Chemical Kinetics CK-1 - Gustavus Adolphus...
Transcript of Chemical Kinetics CK-1 - Gustavus Adolphus...

CK-1Chemical Kinetics
Chemical kinetics is the study of time dependence of the change in the concentration
of reactants and
products.
“The field of chemical kinetics has not yet matured to a point where a set of unifying principles has been identified…There are many different theoretical models for describing how chemical reactions occur.” (M&S, 1137)
Generally, we want to understand the rate of reaction:

CK-2Recall from Slide CEq-2…
)()()()( gZvgYvgBvgAv ZYBA +→+
dttdv
dttdn
AA )()( ξ
−=
)()0()( tvntn AAA ξ−=
)()0()( tvntn BBB ξ−= )()0()( tvntn ZZZ ξ+=
)()0()( tvntn YYY ξ+=Reactants Products
For each constituent…
dttd
Vv
dtAd
dtdn
VAA )(][1 ξ
−==

CK-3Rate of reaction, v(t)
dtZd
vdtYd
vdtBd
vdtAd
vdttd
Vtv
ZYBA
][1][1][1][1)(1)( ==−=−==ξ
v(t), the rate of reaction, is defined as the rate of change in ξ(t) with time per unit volume
Note all quantities are positive. What are units of v(t)?
2NO(g) + O2 (g) 2NO2 (g)Examples:
H2 (g) + I2 (g) 2HI (g)
==dt
tdV
tv )(1)( ξ
==dt
tdV
tv )(1)( ξ

CK-4The integrated rate law
nm BAkdtd
Vtv ][][1)( ==
ξ
)()()()( gZvgYvgBvgAv ZYBA +→+
nm BAktv ][][)( =
Rate laws must be determined experimentally
and, generally, cannot
be deduced from the balanced reaction!!
The rate can be expressed as a function of the reactant concentrations. Most common function is of form:
2NO(g) + O2 (g) 2NO2 (g)
]O[]NO[)( 22ktv =
General Example
The Order:

CK-5Units of k, rate constant
nm BAkdtd
Vtv ][][1)( ==
ξ
Rate Law Order Units of kv = k 0 mol·dm-3·s-1
v =k[A] 1 s-1
v = k[A]2 2 dm3·mol-1·s-1
v = [A][B] 1 in [A], [B] 2 overall
dm3·mol-1·s-1
v = k[A]1/2 1/2 dm-3/2·mol1/2·s-1
concentrationtime (concentration)m
(concentration)n

CK-6Rate laws can be complicated
]I][H[)( 22ktv =H2 (g) + I2 (g) 2HI (g)
H2 (g) + Br2 (g) 2HBr (g) 12
2/122
]Br][HBr[1]Br][H[2)( −′′+
′=
kktv
These rate laws suggest that these two reactions occur via different mechanisms (sets of individual steps).
The first may be a elementary reaction (one step) whereas the latter is certainly a multistep
process.
We will soon explore how to obtain complicated rate laws from suggested mechanisms.
EX-CK1

CK-7Elementary Rxns
vs. Complex Reactions
products→A
products→++ CBA
products→+ BA
Elementary ReactionsComplex Reactions
Reactants Products
Reactants Intermediates Products
Molecularity
of Elementary Reactions:
Unimolecular
Bimolecular
Termolecular

CK-8Finding rate laws experimentally
nBkv ][′=
Method of isolationSet up reaction so one reactant is in excess. Any change in rate
will be due to changes in other reactant. Repeat for other reactant.
Method of initial ratesMeasure concentration change as a function of time, ~v(t),
for a
series of experimental conditions. (Conditions must include sets where the reactant A has the same initial concentration but B
changes and vice versa).
There are two common methods for determining rate laws:
mAkk ][=′
EX-CK2
where

CK-9First order reactions
products→+ BA ][][)( AkdtAdtv =−=
kdtAAd
−=][][
∫∫ −=tA
AkdtAd
At
0
][
][ 0
][][
1
ktAA t −=
0][][ln ktAA t −= 0]ln[]ln[
ktt eAA −= 0][][
The reaction: has rate law:
Let’s integrate…
Solution:
First order reactions decay exponentially.

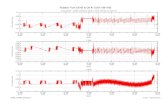
CK-10Ozone decays via first order kinetics
)(O)(O)(O 23 ggg +→
ktt −=03
3
]O[]O[lnkt
t e−= 033 ]O[]O[
k
= 1.078 ×
10-5
s-1
at 300 K
What is slope?

