§Chapter 15 - The Digestive System §Irregular tube; open at both ends, called “Alimentary...
-
Upload
nevaeh-crick -
Category
Documents
-
view
222 -
download
3
Transcript of §Chapter 15 - The Digestive System §Irregular tube; open at both ends, called “Alimentary...
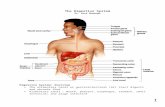
Chapter 15 - The Digestive System
Irregular tube; open at both ends, called “Alimentary canal” or “Gastrointestinal (GI) Tract” 29 feet long (adults) - 9 meters Food & other substances that enter tube are not really
inside body Passageway of food: broken down (digested) and
absorbed thru walls < entering body - cells
Both - Mechanical & Chemical Digestion
Break Down of Food
Teeth- first physical breakdownStomach-churning of food (physical)Mouth- first chemical breakdown (salvia)Digestive enzymes throughout GI tractDigestion - Process where large food particles
reduced to absorbable molecules Absorption - Process of small molecules passing
thru digestive system walls into body
Key Organs of the GI Tract
Know Main & Accessory organs, Table 16-2; page 476
Small Intestine : Duodenum, Jejunum, & IleumLarge Intestines (elimination > feces): Cecum, Colon: Ascending, Transverse, Descending,
Sigmoid
Wall of Digestive Tract -
Mouth to anus Four layers of tissue; surrounding the hollow
space within the tube “lumen” May vary in structure in different organs Mucosa or mucous membrane - tough in
esophagus, delicate, for absorption or secretion in rest of tract
Submucosa - connective tissue, blood vessels & nerves
Muscularis - 2 layers, responsible for
wavelike, rhythmic contractions (peristalsis), moves contents, assists in mixing & mechanical breakdown
Serosa - outermost covering, composed of visceral peritoneum
Mesentery - double folded peritoneal tissue, anchors loops of digestive tract to posterior wall of abdominal cavity
Mouth - Oral cavity - hollow chamber (roof, a floor, & walls) Entrance of food; digestion begins immediately Mucous membranes > mucus, protects against
digestive juices & lubricates food passage This mucous protects & lubricates Hard palate - bony structure, front portion Soft palate - posterior, chiefly muscles Uvula - cone-shaped process hanging down from
soft palate. W/ help of soft pal., prevents food or liquid from entering nasal cavity
Floor of the mouth - Tongue - skeletal muscular structure, covered w/
mucous membrane Anchored to bones in skull > hyoid bone
Frenulum- thin membrane; attaches tongue to floor of mouth Tongue-tied: too short
Papillae: small elevations on surface Vallate type - largest, inverted V-shaped row of
about 10-12 mushroomlike elevations - tastebuds
Teeth - Four major types -
Incisors - (sharp/cutting) Canines - cuspids (pierce/tear) Premolars - bicuspids & Molars - tricuspids
(grinding/crush)Mastication > chewing of foodForms a bolus > ready for swallowingBy age 2 - full set 20 teeth (cut 1st - 2 yrs.)By age 17 to 24 - 32 permanent teeth (cut 1st - 6
yrs.)
Typical Tooth -Three main parts -
Crown - visible, covered w/ enamel (hardest tissue in body)
Neck - narrow portion surrounds by gum tissue (gingiva)
Root - fitted into socket in upper or lower jaw, lined by fibrous, periodontal membrane
Inside Structure - Enamel on outside, Dentin, Pulp cavity (blood vessels & nerves) moving inward
Salivary Glands - 3 Pairs - ducts drain saliva into oral cavity,
secretes about 1 liter/day Parotid - in front of each ear (mumps -
tender) Submandibular - ducts by fernullum Sublingual - ducts into floor of mouth
Saliva contents - salivary amylase (begins CHO digestion), mucus (moistens food)
Pharynx - Behind nasal cavity & mouth Tubelike structure made of muscles, lined
w/ mucous membrane Part of respiratory & digestive systems
Esophagus - Passage for food to stomach Tube-like structure, 10 inches long Mucous lined GERD - often caused by hiatal hernia
Stomach - Upper part of abdominal cavity, under
diaphragm Pouch for food, hollow, expands (can push up
on diaphragm > discomfort) Lower esophageal sphincter (LES) or cardiac
sphincter - rings of muscle tissue at end of esophagus - keeps food from reentering the esophagus when the stomach contracts
Chyme - semi-solid mixture, produced by contraction of stomach muscles that mixes food w/ gastric juices
Stomach contractions - Created by 3 layers of muscles, run
