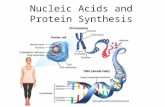
Chapter 10 Nucleic Acids & Protein Synthesis
description
Transcript of Chapter 10 Nucleic Acids & Protein Synthesis

Chapter 10Chapter 10Nucleic Acids & Protein SynthesisNucleic Acids & Protein Synthesis
OverviewOverviewLiving organisms are constructed Living organisms are constructed from thousands of different proteins. from thousands of different proteins. Each protein is constructed by Each protein is constructed by ribosomes according to instructions ribosomes according to instructions held in the DNA of every cell.held in the DNA of every cell.

Remember: Structure of Remember: Structure of DNADNA DNA is a double helixDNA is a double helix It is made of nucleotides.It is made of nucleotides. There are four different There are four different
types of nucleotides in types of nucleotides in DNA, each containing a DNA, each containing a different one of these different one of these nitrogen basesnitrogen bases Adenine (A)Adenine (A) Guanine (G)Guanine (G) Thymine (T)Thymine (T) Cytosine (CCytosine (C

Structure of RNAStructure of RNA RNA is a single helix, RNA is a single helix,
(although it can twist (although it can twist back on itself)back on itself)
It is also made of It is also made of nucleotides, but the four nucleotides, but the four nitrogen bases in RNA nitrogen bases in RNA are:are: Adenine (A)Adenine (A) Guanine (G)Guanine (G) Uracil (U)Uracil (U) Cytosine (C)Cytosine (C)

Types of RNATypes of RNA Messenger RNAMessenger RNA
The type of RNA that carries the genetic The type of RNA that carries the genetic protein blueprint from the nucleus to the protein blueprint from the nucleus to the ribosomesribosomes
Transfer RNATransfer RNA The type of RNA that bonds to amino acid The type of RNA that bonds to amino acid
and helps carry them to the ribosome and and helps carry them to the ribosome and assemble them in the correct order.assemble them in the correct order.
Ribosomal RNARibosomal RNA Structural material that makes up the Structural material that makes up the
ribosomes. Stored in the nucleolus of ribosomes. Stored in the nucleolus of animal cellsanimal cells

ReplicationReplication DNA molecules can copy their entire DNA molecules can copy their entire
structure, ie. Make new copies of structure, ie. Make new copies of themselvesthemselves
All the information stored in the DNA is All the information stored in the DNA is copiedcopied

Protein Synthesis: The four T’sProtein Synthesis: The four T’s 1. Transcription1. Transcription
In the nucleus: copying the plans In the nucleus: copying the plans DNADNAmRNAmRNA
2. Transport2. Transport Between the nucleus and the ribosomeBetween the nucleus and the ribosome mRNA in transitmRNA in transit
3. Translation3. Translation At the Ribosome: The plans are decodedAt the Ribosome: The plans are decoded mRNA mRNA tRNA tRNA
4. Transfer 4. Transfer and and Protein SynthesisProtein Synthesis tRNA + Amino Acid tRNA + Amino Acid builds protein chain. builds protein chain.

TranscriptionTranscription DNA can also copy short pieces of its DNA can also copy short pieces of its
code onto RNA molecules.code onto RNA molecules. These RNA copies are called These RNA copies are called
messenger RNA (mRNA for short)messenger RNA (mRNA for short)

Steps of Protein Steps of Protein SynthesisSynthesis
1. Transcription1. Transcription DNADNAmRNA (or tRNA or rRNA)mRNA (or tRNA or rRNA)
2. Transport: Movement of RNA2. Transport: Movement of RNA mRNAmRNAribosomesribosomes
3. Transfer of amino acids at the ribosome3. Transfer of amino acids at the ribosome tRNA molecules bring amino acids to the ribosometRNA molecules bring amino acids to the ribosome
4.4. Translation of mRNA into a polypeptide chainTranslation of mRNA into a polypeptide chain The tRNA molecules line up according to the mRNA The tRNA molecules line up according to the mRNA
template, positioning the amino acids to be joined template, positioning the amino acids to be joined together together

TranscriptionTranscriptionDNA transcribed to mRNADNA transcribed to mRNA
Transcription happens in the
nucleus

Transcription: Transcription: DNA anticodons to mRNA codonsDNA anticodons to mRNA codons
The sequence of The sequence of DNA anticodons is DNA anticodons is transcribed as transcribed as codons in mRNAcodons in mRNA
AA UU CC GG GG CC TT AA

2. Transport: 2. Transport: Messenger RNA Messenger RNA moves from the Nucleus to Ribosomesmoves from the Nucleus to Ribosomes
The mRNA moves The mRNA moves through the ER through the ER (endoplasmic reticulum)(endoplasmic reticulum) and the cytoplasm and the cytoplasm to find a ribosome.to find a ribosome.
The Ribosome is The Ribosome is where protein where protein synthesis occurs.synthesis occurs.

3. Transfer:3. Transfer:(at the ribosome)(at the ribosome) Transfer RNA (tRNA) Transfer RNA (tRNA)
bring amino acids to bring amino acids to the ribosome to make the ribosome to make the protein (AKA the protein (AKA polypeptide chain).polypeptide chain).
Each tRNA has a Each tRNA has a specific, 3 nucleotide specific, 3 nucleotide anticodon sequence anticodon sequence exposed.exposed.