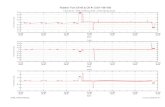
CK-11What happens as k
increases?
ktAA t −=
0][][lnkt
t eAA −= 0][][
k = 0.0125 s-1
k = 0.0250 s-1
k = 0.0500 s-1
k = 0.1000 s-1

CK-12Half-life of a first order reaction
2/1tt =
2/1
21
][][
0
2/1 kteA
A −==
0][21][
2/1AA t =
Figure 28.3
kt )2ln(
2/1 =
The half-life, t1/2
,
is the time it takes to fall to ½ of the starting concentration:
At ,

CK-13Other order reactions…
products2 →A products→+ BA
2][][21)( Ak
dtAdtv =−=
Second order reaction:
Second order rate:
Integrated rate law:
]][[][)( BAkdtAdtv =−=
ktAA t
2][
1][
1
0
+= ( ) ktBAAB
BA t
t =⎟⎟⎠
⎞⎜⎜⎝
⎛− ][][
][][ln][][
1
0
0
00
Zero order reaction:
Zero order rate:
Integrated rate law:
products→A
kdtAdtv =−=
][)(
ktAA t −= 0][][

CK-14Pseudo-first order reactions
You can “overload” the other reactants to determine the order with respect to one individual reactant (method of isolation).
products→+ BA
]][[][)( ABkdtAdtv =−=
For , what happens if [B] >> [A]?

CK-15Reversible reactions (small Δr G)
( ) tkkBkAk
ABAkAk tt )(][][
][][][][ln 110101
0011−
−
− +−=⎟⎟⎠
⎞⎜⎜⎝
⎛−
−+−
][][][11 BkAk
dtAd
−−=−
( )][][][][][0011 ABAkAk
dtAd
−+−=− −
][][][][ 00 BABA +=+][][][][ 00 ABAB −+=
A Bk1
k-1Assume first order, elementary rxn
in both directions
Rate:
Conservation of Mass:
Integrate:

CK-16At equilibrium
0][=−
dtAd
eqeq BkAk ][][ 11 −=
][][][11 BkAk
dtAd
−−=−A Bk1
k-1
At equilibrium…
What is the equilibrium constant for this reaction?
The forward rate equals the reverse at equilibrium.
In terms of rate constants?

CK-17Temperature Dependence of k
Svante
ArrheniusWinner of the 3rd
Nobel Prize in Chemistry
The rate constant can vary in different ways with T.
Most typicalfollows Arrhenius
Eq Enzyme KineticsExploisive
Rxn
2
lnRTE
dTkd a=
Differential form of the Arrhenius
Equation:

CK-18Arrhenius
Parameters
RTEAk a−= lnln RTEaAek /−=
Ea is the activation energy. This is the energy required to get over a barrier (at the activated or transition state) between the reactants and products. Ea has units of energy and is T independent.
Integrated forms of Arrhenius
equation:Activated (or transition) state
A is the pre-exponential or Arrhenius factor
and is also T independent. A is
a measure of rate at which collisions occur
(and takes lots of things into
acct such as orientation, molecular size, number of molecules per volume, molecular velocity, etc). 2HI(g)→I2
(g) + H2
(g)

CK-19Transition-State Theory
CB KhTkk =
RTGeK /Δ−=
AB‡
is the transition state (or activated complex.)
Transition state theory assumes that the transition state and reactants are in equilibrium with each other, and uses concepts from chemical equilibrium and statistical mechanics to find kinetic info such as rate constants!
‡
‡
Eyring
Equation (key to transition-state theory)
From CEq:
So…
‡

CK-20Relating Ea to thermodynamics!
RTEAk a−= lnln
2
lnRTE
dTkd a=
dTkdRTEa
ln2=
2
lnRT
UdT
Kd C Δ=
dTKd
TdTkd Cln1ln
+=
Arrhenius
Equation:
Differentiate wrt
T: or
From Eyring
Equation:
van’t
Hoff Equation (for Kc
):
Putting it all together…
Necessary Pieces…
‡

CK-21What about A, the pre-exponential?
gnRTHU Δ−Δ=ΔURTEa Δ+=
nRTHRTEa Δ−Δ+=
and
so
A A‡ Products
A+B AB‡ Products
Unimolecular
Gas Phase Reaction
Bimolecular Gas Phase Reaction
so
so
‡ ‡ ‡ ‡
‡ ‡

CK-22Transition State Theory and NMR Lab
SΔHΔ
In the NMR/N,N-DMA Paper, Gasparro
et al. found an activation energy of 70.3 kJ/mol and a pre-factor of 1.87 ×
1010
s-1. Using these values find…
GΔ‡ ‡ ‡
Why is TST important?