CHAPTER 3 CHAPTER 3 CELLS AND TISSUES CELLS AND TISSUES PART 1 – CELLS PART 2 - TISSUES.
-
Upload
julianna-snow -
Category
Documents
-
view
241 -
download
0
Transcript of CHAPTER 3 CHAPTER 3 CELLS AND TISSUES CELLS AND TISSUES PART 1 – CELLS PART 2 - TISSUES.

CHAPTER 3CHAPTER 3
CELLS AND TISSUESCELLS AND TISSUES
PART 1 – CELLSPART 1 – CELLS
PART 2 - TISSUESPART 2 - TISSUES

PART 1 - CELLSPART 1 - CELLS
Made up primarily of C, O, H, N Made up primarily of C, O, H, N and important trace elementsand important trace elements
Vary greatly in structure and Vary greatly in structure and functionfunction

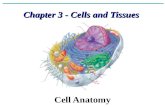
Generalized Generalized Cell Cell StructureStructure All cells contain: nucleus, All cells contain: nucleus,
cytoplasm, plasma membrane cytoplasm, plasma membrane (cell membrane)(cell membrane)
Actual structure of cell depends Actual structure of cell depends on its functionon its function– Blood cells – disk-shapedBlood cells – disk-shaped– Nerve cells – have long extensionsNerve cells – have long extensions– Muscle cells – taperedMuscle cells – tapered– Epithelial cells - cubelikeEpithelial cells - cubelike

NucleusNucleus
Control center of cellControl center of cell Contains DNAContains DNA Composed of 3 regions: nuclear Composed of 3 regions: nuclear
envelope, nucleolus, chromatinenvelope, nucleolus, chromatin Figure 3.1Figure 3.1

Nuclear envelope (membrane)Nuclear envelope (membrane)– Double membraneDouble membrane– Membrane fuses at certain points to Membrane fuses at certain points to
produce nuclear poresproduce nuclear pores– Selectively permeableSelectively permeable
NucleolusNucleolus– Site where ribosomes are assembledSite where ribosomes are assembled

ChromatinChromatin– Loose network of threads of DNA Loose network of threads of DNA
and proteinand protein– Forms chromosomes during cell Forms chromosomes during cell
divisiondivision


Plasma MembranePlasma Membrane
Figure 3.2Figure 3.2 Phospholipid bilayerPhospholipid bilayer
– Polar heads of phosphate part of lipid, line Polar heads of phosphate part of lipid, line the inner and outer surfaces of the the inner and outer surfaces of the membrane and are hydrophilic or membrane and are hydrophilic or attracted to waterattracted to water
– Lipid layers are arranged tail to tail Lipid layers are arranged tail to tail forming the center of the membrane and forming the center of the membrane and are hydrophobic or impermeable to water-are hydrophobic or impermeable to water-soluble moleculessoluble molecules

CholesterolCholesterol ProteinsProteins
– Responsilble for specialized functionsResponsilble for specialized functions– Involved in transport across the membrane Involved in transport across the membrane
by forming protein channels for water-by forming protein channels for water-soluble moleculessoluble molecules
– Glycoproteins contains sugars that extend Glycoproteins contains sugars that extend into the extracellular space, acting as into the extracellular space, acting as receptors, and involved in cell to cell receptors, and involved in cell to cell interactionsinteractions


Special structures of the Special structures of the membrane include microvilli and membrane include microvilli and membrane junctionsmembrane junctions
MicrovilliMicrovilli – fingerlike projections – fingerlike projections that increase surface areathat increase surface area
Membrane junctionsMembrane junctions vary vary according to functionsaccording to functions

Membrane junctions – figure 3.3Membrane junctions – figure 3.3– Tight junctionsTight junctions – bind cells together – bind cells together
to prevent substances from passing to prevent substances from passing between cellsbetween cells
– DesmosomesDesmosomes – buttonlike thickening – buttonlike thickening of adjacent membranes connected of adjacent membranes connected by fine protein filaments which by fine protein filaments which prevent cells from being pulled apartprevent cells from being pulled apart

– Gap junctionsGap junctions – neighboring cells are – neighboring cells are connected by connected by connexonsconnexons made of made of proteins between membranes that proteins between membranes that allow communication between cellsallow communication between cells


CytoplasmCytoplasm
Contains cytosol, organelles, Contains cytosol, organelles, inclusionsinclusions
CytosolCytosol –semitransparent fluid, –semitransparent fluid, largely water, nutrients and soluteslargely water, nutrients and solutes
OrganellesOrganelles – specialized for specific – specialized for specific functionsfunctions
InclusionsInclusions – depend on cell type, – depend on cell type, include lipid drops, glycogen, include lipid drops, glycogen, pigments, mucus, etc.pigments, mucus, etc.


