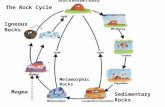
Igneous Rocks: crystallization of magma. They include two types of igneous rocks
Chapter 5 “Igneous Rock”. Objectives Describe how the cooling rate of magma & lava affects the...
-
Upload
melvyn-julius-houston -
Category
Documents
-
view
227 -
download
4
Transcript of Chapter 5 “Igneous Rock”. Objectives Describe how the cooling rate of magma & lava affects the...

Chapter 5 “Igneous Rock”

Objectives
• Describe how the cooling rate of magma & lava affects the texture of igneous rocks.
• Classify igneous rocks according to their mineral composition.
• Describe a number of identifiable rock structures.

2 types of Igneous Rocks
• Intrusive– Created inside the earth
• Extrusive– Created on top of the ground

Intrusive Igneous Rocks
• Magma cools slowly underground
• Creates large, well-developed crystals
• Example:– Granite

Extrusive Igneous Rocks
• Created when lava cools rapidly
• Examples:– Basalt (oceans)
– Obsidian (glass)
– Pumice (has gas bubbles)

What happens if the outside cools rapidly – but the inside cools slowly?
• Creates a rock with a porphyritic texture.
• Small crystals outside– Quickly formed
• Larger crystals embedded inside– Formed slowly

Mineral Composition of
Igneous Rocks
• #1 Felsic– High in silica (SiO)
– Examples:
– Feldspar, quartz, mica
– Granite, Rhyolite, Obsidian
• #2 Intermediate• #3 Mafic

Mineral Composition of
Igneous Rocks (cont.)
• #2 Intermediate– Medium colored
(grays/browns/reds)
– Pink Feldspar
– Diorite, Andesite

Mineral Composition of
Igneous Rocks (cont.)
• #3 Mafic• Rich in Magnesium & Iron• Heavy & dense• Olivine, Hornblende• Basalt, Gabbro

Igneous Rock Structures
• Intrusions– Formed inside the earth
• Extrusions– Formed on the surface
3rd start here wed

Igneous Intrusions
• Batholiths– Means “deep rock”– Large igneous
formations• Must be over 100 km2
• The continents are underlain by large batholiths
• Similar, smaller areas are called “stocks”

Intrusions (cont.)
• Laccolith– Means “layer of rock”
– Found in groups
– Bubbles of magma that have cooled underground
– Usually mushroom shaped

Intrusions (cont.)
• Sill– A flat layer of
solidified magma
• Dikes– Vertical columns of
solidified magma

Igneous Extrusions• Volcanic Neck
– What’s left of an ancient volcano
– May also include exposed fingers of hardened lava known as dikes

Igneous Extrusions (cont.)
• Lava flows– Flat layers of solidified lava

Igneous Extrusions (cont.)
• Lava plateau– Wide, flat areas of hardened lava

Assignments:• Complete Chapter 4 interactive notes for Homework

Groups
Intrusive VS Extrusive
Felsic
Intermediate
Mafic