1 DNT 200 NUTRITION FOR HEALTH SCIENCES METABOLISM AND ENERGY BALANCE.
Chapter 22a Metabolism and Energy Balance. About this Chapter Appetite and satiety Energy balance...
-
Upload
trevin-lusher -
Category
Documents
-
view
235 -
download
1
Transcript of Chapter 22a Metabolism and Energy Balance. About this Chapter Appetite and satiety Energy balance...

Chapter 22a
Metabolism and Energy Balance

About this Chapter
• Appetite and satiety• Energy balance• Metabolism• Homeostatic control of metabolism• Regulation of body temperature

Appetite and Satiety
• Food intake is carefully controlled• Two competing behavioral states• Appetite (or hunger) = desire for food• Satiety = sense of fullness (or satisfaction)
• Hypothalamus contains two key control centers• Feeding center• Satiety center

Four Types of Input to the Hypothalamus
• Neural input from the cerebral cortex• Neural input from the limbic system• Peptide hormones from the GI tract• Adipocytokines from adipose tissue

Two Theories for Regulation of Food Intake
• Glucostatic theory• Theory proposes that blood glucose levels
ultimately control the feeding and satiety centers
• Lipostatic theory• Theory proposes that the level of body fat
regulates the feeding and satiety centers• Recent discovery of several peptides
(especially leptin and neuropeptide Y) seems to support this theory

Figure 22-1
Peptides Regulate the Feeding Center

Table 22-1
Many Peptides Alter Food Intake

Energy Balance - The Key to Weight Control
• Energy input = energy output• Energy output = work heat• Three categories of work done by our cells• Membrane transport• Mechanical work• Chemical work = building molecules, including
synthesis of energy storage molecules• Short-term energy storage (ATP)• Long-term energy storage (glycogen, fat)

Energy Balance
• Methods for measuring energy use• Direct calorimetry• Measures the energy content of food• Fat 9 Kcal/g / protein and CHO ~ 4 Kcal/g
• Indirect calorimetry• Estimates metabolic rate as a measure of energy
use• Oxygen consumption• Carbon dioxide production
• Ratio of CO2 to O2 (RQ or RER)

Metabolic Rate
• Basal metabolic rate (BMR) is most common measure of metabolic rate
• Six factors affecting metabolic rate1 - Age and gender2 - Amount of lean muscle mass3 - Activity level4 - Energy intake (diet) – fat vs protein thermogenesis
5 – Hormones – thyroid hormone thyroxin
6 - Genetics• Only energy intake and level of physical
activity can be voluntarily changed

Two Chemical Forms of Energy Storage
• Glycogen (highly branched polymer of glucose)• Stored glycogen binds water• Liver glycogen is used to regulate blood
glucose• Muscle glycogen is used to power muscle
contraction
• Fat (triglycerides)• Fats have higher energy content per gram• Little water is required for fat storage• Energy in fats is harder and slower to access

Metabolism
• Metabolism is all of the chemical reactions in the body1 - Extract energy from nutrients
2 - Use energy for work and synthesis
3 - Store excess energy
• Two types of metabolic pathways• Anabolic pathways build large molecules• Catabolic pathways break down large molecules
• Metabolism can be divided into two states• Absorptive (“fed”) state is anabolic• Post-absorptive (“fasted”) state is catabolic

Metabolic Fates and Nutrient Pools
• Ingested biomolecules have three fates1. Immediate use in energy production
2. Synthesis into needed macromolecules
3. Storage for later use in energy production
• Nutrient pools are available for immediate use• Free fatty acids• Plasma glucose pool• Amino acid pool
Know definitions of:Glycogenesis / glycogenolysis / lipogenesis / lipolysis / ketosis

Overview of Metabolism
Figure 22-2
CarbohydratesFats
Free fatty acids + glycerol
Fatstores
Glucose
Excess glucose
Glycogenstores
Aminoacids
Proteins
DIET
Lipogenesis
Brainmetabolism
Range of normalplasma glucose
Gluconeogenesis
Bodyprotein
Glycogenolysis
GlycogenesisProtein
synthesis
Metabolism inmost tissues
Free fattyacid pool
Urine
Excess nutrients
Lipolysis
Glucose pool
Amino acidpool
Lip
og
enes
is