OrganellesOrganelles
Figure 3.4Figure 3.4 Mitochondria Mitochondria
– Structure – double membrane, Structure – double membrane, generally sausage-shapedgenerally sausage-shaped Inner membrane forms Inner membrane forms cristea, cristea,
partitionspartitions
– Function - Function - Oxygen is used to break down food and Oxygen is used to break down food and
produce ATP to store energyproduce ATP to store energy

RibosomesRibosomes – –– Structure – bilobed bodies made of Structure – bilobed bodies made of
protein and ribosomal RNA protein and ribosomal RNA – Function – site of protein synthesisFunction – site of protein synthesis

Endoplasmic ReticulumEndoplasmic Reticulum – network of – network of channels to transport substances channels to transport substances from one part of the cell to anotherfrom one part of the cell to another– Rough ERRough ER – studded with ribosomes – studded with ribosomes
Proteins made on ribosomes are carried Proteins made on ribosomes are carried through tubules of rough ER, folded into through tubules of rough ER, folded into shape and transported throughout the cellshape and transported throughout the cell
– Smooth ERSmooth ER Functions in lipid metabolismFunctions in lipid metabolism


Golgi ApparatusGolgi Apparatus – Structure – stack of flattened Structure – stack of flattened
membranous sacsmembranous sacs– Function – packages proteins from Function – packages proteins from
rough ER – figure 3.6rough ER – figure 3.6 Proteins transported outside the cellProteins transported outside the cell Proteins & phospholipids transported to Proteins & phospholipids transported to
cell membranecell membrane Proteins (enzymes) packaged into Proteins (enzymes) packaged into
lysosomes to stay inside celllysosomes to stay inside cell


LysosomesLysosomes – Structure – membranous sacs Structure – membranous sacs
containing digestive enzymescontaining digestive enzymes– Function – digest worn out or Function – digest worn out or
nonusable cell structures, also nonusable cell structures, also digest foreign substances that enter digest foreign substances that enter the cell such as bacteriathe cell such as bacteria

PeroxisomesPeroxisomes– Structure – membranous sacs Structure – membranous sacs
containing enzyme oxidasecontaining enzyme oxidase– Function - Detoxify the cell by Function - Detoxify the cell by
removing dangerous chemicals, free removing dangerous chemicals, free radicals, from the cell radicals, from the cell
– Convert free radicals to hydrogen Convert free radicals to hydrogen peroxide which is then converted to peroxide which is then converted to waterwater

Microfilaments and microtubulesMicrofilaments and microtubules– Structure - Composed of thin, threadlike Structure - Composed of thin, threadlike
strands of proteinstrands of protein– Function - an internal skeleton or a Function - an internal skeleton or a
cytoskeletoncytoskeleton– Microtubules, larger than microfilaments, Microtubules, larger than microfilaments,
function during cell divisionfunction during cell division– Microfilaments function in cell contraction Microfilaments function in cell contraction


CentriolesCentrioles– Structure - Rod-shaped bodies, Structure - Rod-shaped bodies,
made of microtubules, at right made of microtubules, at right angles to each otherangles to each other
– Function - during cell division as a Function - during cell division as a mitotic spindlemitotic spindle

Cilia and flagellaCilia and flagella– Structure - Extensions from the cell Structure - Extensions from the cell
membrane composed of membrane composed of microtubulesmicrotubules
– Function - Cilia, small hair-like Function - Cilia, small hair-like structures that move substances structures that move substances across cell surfaceacross cell surface
– Function - Flagella, single long tail-Function - Flagella, single long tail-like structure that moves the celllike structure that moves the cell

Cell DiversityCell Diversity
Figure 3.8Figure 3.8 Shapes of cells and numbers of Shapes of cells and numbers of
various organelles relate to cell various organelles relate to cell functionfunction

Cell PhysiologyCell Physiology
Most cells are designed to Most cells are designed to perform the following functions: perform the following functions: metabolize nutrients, digest food, metabolize nutrients, digest food, dispose of wastes, reproduce, dispose of wastes, reproduce, grow, move, respond to stimulusgrow, move, respond to stimulus
Important to these functions are: Important to these functions are: membrane transport, protein membrane transport, protein synthesis, cell reproductionsynthesis, cell reproduction

Membrane TransportMembrane Transport
Important terms: solution, solvent, Important terms: solution, solvent, solute, intracellular fluid, interstitial solute, intracellular fluid, interstitial fluid, selective permeabilityfluid, selective permeability
Substances enter or leave the cell Substances enter or leave the cell in two general ways: passive or in two general ways: passive or active mechanismsactive mechanisms– Passive transport does not require Passive transport does not require
energy energy – Active transport requires ATP energyActive transport requires ATP energy

