Chapter 37: Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Circulation: Structure and Function Consists of...
-
Upload
godwin-george -
Category
Documents
-
view
218 -
download
1
Transcript of Chapter 37: Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Circulation: Structure and Function Consists of...

Chapter 37: Chapter 37: Circulatory and Circulatory and
Respiratory Respiratory SystemsSystems

Circulation: Structure and Circulation: Structure and FunctionFunction
Consists of heart, blood vessels, and bloodConsists of heart, blood vessels, and blood
TRANSPORTATIONTRANSPORTATION– Cells need to get nutrients and oxygen and get Cells need to get nutrients and oxygen and get
rid of wastesrid of wastes

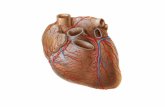
Heart: partsHeart: parts
Hollow muscular organ that pumps bloodHollow muscular organ that pumps blood Enclosed by a protective layer called the Enclosed by a protective layer called the
pericardiumpericardium The thick layer of muscle is called the The thick layer of muscle is called the
myocardiummyocardium Upper chambers are called the atria (where Upper chambers are called the atria (where
blood collects)blood collects) Lower chambers are the ventricles Lower chambers are the ventricles
(muscular chambers from which blood (muscular chambers from which blood exits)exits)

Heart terminologyHeart terminology
Veins go to the heartVeins go to the heart Arteries go away from the heartArteries go away from the heart Capillaries join the two and bring blood Capillaries join the two and bring blood
close to cellsclose to cells Pulmonary circulation refers to blood going Pulmonary circulation refers to blood going
to and from the lungsto and from the lungs Systemic circulation refers to circulation to Systemic circulation refers to circulation to
the rest of the bodythe rest of the body One-way valves in the heart keep One-way valves in the heart keep
circulation efficientcirculation efficient

Blood Flow through the Blood Flow through the HeartHeart
Low oxygenated blood flows into the right Low oxygenated blood flows into the right atrium through the superior and inferior vena atrium through the superior and inferior vena cavacava
As the heart contracts the blood flows into As the heart contracts the blood flows into the right ventricle and out the pulmonary the right ventricle and out the pulmonary arteries (to the lungs)arteries (to the lungs)
Oxygenated blood flows into the left atrium Oxygenated blood flows into the left atrium through the pulmonary veinsthrough the pulmonary veins
As the heart contracts the blood flows into As the heart contracts the blood flows into the left ventricle and out the aorta to the rest the left ventricle and out the aorta to the rest of the bodyof the body
See page 945See page 945


Blood vesselsBlood vessels Arteries:Arteries:
– Super highways, Super highways, large, and muscularlarge, and muscular– Carry oxygenated blood Carry oxygenated blood (except pulm. art.)(except pulm. art.)
Veins:Veins:– Large and muscularLarge and muscular– contain valves and return blood to contain valves and return blood to
heartheart Capillaries:Capillaries:
– Smallest with walls only one-cell thickSmallest with walls only one-cell thick– Bring oxygen and nutrients to tissues Bring oxygen and nutrients to tissues
and absorb CO2and absorb CO2– ““Side streets and alley ways”Side streets and alley ways”


BloodBlood
Body contains about 4-6 litersBody contains about 4-6 liters 45% consists of cells45% consists of cells
– Red blood cells called erythrocytes transport Red blood cells called erythrocytes transport oxygen (hemoglobin)oxygen (hemoglobin)
– White blood cells called leukocytes fight White blood cells called leukocytes fight infectioninfection
– Platelets are cell fragments that aid in clottingPlatelets are cell fragments that aid in clotting 55% consists of straw colored fluid called plasma55% consists of straw colored fluid called plasma
– 90% water90% water– Contains albumins, globulins, and fibrinogenContains albumins, globulins, and fibrinogen


Lymphatic SystemLymphatic System
Consists of a network of vessels, Consists of a network of vessels, nodes, and organs that collects fluid nodes, and organs that collects fluid that is lost by the blood and returns it that is lost by the blood and returns it to the circ. sys.to the circ. sys.
The fluid is called lymph and travels in The fluid is called lymph and travels in vessels and sometimes collect in lymph vessels and sometimes collect in lymph nodes (p 955) which can act as filtersnodes (p 955) which can act as filters
The thymus and spleen contribute to The thymus and spleen contribute to fighting infections along with the fighting infections along with the lymphatic systemlymphatic system

Summary

Respiratory SystemRespiratory System
Function: to bring about exchange of Function: to bring about exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between oxygen and carbon dioxide between the blood, air and tissuesthe blood, air and tissues
Parts: Parts: – Air flows from the mouth and nose into Air flows from the mouth and nose into
the pharynx, larynx (voice box), then the pharynx, larynx (voice box), then trachea, bronchus tubes, bronchioles, and trachea, bronchus tubes, bronchioles, and finally alveoli (air sacs surrounded by finally alveoli (air sacs surrounded by capillaries)capillaries)
– Cilia and mucus act as filters along the Cilia and mucus act as filters along the pathwaypathway

Respiratory System diagramRespiratory System diagram


BreathingBreathing
Movement of air into (inspiration) Movement of air into (inspiration) and out of (expiration) the lungsand out of (expiration) the lungs
Process is driven by air pressure (p Process is driven by air pressure (p 959):959):– When diaphragm contracts, air comes inWhen diaphragm contracts, air comes in– When diaphragm relaxes, air is exhaledWhen diaphragm relaxes, air is exhaled


Cellular RespirationCellular Respiration
OO22 + C + C66HH1212OO66 CO CO22 + H + H22O and ATPO and ATP