lengthwise, around, obliquelyMakes stomach one of strongest organs >
peristalsisBreaks food into tiny particles
Mucous membranes line stomach -
contains gastric glands > secrete gastric juice & hydrochloric acid
When empty, wrinkled folds - rugaeThree divisions of stomach -
Fundus, body, pylorusPyloric sphincter - holds food in stomach,
empties contents slowly into small intestine
Ulcer - carterlike wound or sore in membrane of stomach• 1 in 10 persons suffer in USA• Helicobacter pylori bacterium (H. pylori)
Small Intestines - Portion of digestion tract that extends from the pylorus
to the ileocecal valve 12- 20 feet in length, coiled, convoluted, and occupies
most of the abdominal cavity Intestinal glands - secrete digestive juices Smooth muscle wall - contracts > peristalsis
Plicea - circular folds covered w/ villi, increases surface area > absorption
In or on the villi - Blood capillaries - absorb CHO & protein end
products (glucose & amino acids) Lacteal - lymphatic vessel - absorb lipids Microvilli - brushlike border, > surface more Chemical digestion - most occurs in 1st
subdivision of duodenum Minor & major duodenal papillae - ducts where
pancreatic enzymes & bile enter small intestine
Liver - Large organ, fills R upper abdominal cavity Exocrine gland - secretes bile into ducts Hepatic - means liver Bile - essential for breaking up or emulsification
of fats CCK (cholecystokinin) - hormone secretion
triggered by lipids in chyme > makes gallbladder contract & release bile
Drains from common bile duct into duodenum
Gallbladder - concentrates & stores bile
Pancreas -C-shaped, exocrine gland that lies behind the
stomach & duodenumPancreatic juice - most important digestive juice
- contains enzymes for all 3 food groupsSodium bicarbonate (alkaline substance) -
neutralizes hydrochloric acidEnters small intestine thru same duct as bileIslets of Langerhans - hormones producedPancreatitis - inflammation (blockage, CF)
Large Intestine -Begins with the ending of the ileum at the
ileocecal valve - called the cecumApproximately 5 feet in length, much larger in
diameter than small intestineContents - not called chymeFunction - reabsorb water & saltsMaterial acted on by bacteria > more nutrients
from cellulose & other fibers Synthesis Vit. K needed for blood clotting, Production of some B-complex vit.
Not as well suited for absorption as small intestine - no villi
Normal passage of material thru large intestine - 3 to 5 days
Subdivisions - flow in GI Tract one-wayCecum - pouchlike areaAscending colon - right side of body
Bends at hepatic or right colic flexure
Transverse colon - extends across front Bends at splenic or left colic flexure
Descending colon - left side abdomen
Sigmond colon - S-shaped segment,
terminates in rectumAnal canal - terminal end of rectum, ends at
external opening - anusInner anal sphincter - involuntary, smooth
muscle, keeps anus closed except during defecation
Outer anal sphincter - striated, voluntary muscle
Appendix - Vermiform appendix - “worm-shaped”, tubular
structure, blind tube No important digestive fnc. - digest cellulose Appendicitis - inflammation
Peritoneum - Large, moist, slippery sheet of serous membrane Peritoneal space - small space between parietal &
visceral layers - surfaces slide freely Retroperitoneal - organs outside peritoneum Extensions of peritoneum-mesentary, greater omentum
- both assist in anchoring abd. contents
Digestion -Chemical & mechanical
breakdownCHO - amylase in mouth, slight effectamylase from pancreas - into small intestine
Absorption of simple sugars (glucose)
Proteins - stomach (HCL/pepsinogen> pepsin) Finished in small intestine by pancreatic (trypsin)
& peptidases in intestinal juice Amino acids - basic protein units




























![Gastrointestinal System Chapter 23. GI: Overview: Organ systems Gastrointestinal (GI) tract [Alimentary canal] a continuous muscular digestive tube.](https://static.fdocuments.net/doc/165x107/56649dc75503460f94abc510/gastrointestinal-system-chapter-23-gi-overview-organ-systems-gastrointestinal.jpg)

![GI: Overview: Organ systems Gastrointestinal (GI) tract [Alimentary canal] a continuous muscular digestive tube Digests: breaks food into smaller.](https://static.fdocuments.net/doc/165x107/56649dba5503460f94aabbcd/gi-overview-organ-systems-gastrointestinal-gi-tract-alimentary-canal.jpg)