Passive TransportPassive Transport
Passive mechanisms move Passive mechanisms move substances from areas of higher substances from areas of higher concentration to areas of lower concentration to areas of lower concentration – concentration – down the down the concentration gradientconcentration gradient
Passive mechanisms include: Passive mechanisms include: diffusion, osmosis, facilitated diffusion, osmosis, facilitated diffusion, filtrationdiffusion, filtration

DiffusionDiffusion – spreading of particles until – spreading of particles until equilibrium is reached, evenly distributedequilibrium is reached, evenly distributed
Plasma membrane is a barrier to Plasma membrane is a barrier to diffusion and molecules will diffuse diffusion and molecules will diffuse passively through the membrane if they passively through the membrane if they are small enough to pass through its are small enough to pass through its pores or they can dissolve in the fatty pores or they can dissolve in the fatty portion of the membraneportion of the membrane
Fats, fat-soluble vitamins, oxygen, COFats, fat-soluble vitamins, oxygen, CO22

OsmosisOsmosis – Diffusion of water through a – Diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membraneselectively permeable membrane
Osmotic pressure is the tendency of a Osmotic pressure is the tendency of a solution to “pull” water into it. solution to “pull” water into it. – Hypertonic solutions have high solute Hypertonic solutions have high solute
concentrations and high osmotic pressureconcentrations and high osmotic pressure– Hypotonic solutions have low solute Hypotonic solutions have low solute
concentrations and low osmotic pressureconcentrations and low osmotic pressure

Hypertonic solutions will pull water Hypertonic solutions will pull water from cells, and cells will shrinkfrom cells, and cells will shrink
Hypotonic solutions will force water Hypotonic solutions will force water into cells, and cells will swellinto cells, and cells will swell
Isotonic solutions have same Isotonic solutions have same osmotic pressure as cells, and will osmotic pressure as cells, and will cause no change to cellscause no change to cells
A Closer Look, page 75A Closer Look, page 75

Water is highly polar and Water is highly polar and therefore cannot pass through the therefore cannot pass through the lipid portion of the membranelipid portion of the membrane
Water molecules pass through Water molecules pass through special pores in the membrane - special pores in the membrane - aquaporinsaquaporins

Facilitated DiffusionFacilitated Diffusion – protein – protein membrane channel or protein membrane channel or protein carrier molecule is used because carrier molecule is used because molecules are lipid-insoluble and molecules are lipid-insoluble and too large to pass through too large to pass through membrane poresmembrane pores
Glucose enters the cell through Glucose enters the cell through facilitated diffusionfacilitated diffusion
Figure 3.10Figure 3.10


FiltrationFiltration – substances are pushed – substances are pushed through a membrane by fluid or through a membrane by fluid or hydrostatic hydrostatic pressurepressure
Usually occurs in blood capillaries Usually occurs in blood capillaries with thin wallswith thin walls

Active TransportActive Transport
Active mechanisms move substances Active mechanisms move substances from area of lower concentration to from area of lower concentration to area of higher concentration – moving area of higher concentration – moving uphill,uphill, or against the concentration or against the concentration gradientgradient
Active mechanisms include: solute Active mechanisms include: solute pumping, bulk transport by exocytosis pumping, bulk transport by exocytosis or endocytosis, receptor-mediated or endocytosis, receptor-mediated endocytosisendocytosis

Solute pumpingSolute pumping – membrane protein – membrane protein carriers used to transport carriers used to transport substances too large to pass substances too large to pass through membrane channels or through membrane channels or lipid-insoluble lipid-insoluble against concentration against concentration gradient gradient
Sodium-potassium pump carries NaSodium-potassium pump carries Na++ out of cell and Kout of cell and K++ into cell using ATP into cell using ATP
Figure 3.11Figure 3.11


ExocytosisExocytosis – removes substances – removes substances from cellsfrom cells
Substance is packaged by golgi, Substance is packaged by golgi, migrates to membrane, fuses migrates to membrane, fuses with membrane, ruptures, is with membrane, ruptures, is released outside the cellreleased outside the cell
Figure 3.12Figure 3.12



EndocytosisEndocytosis – encloses extracellular – encloses extracellular substances in a membranous sac substances in a membranous sac formed by the plasma membraneformed by the plasma membrane
Extracellular substances are digested Extracellular substances are digested by fusing with a lysosomeby fusing with a lysosome
Types of endocytosis include: Types of endocytosis include: phagocytosis, pinocytosis, receptor-phagocytosis, pinocytosis, receptor-mediated endocytosismediated endocytosis
Figure 3.13Figure 3.13


Phagocytosis external substances Phagocytosis external substances are large particles captured by are large particles captured by pseudopodspseudopods– Protective mechanism that ingests Protective mechanism that ingests
bacteria and debrisbacteria and debris– Not used to obtain nutrientsNot used to obtain nutrients– White blood cellsWhite blood cells