Translation: the tRNAs Translation: the tRNAs line up in sequence line up in sequence
Proteins are synthesized Proteins are synthesized based on the sequence based on the sequence of bases in the mRNAof bases in the mRNA
The anticodons on the The anticodons on the tRNA must line up with tRNA must line up with the codons on the mRNAthe codons on the mRNA

The Genetic CodeThe Genetic Code The information in the DNA is stored in a The information in the DNA is stored in a
special codespecial code The five symbols that make up the alphabet The five symbols that make up the alphabet
of the genetic code are A.U.C.G. and of the genetic code are A.U.C.G. and sometimes T. (corresponding to adenine, sometimes T. (corresponding to adenine, uracil, cytosine, guanine and sometimes uracil, cytosine, guanine and sometimes Thymine)Thymine)
Each “word” or “codon” consists of three of Each “word” or “codon” consists of three of these symbols. This is why it is sometimes these symbols. This is why it is sometimes called the “triplet code”called the “triplet code”

UUU CUU AAC GGG AAGUUU CUU AAC GGG AAG A “codon” of the genetic code represents A “codon” of the genetic code represents
one specific amino acidone specific amino acid An “anticodon” is a codon with the An “anticodon” is a codon with the
opposite nucleotide bases compared to opposite nucleotide bases compared to original codonoriginal codon
AAT (DNA) or AT (DNA) or AU (RNA), CU (RNA), CG (Both)G (Both)
A “gene” is enough codons to specify all A “gene” is enough codons to specify all the amino acids in a particular protein.the amino acids in a particular protein.
Phenylalanine Leucine Lysine Glycine Lysine

The Amino Acids:
Amino Acids are the building blocks of proteins.
There are only 20 different amino acids used to build all the proteins in a human.
Each codon represents a different amino acid.
There are 64 possible codons, so several of them are used for other purposes (start, stop, duplicates).
Proteins start out as polypeptide chains so the term polypeptide is sometimes used as a synonym for protein.

The 20 Amino Acids and their codons
Amino acid Codons Amino Acid CodonsAlanine GCA, GCC… Leucine UUA, UUG…Arginine AGA, AGG… Lysine AAA, AAGAspartic acid GAC, GAU Methionine AUG*Asparagine AAC, AAU Phenylalanine UUC, UUUCysteine UGC, UGU Proline CCA, CCC…Glutamic acid GAA, GAG Serine AGC, AGU…Glutamine CAA, CAG Threonine ACA, ACCGlycine GGA, GGC… Tryptophan UGGHistine CAC, CAU Tyrosine UAC, UAUIsoleucine AUA, AUC… Valine GUA, GUC…

The 64 Codons and their Amino Acids
This table is also in your textbook
(page 194)
Page 194!

DNA Codons and Anticodons
The Codons are usually listed as they occur on mRNA, but DNA and tRNA have codons too, but they are the opposite codons (or anticodons) of the mRNA ones.
Amino Acid mRNA codon
DNA anticodon
tRNA anticodon
cysteine UGC ACG ACGisoleucine AUC TAG UAGlysine AAA TTT UUUtryptophan UGG ACC ACC

Example: (done together)
A DNA molecule has the following anticodons on part of one chain: TACAGCTTTTCAGATACCCATACT What amino acids do they code for?
Step 1: find the correct codons. AUG UCG AAA AGU CUA UGG GUA UGA
Step 2: find the Amino Acids (short) Start Ser- Lys- Ser- Leu- Try- Val- Stop
Answer: the protein would contain: Serine, lysine, serine, leucine,
tryptophan, and valine (in that order!)
Page 194!

Example: Now you try it
A DNA molecule has the following anticodons on part of one chain: TACAGCTTTACGGGGACCACT What amino acids do they code for?
Step 1: find the correct codons. AUG-UCG-AAA-UGC-CCC-UGG-UGA
Step 2: find the Amino Acids (short) Start-Ser-Lys-Cys-Pro-Try-Stop
Answer: the protein would contain: serine, lysine, cysteine, proline, and
tryptophan (in that order!)

DNA and Protein Synthesis Videos
Protein Synthesis (computer animation) Protein Synthesis (hand made stop motion) Translation (virtual cell)

Protein Synthesis
Lab report (DNA extraction) due ASAP
Reading and assignments Read pages 185 to 196 Create a representation of the process
of protein synthesis in a way that you can remember (group of diagrams, written description, mind-map, list of main ideas)
Answer questions 1-20 on p198











![6 -Fluoro[4.3.0]bicyclo nucleic acid: synthesis ... · acids (LNAs) [13-15], hexitol nucleic acids (HNAs) [16,17], cyclohexenyl nucleic acids (CeNAs) [18,19], tricyclo-DNAs (tc-DNAs,](https://static.fdocuments.net/doc/165x107/600a55cffb08ea5e44429f99/6-fluoro430bicyclo-nucleic-acid-synthesis-acids-lnas-13-15-hexitol.jpg)