Class Index
description
Transcript of Class Index

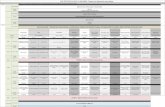
Class Index• Level 1
Lack basic skills, unable to read medicine bottle, aware they have problem
• Level 2Some basic skills, still not completely functioning. May have trouble at the grocery store, etc. Often unaware of problem
• Level 3 Enough basic skills to complete high school and some post secondary. Minimum level needed to get by. Many adults lack this level. This level is still too low to complete complex tasks, such as job advancement.
• Level 4 and 5Strong skills and able to complete complex tasks.

Four Categories
• Prose Literacy:Understand text, such as stories or fiction
• Document Literacy:Find and use information from documents
• Quantities Literacy: Able to do math in your head and apply to real life, such as balancing a checker bookThe majority of Canadians are class 3, which is about a high school levelThe last 60% are level 3 or above that
• Problem Solving

How does it Affect Canadians?
•42% of Canadians are semi-illiterate
•7 out of 9 million people with low literacy in British Columbia, Quebec and Ontario
•Nearly 40% of adult in BC are class 2 or under

Consequences•Most jobs in BC require a reading
level of at least level 3
•Incorrect use of medicationsNearly half the respondents to the survey of the OPHA research study provided illustrations of errors in the use of over-the-counter and prescription medications as a result of literacy difficulties. CPHA says that "there are hundreds of stories of people who failed to respond to prescription drug treatment because they took the incorrect dose at the wrong time of day." The OLC cites the following example of a woman with diabetes
•Safety risks in the workplace, the community and at homeThe Manitoba review of literacy and health indicated that: "Difficulty comprehending precautions on farm and recreational machinery such as all-terrain vehicles, water sleds, snowmobiles and farm equipment of all sorts, makes rural life more dangerous."

•Three Key Ideas•Annual Awareness Day
•Tour (small towns across BC)
•Politician Support (from both parties)
Timeline

•