Clinical Anatomy of the Large Intestine - Ohio University
Transcript of Clinical Anatomy of the Large Intestine - Ohio University
Clinical Anatomy of theClinical Anatomy of theLarge IntestineLarge Intestine
Lawrence M. Witmer, PhDLawrence M. Witmer, PhDProfessor of AnatomyDepartment of Biomedical SciencesCollege of Osteopathic MedicineOhio UniversityAthens, Ohio 45701 [email protected]
Handout download:http://www.oucom.ohiou.edu/dbms-witmer/gs-rpac.htm
23 January 2007
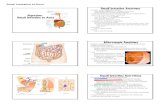
ileum
free (anterior)taenia
omental taenia
mesenterictaenia
right colic(hepatic)flexure
left colic(splenic)flexure
epiploicappendages
haustra
appendix
cecum
ascendingcolon
transversecolon
descendingcolon
sigmoidcolon
rectum
Moore & Dalley 2005
AnatomicalAnatomicalOverviewOverview
Skandalakis’ Surgical Anatomy 2004
free taenia
omental taenia
mesenterictaenia
epiploicappendage
epiploicappendage
mesenterymarginal a.
shortbranch
long branch
AnatomicalAnatomicalOverviewOverview
www.bondisalud.com.ar/1a%20diverticulosis.jpg
DiverticulosisDiverticulosis
http://www.pathology.pitt.edu/lectures/gi/colon-b/06.jpghttp://www.pathology.pitt.edu/lectures/gi/colon-b/06.jpg
diverticula(internal view)
diverticula(internal view)
mucosalherniationmucosal
herniation
Moore & Dalley 2005
diverticula(external view)
Skandalakis’ Surgical Anatomy 2004
mucosa
normalepiploic
appendage
taenia (longitudinal muscularis)
diverticulum intodiverticulum intoepiploic appendageepiploic appendage
fat
circularmuscularis
serosa
vasa rectus& branches
DiverticulosisDiverticulosisantimesenteric anastomosis
injury to injury to vasa rectusvasa rectus
branchbranch
distal ischemiadistal ischemia
DimensionsDimensions
cecum5 cm
ascendingcolon10 cm
transverse colon50 cm
descendingcolon10 cm
sigmoid colon50 cm
anal canal4 cm
rectum15 cm
8cm8
cm
5 cm5 cm
6cm6
cm
5cm5
cm
5cm5
cm
4 cm4 cmwidest:widest:likelylikely
site forsite forperforationperforation
narrowest: likelynarrowest: likelysite for site for obstructionobstruction
Skandalakis’ Surgical Anatomy 2004
transversemesocolon
mesenteryof smallintestine
sigmoidmesocolon
greateromentum
IMV
Paraduodenal fossae: 1) Superior & 2) Inferior
fossae of Trietz3) Mesentericoparietal
fossa of Waldeyer4) Intermesocolic fossa
of Brooke 5) Paraduodenal fossa
of Landzert
• Mobility• Vascularization• Compartments• Volvulus• Internal hernias• many more
Peritoneal RelationsPeritoneal Relations
Skandalakis’ Surgical Anatomy 2004
Paraduodenal fossae: 1) Superior & 2) Inferior
fossae of Trietz3) Mesentericoparietal
fossa of Waldeyer4) Intermesocolic fossa
of Brooke 5) Paraduodenal fossa
of Landzert
SMA
Internal HerniaRight
ParaduodenalHernia
hernialsac
Peritoneal RelationsPeritoneal Relations
free taeniasuperior &
inferiorileocecal
fossa
mesoappendixcecum
superior ileocecalinternal hernia(a pericecal hernia;
6-13% of all internal hernias) Skandalakis’ Surgical Anatomy 2004
appendix
Peritoneal RelationsPeritoneal Relations
Position Nonapp-endicitis
Appendicitis Total %
ABCDEFG
Preileal 1 5 6 4Postileal 7 3 10 8Subileal 11 8 19 15Pelvic 14 11 25 19
Subcecal 9 5 14 11Paracecal 4 9 13 10Retrocecal 18 24 42 33
GGF
ED
C
BA
anterior
post.