Figure 22-2 (1 of 4)
Carbohydrates
Fatstores
Glucose
Excess glucose
Glycogenstores
DIET
Lipogenesis
Brainmetabolism
Range of normalplasma glucose
Glycogenolysis
Glycogenesis
Metabolism inmost tissues
Urine
Glucose pool
Glucose Metabolism
• Most plasma glucose is used for immediate energy production, or is stored as glycogen

Fats
Free fatty acids + glycerol
Fatstores
DIET
Metabolism inmost tissues
Free fattyacid pool
Excess nutrients
Lipolysis
Lip
og
enes
is
Figure 22-2 (2 of 4)
Fat Metabolism
• Free fatty acids are used for immediate energy production, or are stored as fat molecules in adipose tissue

Aminoacids
Proteins
DIET
Range of normalplasma glucose
Gluconeogenesis
Bodyprotein
Proteinsynthesis
Glucose pool
Amino acidpool
Figure 22-2 (3 of 4)
Amino Acid Metabolism
• Amino acids are used for building needed body proteins. Excess amino acids are converted into glucose by the liver.

Summary of Metabolism
Figure 22-2 (4 of 4)
CarbohydratesFats
Free fatty acids + glycerol
Fatstores
Glucose
Excess glucose
Glycogenstores
Aminoacids
Proteins
DIET
Lipogenesis
Brainmetabolism
Range of normalplasma glucose
Gluconeogenesis
Bodyprotein
Glycogenolysis
GlycogenesisProtein
synthesis
Metabolism inmost tissues
Free fattyacid pool
Urine
Excess nutrients
Lipolysis
Glucose pool
Amino acidpool
Lip
og
enes
is

Biochemical Pathways for Energy Production
• Overview of Pathways
Figure 22-3
Glucose
Someaminoacids
Someaminoacids
Lactate
Glycogen
Glucose 6-phosphate
Liver only
Fatty acids
Electron transportsystem
CO2
NH3
+ H2OO2 26-28
CoAKetone bodies (in liver)
Glycerol
2
ATP
Pyruvate
Pyruvate
Acetyl CoA
NH3
Cytoplasm
Mitochondria
Citric acidcycle ATP
ATP2

Interconversions of Glucose
Figure 22-3 (1 of 7)
Glucose
Glycogen
Glucose 6-phosphate
Liver only
Cytoplasm
Mitochondria

Glycolysis is Catabolism of Glucose
Figure 22-3 (2 of 7)
Glucose
Glycogen
Glucose 6-phosphate
Liver only
Pyruvate
Cytoplasm
Mitochondria
ATP2

Some Amino Acids Can Also Supply Pyruvate
Figure 22-3 (3 of 7)
Glucose
Someaminoacids
Glycogen
Glucose 6-phosphate
Liver only
Glycerol
Pyruvate
NH3
Cytoplasm
Mitochondria
ATP2

Anaerobic Metabolism Produces Lactate
Figure 22-3 (4 of 7)
Glucose
Someaminoacids
Lactate
Glycogen
Glucose 6-phosphate
Liver only
Glycerol
Pyruvate
Pyruvate
NH3
Cytoplasm
Mitochondria
ATP2

Mitochondria and the Citric Acid Cycle
Figure 22-3 (5 of 7)
Glucose
Someaminoacids
Lactate
Glycogen
Glucose 6-phosphate
Liver only
CO2
CoA
Glycerol
2
Pyruvate
Pyruvate
Acetyl CoA
NH3
Cytoplasm
Mitochondria
Citric acidcycle ATP
ATP2

Fatty Acids and Some Amino Acids Enter Here
Figure 22-3 (6 of 7)
Glucose
Someaminoacids
Someaminoacids
Lactate
Glycogen
Glucose 6-phosphate
Liver only
Fatty acids
CO2
NH3
CoAKetone bodies (in liver)
Glycerol
2
Pyruvate
Pyruvate
Acetyl CoA
NH3
Cytoplasm
Mitochondria
Citric acidcycle ATP
ATP2

Electron Transport System
Figure 22-3 (7 of 7)
Glucose
Someaminoacids
Someaminoacids
Lactate
Glycogen
Glucose 6-phosphate
Liver only
Fatty acids
Electron transportsystem
CO2
NH3
+ H2OO2 26-28
CoAKetone bodies (in liver)
Glycerol
2
ATP
Pyruvate
Pyruvate
Acetyl CoA
NH3
Cytoplasm
Mitochondria
Citric acidcycle ATP
ATP2

