Chapter 11: Ecosystems & Resources 11.3: Energy flows through ecosystems.
-
Upload
lara-seabury -
Category
Documents
-
view
226 -
download
1
Transcript of Chapter 11: Ecosystems & Resources 11.3: Energy flows through ecosystems.

Chapter 11: Ecosystems & Resources
11.3: Energy flows through ecosystems

Review
• Serena puts a small amount of water in a saucer and leaves it on a sunny windowsill for several hours. What happens to the water? Why?
• The water evaporates. Heat from the Sun changes liquid water into vapor, which escapes into the air. After several hours the saucer may be completely dry.

Living things capture and release energy• All of our life processes require energy• The energy we use is chemical energy, from the
food we eat (chemical bonds of sugars break and release energy)– While running, we use energy, and some is lost as heat
(through sweating)• Most energy comes directly or indirectly from the
__________ .– Living things must capture this energy and store it in a
usable form

Producers• Producer: an organism
that captures energy and stores it in food as chemical energy– Make energy available to
the rest of the ecosystem
• Energy usually enters the ecosystem through photosynthesis– Produce sugars, and
chemical energy is released when these are broken down

Producers• Plants are the most common producers
on land• Photosynthetic bacteria and algae are the
most common in waters• Sun provides most energy stored in food
– Bacteria in the deep ocean perform chemosynthesis: they produced food using heated chemicals from hydrothermal vents
• Producers: “produce food for themselves and for the rest of
the ecosystem”

Consumers
• Consumers: organisms that get their energy by eating, or consuming, other organisms
• Classified by their position in a feeding relationship: Producer primary consumer secondary consumer etc.– Used to study how energy
flows through an ecosystem

Decomposers
• Decomposers: organisms that break down dead plant and animal matter into simpler compounds– Clean-up crew
• Leaves left on a forest floor, dead roots and branches, animal remains and waste materials– All broken down by fungi and bacterial that live in th soil– A pinch of soil may contain almost ½ million fungi and billions of
bacteria• Energy gets used as it flows from organism to organism
– Decomposers• release the last bit of energy from once-living matter• return matter to soil or water to be used again



Ocean Ecosystem

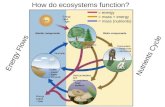
Models help explain feeding relationships
• Used to show the feeding relationships that transfer energy from organism to organism– Food chains and food webs
• Food chain: links that are connected one by one– Describes the feeding relationship between a producer and a single
chain of consumers in an ecosystem– Arrows represent the flow of energy
• Food web: feeding relationships between many different consumers and producers– More complex feeding relationships
• Both show how different organisms receive their energy and how they depend on one another


Food chain vs Food web

Available energy decrease as it moves through an ecosystem
• Energy pyramid: show the amount of energy available at each feeding level of an ecosystem



`Construct a Food web using the following animals.
This ecosystem represents a farm area.
The corn is the main source of food for many of the herbivores in the area.
SNAKE, CORN , CATERPILLAR, DEER, CROW, MOUSE, COUGAR, SQUIRREL, MICROORGANISMS (decomposers)
Pt I: (below) Pt II: (on right)