Pinocytosis – plasma membrane Pinocytosis – plasma membrane invaginates and surrounds liquid invaginates and surrounds liquid extracellular substanceextracellular substance– Liquid contains dissolved proteins or Liquid contains dissolved proteins or
fatsfats– Lining of small intestine, kidneyLining of small intestine, kidney

Receptor-mediated endocytosis – Receptor-mediated endocytosis – plasma membrane receptor plasma membrane receptor proteins bind with specific proteins bind with specific substancessubstances– Membrane invaginates to form vesicleMembrane invaginates to form vesicle– Enzymes, hormones, cholesterol, iron, Enzymes, hormones, cholesterol, iron,
viruses commonly enter cell through viruses commonly enter cell through receptor-mediated processreceptor-mediated process

Cell DivisionCell Division
Cell life cycle consists of the changes Cell life cycle consists of the changes that the cell goes through from time that the cell goes through from time of formation until the time of divisionof formation until the time of division
Cell life cycle consists of Cell life cycle consists of interphase interphase and cell divisionand cell division– DNA replication occurs during interphaseDNA replication occurs during interphase– Mitosis and cytokinesis occur during cell Mitosis and cytokinesis occur during cell
divisiondivision

InterphaseInterphase – DNA replication – DNA replication Figure 3.14Figure 3.14 DNA helix separates and uncoilsDNA helix separates and uncoils Each separate template strand is Each separate template strand is
duplicated with a complementary duplicated with a complementary set of nucleotidesset of nucleotides
Results with 2 identical DNA Results with 2 identical DNA moleculesmolecules


Cell divisionCell division – mitosis – mitosis Results in the formation of 2 Results in the formation of 2
nuclei with same genes (DNA)nuclei with same genes (DNA) Stages of mitosis include: Stages of mitosis include:
prophase, metaphase, anaphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophasetelophase
Figure 3.15Figure 3.15



ProphaseProphase– Chromatin threads coil and become Chromatin threads coil and become
chromosomes made up of 2 chromatids chromosomes made up of 2 chromatids held together by a centromereheld together by a centromere
– Centrioles separate and migrate to Centrioles separate and migrate to opposite sides of cellopposite sides of cell
– Spindle of microtubules is formed between Spindle of microtubules is formed between centrioles, centromeres attach to spindlecentrioles, centromeres attach to spindle
– Nuclear envelope & nucleoli disappearNuclear envelope & nucleoli disappear

Metaphase Metaphase Chromosomes line up in the Chromosomes line up in the
center of the spindle (metaphse center of the spindle (metaphse plate)plate)

AnaphaseAnaphase Centromeres split and single Centromeres split and single
chromosomes appearchromosomes appear Chromosomes are pulled to Chromosomes are pulled to
opposite ends of cell along opposite ends of cell along spindlespindle

TelophaseTelophase Chromosomes uncoil and become Chromosomes uncoil and become
chromatinchromatin Spindle disappearsSpindle disappears Nuclear envelope forms around Nuclear envelope forms around
chromatinchromatin Nucleoli appear Nucleoli appear

CytokinesisCytokinesis – division of cytoplasm – division of cytoplasm Begins during late anaphase, ends Begins during late anaphase, ends
during telophaseduring telophase Cleavage furrow appears in center Cleavage furrow appears in center
of spindleof spindle Cytoplasm is separated into two Cytoplasm is separated into two
partsparts 2 daughter cells are produced2 daughter cells are produced

Protein SynthesisProtein Synthesis
Genes carry information (DNA) for Genes carry information (DNA) for constructing proteinsconstructing proteins– Sequence of 3 bases (triplets) code Sequence of 3 bases (triplets) code
for each amino acidfor each amino acid Proteins are important substances Proteins are important substances
for cellsfor cells– Major building material for cellsMajor building material for cells– ENZYMESENZYMES

DNA is in the nucleus, protein DNA is in the nucleus, protein synthesis occurs on the synthesis occurs on the ribosomes in the cytoplasmribosomes in the cytoplasm
Information in DNA code must be Information in DNA code must be transcribed, transferred to transcribed, transferred to ribosomes, translated into ribosomes, translated into proteinsproteins
mRNA and tRNA are instrumental mRNA and tRNA are instrumental in protein synthesisin protein synthesis


TRANSCRIPTION – Figure 3.16TRANSCRIPTION – Figure 3.16 mRNA copies the protein code from mRNA copies the protein code from
the nuclear DNAthe nuclear DNA– DNA unzips, complementary bases of DNA unzips, complementary bases of
RNA, codons, match up with DNA RNA, codons, match up with DNA tripletstriplets
– Single stranded mRNA has the protein Single stranded mRNA has the protein code from the DNAcode from the DNA
– mRNA leaves the nucleusmRNA leaves the nucleus

