Chapter 15.1-pages 450-454. Describe a pure substance and a mixture. Compare and contrast pure...
-
Upload
darcy-leo-mcdowell -
Category
Documents
-
view
244 -
download
0
description
Transcript of Chapter 15.1-pages 450-454. Describe a pure substance and a mixture. Compare and contrast pure...

Composition of Matter:Elements, compounds, and mixtures
Chapter 15.1-pages 450-454

Key Concepts:
Describe a pure substance and a mixture.
Compare and contrast pure substances and mixtures.
List examples of characteristics of elements, compounds and mixtures.

Questions to Ponder:
1. What is an element?2. How is an element different
from an atom?3. How is pure different from
impure?4. What is differences between an
element, compound and mixture?
5. What is the difference between pure and impure substances?

Key Vocabulary:
AtomElementPure substance
CompoundMixture

Imagine a world of Legos:

Composition of Matter: What does
pure mean?
What are the two examples of pure?
All matter is composed of atoms Smallest particle of an element
that still retains the properties of the element ▪ (H, Cl, O)
When we say PURE… ANYWHERE else that you see that
element, it will be EXACTLY the same ▪ Same properties▪ Same number of electrons, protons,
and neutrons Pure substances are either an
ELEMENT or a COMPOUND

Pure Substances: What do you
notice?

SAY WHAT!
What do you already know about atoms and elements??? Write on the post-it note on your desk.
List 3 things that you already know. What do you know?

What is the composition of matter?
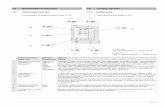
Matter
Pure Matter Substance
Impure Matter Mixture
only 1 set of chemical and
physical properties
Each substance in the mixture retains its own
set of chemical and physical properties

Elements: What does
pure mean?
What are some examples of chemical and physical changes?
What is an atom? Where have we seen this before?
An element is a pure substance that cannot be broken down into a simpler substance by physical or chemical means.
All elements are PURE! Means…a substance that is made
of one type of particle ON Periodic Table: shown as only
having 1 capital letter:▪ O for oxygen; C for carbon; Ca for
calcium

Compound: How is this
different from an element?
What makes up compounds?
A compound is a pure substance in which 2 or more elements are joined in a fixed proportion
All c0mpounds are PURE! Means…a substance that is
made of same type of particles
Has 2 or more capital letters Examples: salt, water, rust

Compound:A compound can be
made or broken down into elements through a chemical change. This means…something new is
made that has DIFFERENT properties from the original

Mixture: How is this
different from an element? From a compound?
What makes up mixtures?
How are they made?
A mixture is a material made up of two or more substances (elements or compounds) that can be easily separated by physical means.
All mixtures are IMPURE! Means…a substance that is
made of same type of particles Has 2 or more capital letters

Review:

Matter
Mixture Pure Substance
ElementCompoundHeterogeneous Mixture
Homogeneous Mixture
Can be separated physically
Cannot be separated physically
Can see the parts
Cannot see the parts
Can be separated chemically
Cannot be separated
Most impure Most pure

Summary:
1. How is an element different from an atom?
2. What is differences between an element, compound and mixture?
3. What is the difference between pure and impure substances?