Chapter Extra-2 Micro-fabrication process Si wafer fabrication IC fabrication – Deposition Spin...
-
Upload
annabel-copeland -
Category
Documents
-
view
232 -
download
1
Transcript of Chapter Extra-2 Micro-fabrication process Si wafer fabrication IC fabrication – Deposition Spin...
Chapter Extra-2 Micro-fabrication process
• Si wafer fabrication • IC fabrication
– Deposition• Spin coating• PVD – physical vapor deposition• CVD – chemical vapor deposition
– Lithography (Pattern transfer)– Removal (mostly etching process)
• Wet/Dry etching• Plasma etching
• Micro-machining processes (MEMS-specific) Si based: Bulk vs. Surface micro-machining DRIE: Deep reactive ion etch Non-Si based: LIGA & Stereo lithography
(*) 최근의 추세 : Without Lithography… Why? LG 전자 : FIPA (?) 공정 : 이승기 박사
Process flow of IC & MEMS fabrication
Deposition Lithography Etch
Wafers
Chips
• Processes of IC and MEMS are almost same• Process complexity/yield depends on repetition of central loop
Deposition processes- Issues of deposition : Compatibility, Conformability- Process:
Spin casting/Spin coatingPVD – physical vapor depositionCVD – chemical vapor deposition
Barrier layer formation• Materials
- SiO2 : most common
- Si3N4, polysilicon, metals etc…
• Process - Thermal oxidation, Evaporation, Sputtering, CVD
Spin Casting/Coating
• Viscous liquid is poured on center of wafer• Wafer spins at 1000-5000 RPM for ~30s (thickness control)• Baked on hotplate 80-500oC for 10-1000s (volume reduction by 1/2)• Application of etchants and solvents, rinsing• Deposition of polymers, sol-gel precursors (SOG)
E-beam
substrate
target
heating
Vacuum
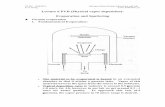
(1) Heating target with desired material to evaporate
in the vacuum chamber
(2) Thin film is formed on the substrate
Disadvantage: high temperature, high vacuum
Physical Vapor Deposition - Evaporation
Physical Vapor Deposition - Sputtering
• Sputtered metals and dielectrics
– Argon plasma sputters material (small #s of atoms) off target
– Ejected material takes ballistic path to wafers
• Typically line-of-sight from a distributed source
• Requires high vacuum depending on material
Mechanism: Physical process by impact of ions (plasma state)
(1) impacting target surface with accelerated ions (Ar+)
(2) knocking out atoms from the target surface
(3) transporting atoms to the substrate for deposition
(4) spin the substrate to achieve uniform thickness
Ar+
target
substrateatoms
Plasma
-
+
RF source
Chemical Vapor Deposition - CVD
To exhaust system
Wafers
SusceptorN2 H2SiCl4+ H2
HCl Dopant+ H2
Process(1) Gas phase is injected into the chamber
(2) Thermal decomposition and/or reaction
of gaseous compounds occur on the substrate surface
(3) Desired material is deposited directly from the gas phase
to form thin layer
Lithography
Pattern transfer: transferring a mask pattern onto wafer
Procedure
(1) Deposit barrier layer (SiO2, Si3N4, metal, etc.)(2) Coat with PR(3) Soft baking (curing)(4) Align mask(5) Expose pattern and develop PR(6) Hard baking and Etching(7) Remove PR
Issues: Light source, Barrier layer, Mask, PR, Etching
Light source
UV, EUV (Extreme UV), X-ray, e-beam, etc.
- Shorter wavelength for higher resolution (e.g. UV)
- UV is difficult to use for nano-scale
due to diffraction
- X-ray or electron beam or EUV for finer resolution
(on-going research topic)
Etching process
- Classification: (Wet vs. Dry), (Isotropic vs. Anisotropic)
- Wet vs. Dry etching
Wet etching : liquid etchant
Dry etching : gas or plasma
Physical vs. Chemical
Plasma, Sputter, RIE
- Issues of etching : Anisotropy, Selectivity
• Isotropic etchants etch at the same rate in every direction
anisotropic
mask
isotropic undercut <111><100>
Silicon Substrate
54.7
Anisotropic etching of Si
Isotropic vs. Anisotropic etching
Bulk micro-machined cavities
• Anisotropic KOH etch (upper left)
• Isotropic plasma etch (upper right)
• Isotropic BrF3 etch
with compressive oxide (lower right)
Reactive Ion Etching (RIE)
Principle : Plasma is struck in the gas mixture and ions accelerated toward the substrate
Reaction occurs on the surface (chemical)Impact of ion is similar to sputter etching (physical)
Controlling balance between chemical and physicalPhysical : AnisotropicChemical : Isotropic
Deep RIE (DRIE) : altering two gas compositions High aspect ratio of 50:1, High etching rate
MEMS-specific fabrication processes
MEMS utilizes IC fabrication process for electric circuit,
MEMS-specific process for mechanical structure.
• Bulk micro-machining• Surface micro-machining• Deep reactive ion etching (DRIE)• LIGA• Other materials/processes
• Terminology
MEMS ( 미국 )
Micro-machining ( 일본 )
Micro system (EU)
Bulk & Surface micro-machining, DRIE & LIGA
• Bulk micro-machining involves removing material from silicon wafer itself.
– Typically wet etched– Traditional MEMS industry– Artistic design, inexpensive equipment
• Surface micro-machining leaves the wafer untouched, but adds/removes additional layers above the wafer surface. First widely used in 1990s.
– Typically plasma etched– IC-like design philosophy, relatively expensive equipment
• Deep Reactive Ion Etching (DRIE) removes substrate but looks like surface micromachining.
LIGA process
• LIthographie Galvanoformung Adformung
(Lithography/Electroplating/Plastic molding)
• Developed during 1980s at Research Center KarlsruheDeveloped during 1980s at Research Center Karlsruhe
• Possible to produce microstructures with Possible to produce microstructures with very highvery high aspect ratios (up to 100),aspect ratios (up to 100), very small structures (in the submicron range),very small structures (in the submicron range), and with very smooth walls (surface roughness and with very smooth walls (surface roughness < < 50 nm)50 nm)
• To manufacture a tool in a molding step to replicate the microstructure of polymerTo manufacture a tool in a molding step to replicate the microstructure of polymer
• Processes : Basic LIGA
SLIGA (Sacrificial LIGA)
LIGA-like process