TRANSLATION – figure 3.16TRANSLATION – figure 3.16 Occurs in the cytoplasmOccurs in the cytoplasm mRNA attaches to ribosomemRNA attaches to ribosome tRNA molecules present in cytoplasm tRNA molecules present in cytoplasm
contain a sequence of 3 bases that contain a sequence of 3 bases that represent an anticodon that is represent an anticodon that is complementary to the mRNA codoncomplementary to the mRNA codon– Different tRNA’s have different Different tRNA’s have different
anticodonsanticodons

tRNA picks up an amino acid that is tRNA picks up an amino acid that is specific to its anticodonspecific to its anticodon
tRNA carries its amino acid to the tRNA carries its amino acid to the mRNA on the ribosome and matches mRNA on the ribosome and matches up with the mRNA codon up with the mRNA codon
Ribosome moves the mRNA to bring Ribosome moves the mRNA to bring the next codon into place, and another the next codon into place, and another tRNA with a new amino acid attaches tRNA with a new amino acid attaches to the mRNAto the mRNA
Amino acids of each tRNA attach to Amino acids of each tRNA attach to each other and form a peptide chaineach other and form a peptide chain

Once the amino acids attach to Once the amino acids attach to each other (forming a peptide each other (forming a peptide bond), the tRNA is released from bond), the tRNA is released from the ribosomethe ribosome

PART 2 - TISSUESPART 2 - TISSUES
Soon after cell division, cells Soon after cell division, cells develop different characteristics develop different characteristics in structure and function – cell in structure and function – cell differentiationdifferentiation
Certain groups of specialized cells Certain groups of specialized cells perform specific functionsperform specific functions
Groups of cells that are similar in Groups of cells that are similar in structure and function are called structure and function are called tissuestissues

There are four major types of There are four major types of tissuestissues– Epithelial – protection, secretion, Epithelial – protection, secretion,
absorption, filtration, coveringabsorption, filtration, covering– Connective – support, binding Connective – support, binding
structures togetherstructures together– Muscle – body movementMuscle – body movement– Nervous – conduct impulses, Nervous – conduct impulses,
coordinate activities, controlcoordinate activities, control

EpitheliumEpithelium
Fit closely together to form sheets with Fit closely together to form sheets with cells bound by cell junctionscells bound by cell junctions
Always has a free surface exposed to Always has a free surface exposed to an open space (apical surface).an open space (apical surface).
The underside is attached to a The underside is attached to a basement membrane which connects basement membrane which connects to connective tissue.to connective tissue.
Contains no blood supply. Nutrients Contains no blood supply. Nutrients diffuse through connective tissue.diffuse through connective tissue.

Will readily divide. Damaged Will readily divide. Damaged cells are easily replaced.cells are easily replaced.
Free surfaces are modified for Free surfaces are modified for secretion, absorption, excretion, secretion, absorption, excretion, sensory reception.sensory reception.

Identifying epithelial Identifying epithelial cellscells Simple – single layerSimple – single layer Stratified – several layersStratified – several layers Pseudostratified – looks layered, but is notPseudostratified – looks layered, but is not Transitional – can change if tissue Transitional – can change if tissue
stretches or contractsstretches or contracts Squamous – flat or scalelike cellsSquamous – flat or scalelike cells Cuboidal – cube-shaped cellsCuboidal – cube-shaped cells Columnar – elongated cellsColumnar – elongated cells Glandular – cells specialized to produce & Glandular – cells specialized to produce &
secrete substances into ducts or body secrete substances into ducts or body fluidsfluids


Types of epithelial Types of epithelial tissuetissue Figure 3.18Figure 3.18 1 – Simple squamous epithelial1 – Simple squamous epithelial
– Single layer, flat cellsSingle layer, flat cells– Sites of diffusion and filtrationSites of diffusion and filtration– Easily damagedEasily damaged
2 – Simple cuboidal epithelial2 – Simple cuboidal epithelial– Single layer, cube-shaped cellsSingle layer, cube-shaped cells– Sites of secretion and absorptionSites of secretion and absorption– Central nucleusCentral nucleus



3- Simple columnar epithelial3- Simple columnar epithelial– Single layer, elongated cells (thick Single layer, elongated cells (thick
tissue)tissue)– Nuclei located at same level near Nuclei located at same level near
basement membranebasement membrane– Sites of secretion, absorption along Sites of secretion, absorption along
digestive tractdigestive tract– Goblet, glandular, cells exist among Goblet, glandular, cells exist among
simple columnar that secrete simple columnar that secrete protective fluid called mucusprotective fluid called mucus


