in 1 yr retention

Tindlund and coworkers reported 0.3mm and 1.1mm anterior displacement of the posterior and anterior maxilla.
Ishii et al showed 1.5mm anterior movement of ANS for 63 subjects treated an average of 18 months
Nanda reported 1.3mm of protraction for 20 patients over a 4-6 month period
First molars produced significantly more anterior displacement than protraction from the first premolars.
Can be stabilized with TPA with palatal extensions to maintain the expansion
Bull Tokyo dent Coll Nov 2002 Vol 43; 223 - 229

Alveolar bone grafting typically done between 9 and II years of age, when the permanent lateral incisor or the canine tooth roots are approximately one-third developed
Alveolar bone grafting

It provides bony support to adjacent teeth. Provide bony matrix for eruption of teeth in the cleft site.
Eliminate oronasal fistulae. Elevate the alar base. adequate bone for future dental implant.

Endosseous implant placementIt is done in case of congenitally missing lateral
incisor.


Length of implantIt is reported that implants
of shorter dimensions, less than 10mm in length may result in early failure and subsequent need for replacement.
Matsui et al placed 71 implants, 13 to 15mm in length and followed for an average for 60 months. The overall survival rate reported in the study was 99%.

Long term follow up study demonstrated that use of dental implants placed in the alveoli after bone grafting is an excellent treatment modality for dental rehabilitation of patients with alveolar cleft and congenitally missing teeth
Oral surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 2008

Distraction Osteogenesis
Distraction osteogenesis is a powerful technique that already has revolutionized pediatric oral and maxillofacial surgery by providing a means of reliably lengthening the bones of the midface and mandibleMaxillary advancement between 4 and 12 mm is achieved during 3-4 weeks and a satisfactory class 1 or class 2 molar relationship can be obtained.
It allows changes to the vectors of growth and results in the genesis of new tissues.

ADVANTAGES OF EXTERNAL DEVICES Rigid and easily adjustable
No need for fixing screws and devices on the lateral walls of the maxilla in growing children where developing dental follicles and roots of the permanent dentition can be damaged.
.
George K. B Sandor Oral Maxillofacial Surg Clin N Am 2005;17: 485-501
Osteotomy LatencyDistractionConsolidation and Remodeling.

For class III occlusion mandibular osteotomy is done after skeletal maturity(16 -18 yrs)
Preoperative and post operative orthodontic treatment is needed to achieve proper alignment, position and inclination of tooth

Psychological factors in cleft surgeryEducation and communication problems Facial appearance and teacher perception. Behavioral inhibition and lower school achievement.Speech defectiveness and self esteem. Communication disorders are more the result of psychological problems than phonological which influences the entire development of an affected child.Anxiety and depression in adults with cleft lip and palate have been reported to be twice than normal controls.
Odd one out

Psychological aspects Existing multispeciality care is primarily aimed at physical rehabilitation, psychological issues often being neglected.
Parents of children with clefts are more likely to spoil their child by being over protective.


This is our domain