AppendixAppendixPositionPosition
Skandalakis’ Surgical Anatomy 2004
data from O’Connor & Reed (1994)
Peritoneal RelationsPeritoneal Relations
Moore’s Developing Human 1988
• Elongation of gut tube• Herniation into umbilical cord• Counterclockwise rotations
Peritoneal RelationsPeritoneal Relations
Moore’s Developing Human 1988
• Retraction & return of gut• Final counterclockwise rotation• Descent of cecum• Fixation to posterior abdominal wall
Peritoneal RelationsPeritoneal Relations
Peritoneal RelationsPeritoneal Relations
Skandalakis’ Surgical Anatomy 2004
peritoneum
cecum
appendix
ileum
peritoneum
retroperitonealtissue
paracolic groove
para-colicgutter
mesentery
normalnormal
unfixed,unfixed,mobilemobile
Peritoneal RelationsPeritoneal Relations
Skandalakis’ Surgical Anatomy 2004
Fixation of cecumFixation of cecumFixation of cecum
areas of fixation shown in black areas of fixation shown in black
asc colmesent
ileum
appendix cecum pelvic brim
Type I 11.2% Ia 8.3% Type Ib 22.7%
Type II 9.7% IIa 7.3% III 11.3% III 5.7%
Type IV 17.3% V 4.7% VI 2.7%
stomach aorta
umbilicus
cecum
celiac trunk (foregut)
superior mesenteric A.(midgut)
inferior mesenteric A.(hindgut)
VasculatureVasculature
Skandalakis’ Surgical Anatomy 2004
VasculatureVasculature
Skandalakis’ Surgical Anatomy 2004
marginal a.
m. colic a. SMA
r. colic a.
ileocolic a.
cecal a.
appendiculara.
ileal a.
IMA
acc. left colica. (~ 40%)
marginal a.
l. colic a.
sigmoid aa.
sup. rectal a.
RCARCA--IleocolicIleocolicanastomosisanastomosis
absent 5%absent 5%AnastomosisAnastomosis•• poor 32%poor 32%•• absent 7%absent 7%
VasculatureVasculature
Skandalakis’ Surgical Anatomy 2004
occluded SMAoccluded SMA meanderingmesenteric a.(arc of Riolan)dilateddilated
marginal a.marginal a.
MCA
RCA
ileocolic a. Gourley & Gering 2005
Lymphatic DrainageLymphatic Drainage
Skandalakis’ Surgical Anatomy 2004
Nodes NA Ileocolic 29B Right colic 11.1C Midcolic 22.4D Left colic 25.2E Sigmoid &
rectal 32.8
mesenteric nodes
l. lumbar
mesocolic
paracolic
epicolicnodes
AA
BB
CCDD
EE
Lymphatic DrainageLymphatic Drainagelesion
Arterial & lymphatic territoryassociated with a lesion
Arterial & lymphatic territoryArterial & lymphatic territoryassociated with a lesionassociated with a lesion
Skandalakis’ Surgical Anatomy 2004
ReferencesReferences
• Gourley, E. J. and S. A. Gering. 2005. The meandering mesenteric artery: a historical review and surgical implications. Diseases of the Colon and Rectum 48(5):996-1000.
• Mathieu, D. and A. Luciani. 2004. Internal abdominal herniations. American Journal of Roentgenology 183:397-404.
• Moore, K. L. 1988. The Developing Human. Clinically Oriented Embryology, 4th Ed. Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore.
• Moore, K. L. and A. F. Dalley. 2006. Clinically Oriented Anatomy, 5th Ed. Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore.
• O'Connor, C. E. and W. P. Reed 1994. In vivo location of the human vermiform appendix. Clinical Anatomy 7:139-142.
• Skandalakis, J. E., G. L. Colborn, T. A. Weidman, R. S. Foster, A.N. Kingsnorth, L. J. Skandalakis, N. P. Skandalakis, P. Mirilas(Editors). 2004. Surgical Anatomy: The Embryologic And Anatomic Basis Of Modern Surgery. McGraw-Hill, New York.