4 – Stratified squamous epithelial4 – Stratified squamous epithelial– Many layers of flat cells (skin)Many layers of flat cells (skin)– Lower layers can be cuboidal or Lower layers can be cuboidal or
columnarcolumnar– Found at sites that receive abuse or Found at sites that receive abuse or
friction – skin, mouth, esophagusfriction – skin, mouth, esophagus 5 – Stratified cuboidal epithelial5 – Stratified cuboidal epithelial
– 2 to 3 layers that provide more 2 to 3 layers that provide more protection than single layerprotection than single layer


6 – Stratified columnar epithelial6 – Stratified columnar epithelial– Superficial layer is columnar, but basal Superficial layer is columnar, but basal
layer varies in shapelayer varies in shape 7 – Pseudostratified columnar 7 – Pseudostratified columnar
epithelialepithelial– Not layered, but single layer with some Not layered, but single layer with some
shorter cells with nuclei at different shorter cells with nuclei at different levelslevels
– Commonly posses cilia and goblet cells Commonly posses cilia and goblet cells to secrete mucusto secrete mucus


8 – Transitional8 – Transitional– Highly modified stratified squamous Highly modified stratified squamous
epitheliumepithelium– Basal layer is composed of cuboidal Basal layer is composed of cuboidal
or columnar cellsor columnar cells– Surface cells vary Surface cells vary
Cells flatten when organ is stretchedCells flatten when organ is stretched Cells layer and become rounded when Cells layer and become rounded when
not stretchednot stretched


9 – Glandular epithelial – 9 – Glandular epithelial – specialized to produce and specialized to produce and secrete substances secrete substances – Exocrine glands – secrete into ducts Exocrine glands – secrete into ducts
that open onto a surfacethat open onto a surface– Endocrine glands – secrete into Endocrine glands – secrete into
tissue fluid or bloodtissue fluid or blood

Connective TissueConnective Tissue
Functions to protect, support, bind Functions to protect, support, bind together other tissuestogether other tissues
Most is well vascularized, some is notMost is well vascularized, some is not– Tissues with poor blood supply heal slowlyTissues with poor blood supply heal slowly
Consists of various cell types and Consists of various cell types and nonliving extracellular matrixnonliving extracellular matrix– Some types of tissue are mostly cells in soft Some types of tissue are mostly cells in soft
matrix, other types of tissue have few cells matrix, other types of tissue have few cells in hard matrix, other types vary in betweenin hard matrix, other types vary in between

MatrixMatrix– Produced by cells and secretedProduced by cells and secreted– Consists of ground substance and fibersConsists of ground substance and fibers
Matrix ground substancesMatrix ground substances– Composed of water, adhesion proteins, Composed of water, adhesion proteins,
charged polysaccaridescharged polysaccarides Protiens allow fibers to attach to ground subs.Protiens allow fibers to attach to ground subs. Abundance of polysaccarides changes Abundance of polysaccarides changes
consistency from liquid to gel to firm to rock-consistency from liquid to gel to firm to rock-hardhard

Matrix fibersMatrix fibers– Collagen (white) fibers – high tensile Collagen (white) fibers – high tensile
strengthstrength– Elastic (yellow) fibers – can be Elastic (yellow) fibers – can be
stretched and will recoilstretched and will recoil– Reticular fibers – fine collagen fibers Reticular fibers – fine collagen fibers
that form an internal skeletonthat form an internal skeleton

Connective tissue cell typesConnective tissue cell types– Bone tissue cells – osteocytesBone tissue cells – osteocytes– Cartilage cells – chondrocytes, Cartilage cells – chondrocytes,
fibroblastsfibroblasts– Loose tissue cells – fibroblasts, fat Loose tissue cells – fibroblasts, fat
cells, reticular cells which resemble cells, reticular cells which resemble fibroblastsfibroblasts
– Blood tissue cells – variety of white Blood tissue cells – variety of white blood cells and red blood cellsblood cells and red blood cells

Types of Connective Types of Connective TissueTissue
Major differences in connective Major differences in connective tissue types depend on types and tissue types depend on types and numbers of fibers in the matrixnumbers of fibers in the matrix
Connective tissue types from Connective tissue types from most rigid to softest include: most rigid to softest include: bone, cartilage, dense connective bone, cartilage, dense connective tissue, loose connective tissue, tissue, loose connective tissue, bloodblood

Figure 3.19Figure 3.19 1 – Bone –osseous tissue1 – Bone –osseous tissue
– Composed of bone cells in cavities Composed of bone cells in cavities called called lacunae lacunae and surrounded by and surrounded by layers of hard matrix called layers of hard matrix called lamellalamella
– Contains calcium saltsContains calcium salts– Protect and support body partsProtect and support body parts


2 – Cartilage2 – Cartilage– More flexible than boneMore flexible than bone– 3 types of cartilage: hyaline 3 types of cartilage: hyaline
cartilage, fibrocartilage, elastic cartilage, fibrocartilage, elastic cartilagecartilage
– Hyaline cartilageHyaline cartilage Collagen fibers hidden in a rubbery Collagen fibers hidden in a rubbery
matrix, chondrocyte cells in lacunaematrix, chondrocyte cells in lacunae Found in larynx, attaching ribs to Found in larynx, attaching ribs to
breastbone, ends of bonesbreastbone, ends of bones


