Classification of Epithelium. Each epithelial type has two parts to its name: 1) Number of layers...
-
Upload
stewart-shepherd -
Category
Documents
-
view
225 -
download
0
Transcript of Classification of Epithelium. Each epithelial type has two parts to its name: 1) Number of layers...
Classification of Epithelium
• Each epithelial type has two parts to its name:
• 1) Number of layers present
Classification of Epithelium
• Each epithelial type has two parts to its name:
• 1) Number of layers present
• 2) General shape of the cell
Number of Layers
• Those having a single layer are called simple
• Those having multiple layers are called stratified.
Simple Squamous Epithelium
• These are very thin cells which are typically are very permeable.
• Diffusion is a high priority.
2 epithelial surfaces have special names:
• Endothelium – cells that line the blood vessels, heart and lymph vessels
2 epithelial surfaces have special names:
• Endothelium – cells that line the blood vessels, heart and lymph vessels
• Mesothelium – cells that line the serous membranes and their organs.
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
• Their role is secretory and absorption.
• They have a cube shape with a centrally placed nucleus.
Simple Columnar Epithelium
• These are a single layer of oblong cells which are tightly packed.
• Seen with organs involved with absorption, they are usually modified with microvilli or cilia.
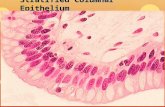
Pseudo stratified Columnar Epithelium
• These are columnar epithelial cells that vary in height
• The nuclei do not appear at the same height
Stratified Epithelium
• These have multiple layers and are more durable
• Their major function is protection.
Stratified Epithelium
• These have multiple layers and are more durable
• Their major function is protection.
• Mitotic figures are not uncommon in the basilar levels.
Stratified Squamous Epithelium
• This is the most common type of stratified epithelium.
• The upper most layers are flat and are made up of dead or dying cells
Stratified Squamous Epithelium
• The major example is skin
• The outer most layers contains cells filled with keratin
• Correctly called keratinized squamous epithelium
Stratified cuboidal and columnar epithelium
• Neither of these is very common
• Stratified cuboidal is found in some sweat ducts and in mammary glands
Transitional Epithelium
• This type has cells that are cuboidal in the basal layer
• The shape of the apical cells varies.
• Epithelial cells that can stretch flat