Metabolism: Push-Pull Control
• Metabolic balance can shift when enzyme activity is controlled
Figure 22-4

Metabolism: Fates of Nutrients in the Fed State
Table 22-2

Transport and Fate of Dietary Fats
Figure 22-5
Dietaryfats
apo
Chylomicron
MonoglyceridesPhospholipidsFree fatty acids (FFA)Cholesterol
FFA
FFA
CM
CM
CMremnants
Lymph
Bileduct
Blood Adipose cells
Most cells
Liver
Intestinallumen
Intestinalcells
lpl
Glycerol
HDL-C LDL-C
Cholesterol + FFA + Lipoproteins
Lipoproteincomplexes
Bile salts
Metabolized
Reassembleto triglycerides
(TG)
TGstorage
Lipolysis by lipases
FFA oxidizedfor energy
Cholesterolfor synthesis
KEYapo=apoproteinslpl=lipoprotein lipaseLDL=low-density lipoproteinHDL = high-density lipoproteinC=cholesterol

High LDL-C Levels Increase Heart Disease Risk
• LDL-C takes cholesterol from liver to most cells
• High LDL-C increases risk of atherosclerosis• Many drugs try to lower cholesterol levels by
changing its metabolism• Low HDL is another risk
factor for atheroslerosis
Figure 22-6

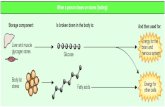
Fasted-State Metabolism
Figure 22-7
Liverglycogen
stores
Energyproduction
Energy production
Free fattyacids
Free fattyacids
Glycerol
Aminoacids
KetonebodiesGlucose
Adipose lipidsbecome freefatty acids andglycerol thatenter blood.
Muscle glycogen can be used for energy.Muscles also use fatty acids and breakdown their proteins to amino acids thatenter the blood.
Liver glycogenbecomes glucose.
Brain can useonly glucose andketones for energy.
or
Triglyceride stores
Glycogen
Pyruvate
Lactate
Energy production
Glucose
Proteins
Ketonebodies
-oxidationGlycogenolysis
Gluconeogenesis
Gluconeogenesis
1 2
34

Fasted-State Metabolism
Figure 22-7 (1 of 4)
Liverglycogen
stores
Free fattyacids
KetonebodiesGlucose
1
Energyproduction
Liver glycogenbecomes glucose.
-oxidationGlycogenolysis

Fasted-State Metabolism
Figure 22-7 (2 of 4)
Liverglycogen
stores
Free fattyacids
Free fattyacids
Glycerol
KetonebodiesGlucose
Adipose lipidsbecome freefatty acids andglycerol thatenter blood.
Triglyceride stores
Gluconeogenesis
1 2
Energyproduction
Liver glycogenbecomes glucose.
-oxidationGlycogenolysis

Fasted-State Metabolism
Figure 22-7 (3 of 4)
Liverglycogen
stores
Free fattyacids
Free fattyacids
Glycerol
Aminoacids
KetonebodiesGlucose
Adipose lipidsbecome freefatty acids andglycerol thatenter blood.
Muscle glycogen can be used for energy.Muscles also use fatty acids and breakdown their proteins to amino acids thatenter the blood.
or
Triglyceride stores
Glycogen
Pyruvate
Lactate
Energy production
Proteins
Gluconeogenesis
Gluconeogenesis
1 2
3
Energyproduction
Liver glycogenbecomes glucose.
-oxidationGlycogenolysis

Fasted-State Metabolism
Figure 22-7 (4 of 4)
Liverglycogen
stores
Energy production
Free fattyacids
Free fattyacids
Glycerol
Aminoacids
KetonebodiesGlucose
Adipose lipidsbecome freefatty acids andglycerol thatenter blood.
Muscle glycogen can be used for energy.Muscles also use fatty acids and breakdown their proteins to amino acids thatenter the blood.
Brain can useonly glucose andketones for energy.
or
Triglyceride stores
Glycogen
Pyruvate
Lactate
Energy production
Glucose
Proteins
Ketonebodies
Gluconeogenesis
Gluconeogenesis
1 2
34
Energyproduction
Liver glycogenbecomes glucose.
-oxidationGlycogenolysis