– Fibrocartilage Fibrocartilage More collagen fibers than hyaline More collagen fibers than hyaline
cartilage, chondrocyte cells in lacunaecartilage, chondrocyte cells in lacunae Forms intervertebral disks of spinal Forms intervertebral disks of spinal
columncolumn
– Elastic cartilageElastic cartilage More elastic fibersMore elastic fibers Found in structures that need elasticity, Found in structures that need elasticity,
external earexternal ear


3 – Dense Connective Tissue3 – Dense Connective Tissue– Closely packed collagen fibers Closely packed collagen fibers
containing rows of fibroblastscontaining rows of fibroblasts– Strong tissue composing tendons Strong tissue composing tendons
and ligamentsand ligaments Tendons connect muscle to boneTendons connect muscle to bone Ligaments connect bones to bones, also Ligaments connect bones to bones, also
contain elastic fibers contain elastic fibers


4 – Loose Connective Tissue4 – Loose Connective Tissue– Tissue is softer and contains more Tissue is softer and contains more
cells and less fiberscells and less fibers– 3 types of loose connective tissue 3 types of loose connective tissue
include: areolar tissue, adipose include: areolar tissue, adipose tissue, reticular connective tissuetissue, reticular connective tissue

– Areolar tissue – most widely Areolar tissue – most widely distributeddistributed
Loose network of various fibers and Loose network of various fibers and fibroblasts - cobwebfibroblasts - cobweb
Cushions and protects body organsCushions and protects body organs– Helps to hold internal organs in positionHelps to hold internal organs in position
Provides a reservoir of water and salts for Provides a reservoir of water and salts for surrounding tissue – soft, fluid matrixsurrounding tissue – soft, fluid matrix
All cells obtain nutrients and release All cells obtain nutrients and release wastes into areolar tissue fluidwastes into areolar tissue fluid
– Excess fluid in areolar tissue causes swelling, Excess fluid in areolar tissue causes swelling, edemaedema


– Adipose tissueAdipose tissue Composed of mostly fat cellsComposed of mostly fat cells Fat cells are composed mainly of oil Fat cells are composed mainly of oil
with a thin rim of cytoplasm and a with a thin rim of cytoplasm and a bulging nucleusbulging nucleus
Found in tissue beneath the skin and Found in tissue beneath the skin and insulates the body from extreme insulates the body from extreme temperature changestemperature changes
Protects organsProtects organs Fat is available as energy sourceFat is available as energy source


– Reticular connective tissueReticular connective tissue Composed of network of reticular fibers Composed of network of reticular fibers
and reticular cellsand reticular cells Found in limited sites: lymph nodes, Found in limited sites: lymph nodes,
spleen , bone marrowspleen , bone marrow


5 – Blood5 – Blood– Consists of blood cells surrounded Consists of blood cells surrounded
by fluid matrix called blood plasmaby fluid matrix called blood plasma– Fibers are made of protein that is Fibers are made of protein that is
visible when blood clotsvisible when blood clots– Transports nutrients , wastes, Transports nutrients , wastes,
respiratory gasesrespiratory gases


Muscle TissueMuscle Tissue
Composed of many muscle Composed of many muscle cellscells called muscle called muscle fibersfibers
Specialized to contract to produce Specialized to contract to produce movementmovement
3 types of muscle tissue include: 3 types of muscle tissue include: skeletal, cardiac, smoothskeletal, cardiac, smooth
Figure 3.20Figure 3.20

Types of Muscle TissueTypes of Muscle Tissue
1 – Skeletal muscle1 – Skeletal muscle– Found in muscles that attach to bone Found in muscles that attach to bone – Are controlled by conscious effort, Are controlled by conscious effort,
therefore they are called voluntary therefore they are called voluntary musclesmuscles
– Provide gross body movementsProvide gross body movements– Cells are long and threadlike with Cells are long and threadlike with
light and dark striations and many light and dark striations and many nucleinuclei


2 – Cardiac muscle2 – Cardiac muscle– Found only in the heartFound only in the heart– Are involuntary musclesAre involuntary muscles– Cells are striated, have one nucleus, are Cells are striated, have one nucleus, are
shorter than skeletal muscles, are shorter than skeletal muscles, are branchedbranched
– Cells fit together at junctions calledCells fit together at junctions called intercalated disksintercalated disks which contain gap which contain gap junctions that allow rapid conduction of junctions that allow rapid conduction of impulsesimpulses


3 – Smooth muscle (visceral)3 – Smooth muscle (visceral)– Found in walls of hollow internal organsFound in walls of hollow internal organs– Involuntary musclesInvoluntary muscles– Cells are shorter and spindle-shaped with Cells are shorter and spindle-shaped with
a central nucleus and no striationsa central nucleus and no striations– Smooth muscle contraction Smooth muscle contraction constrictsconstricts an an
organ, smooth muscle relaxation organ, smooth muscle relaxation dilatesdilates an organan organ
– Wavelike constriction and dilation Wavelike constriction and dilation produces produces peristalsisperistalsis which moves food in which moves food in the digestive tractthe digestive tract


Nervous TissueNervous Tissue
Found in the brain, spinal cord, and Found in the brain, spinal cord, and nervesnerves
Nerve cells are called neuronsNerve cells are called neurons– Neuroglial cells – supporting cells that Neuroglial cells – supporting cells that
insulate, support and protect neurons insulate, support and protect neurons Neurons have nerve fiber extensions Neurons have nerve fiber extensions
which transmit impulses to other which transmit impulses to other neurons, muscles, or glandsneurons, muscles, or glands
Neurons have single nucleusNeurons have single nucleus Figure 3.21Figure 3.21


Tissue RepairTissue Repair
Response to tissue injury involves Response to tissue injury involves an inflammatory response and an an inflammatory response and an immune responseimmune response– Inflammation prevents further injuryInflammation prevents further injury– Immune response attacks against Immune response attacks against
bacteria and viruses bacteria and viruses

Tissue repair involves Tissue repair involves regeneration and fibrosisregeneration and fibrosis– Regeneration involves the Regeneration involves the
replacement of destroyed cells by replacement of destroyed cells by the same kind of cellthe same kind of cell
– Fibrosis involves the repair of an Fibrosis involves the repair of an injury with dense connective tissue injury with dense connective tissue that forms a scarthat forms a scar

Process of tissue repairProcess of tissue repair– Capillaries become very permeableCapillaries become very permeable
Blood seeps into area and forms clotBlood seeps into area and forms clot
– Granulation tissue formsGranulation tissue forms Composed of new, fragile capillariesComposed of new, fragile capillaries Contains phagocytes to dispose of clot, Contains phagocytes to dispose of clot,
fibroblasts to produce collage fibersfibroblasts to produce collage fibers
– Surface epithelium regeneratesSurface epithelium regenerates Above granulation tissue & below clotAbove granulation tissue & below clot Scar forms (fibrosis)Scar forms (fibrosis)

RegenerationRegeneration– Occurs readily in epidermis, mucous Occurs readily in epidermis, mucous
membrane, fibrous connective tissue, bonemembrane, fibrous connective tissue, bone– Skeletal muscle regenerates poorlySkeletal muscle regenerates poorly– Cardiac muscle and nervous tissue are Cardiac muscle and nervous tissue are
replaced by scar tissue replaced by scar tissue Fibrosis – scar tissue lacks the ability to Fibrosis – scar tissue lacks the ability to
perform the normal functions of the perform the normal functions of the tissue it replacestissue it replaces

Development of Cells Development of Cells and and TissuesTissues During embryonic development, cells During embryonic development, cells
begin to specialize to form primary begin to specialize to form primary tissues.tissues.
By birth, most organs are formed and By birth, most organs are formed and functioning.functioning.
During growth throughout childhood During growth throughout childhood and adolescence the body enlarges and and adolescence the body enlarges and forms new tissue through cell divisionforms new tissue through cell division
At adulthood, overall body growth endsAt adulthood, overall body growth ends

After adulthood, only certain cells After adulthood, only certain cells routinely divide.routinely divide.– Skin and intestineSkin and intestine– Liver stops but can be replaced if Liver stops but can be replaced if
damageddamaged– Heart muscle and nerve tissue can Heart muscle and nerve tissue can
no longer divide, they become no longer divide, they become amitoticamitotic

Aging process involves:Aging process involves:– Epithelial tissue thins and loses Epithelial tissue thins and loses
elasticityelasticity– Exocrine glands become less activeExocrine glands become less active– Endocrine glands produce less Endocrine glands produce less
hormonehormone– Bone tissue becomes porous and Bone tissue becomes porous and
weakenweaken– Muscle tissue begins to atrophyMuscle tissue begins to atrophy

Other cell and tissue modifications Other cell and tissue modifications (not associated with aging)(not associated with aging)– Neoplasm – normal cell division is out Neoplasm – normal cell division is out
of control and cells divide continuallyof control and cells divide continually– Hyperplasia – increase in cell number Hyperplasia – increase in cell number
as a result of an irritantas a result of an irritant Usually temporary, no treatment neededUsually temporary, no treatment needed
– Atrophy – decrease in size in an area Atrophy – decrease in size in an area that loses stimulationthat loses stimulation
musclemuscle