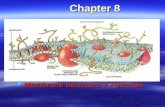
Chapter 10: Membrane Structure. Membrane Structure Membrane Function ► Plasma membrane defines...
-
date post
22-Dec-2015 -
Category
Documents
-
view
226 -
download
2
Transcript of Chapter 10: Membrane Structure. Membrane Structure Membrane Function ► Plasma membrane defines...
Membrane StructureMembrane Structure
Membrane FunctionMembrane Function► Plasma membrane defines cell and maintains differences Plasma membrane defines cell and maintains differences
btwn cytosol and extracellular environmentbtwn cytosol and extracellular environment► Defines individual organellesDefines individual organelles► Establish ion gradientsEstablish ion gradients► Contain proteins act as sensors of external signals allow cell Contain proteins act as sensors of external signals allow cell
to adapt to changing environmentto adapt to changing environment
Membrane StructureMembrane Structure
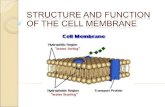
General Membrane Structure
►Thin film of lipid and protein held together by noncovalent interactions
►lipid bilayer serves as basic fluid structure; impermeable barrier
►Proteins mediate all other functions of membrane
The Lipid BilayerThe Lipid Bilayer
Lipids of MembraneLipids of Membrane► 50% of total membrane mass, 5 x 1050% of total membrane mass, 5 x 1066/um/um22
► AmphipathicAmphipathic► Self-sealingSelf-sealing► Phosphlipids, cholestrol, glycolipidsPhosphlipids, cholestrol, glycolipids► Phospholipids= most abundant lipid in membranePhospholipids= most abundant lipid in membrane► Spontaneously aggregate to bury hydrophobic tailSpontaneously aggregate to bury hydrophobic tail
The Lipid BilayerThe Lipid BilayerFluidity of Lipid BilayerFluidity of Lipid Bilayer► Rapid lateral diffusion of phospholipids 10Rapid lateral diffusion of phospholipids 10-8-8cm/seccm/sec► Change places 10Change places 1077 times/sec times/sec► Rarely flip-flopRarely flip-flop► Fluidity depends on composition (phospholipid and cholesterol) Fluidity depends on composition (phospholipid and cholesterol)
and temperatureand temperature► Phase transition= the temperature at which there is a change of Phase transition= the temperature at which there is a change of
state from liquid to solidstate from liquid to solid
The Lipid BilayerThe Lipid Bilayer
Fluidity and length and saturation of FA hydrocarbon chainsFluidity and length and saturation of FA hydrocarbon chains► Short hydrocarbon chain lengths fluidityShort hydrocarbon chain lengths fluidity► Double bonds fluidityDouble bonds fluidity
The Lipid BilayerThe Lipid Bilayer
Fluidity and cholesterol contentFluidity and cholesterol content
Cholesterol fluidityCholesterol fluidity Provides mechanical stabilityProvides mechanical stability 1 cholesterol/phospholipid in eucaryotes1 cholesterol/phospholipid in eucaryotes No cholesterol in procaryotes; mechanical No cholesterol in procaryotes; mechanical
stabililty imparted by cell wallstabililty imparted by cell wall
The Lipid BilayerThe Lipid Bilayer
Lipid RaftsLipid Rafts► Microdomains enriched in sphingolipids, cholesterol and Microdomains enriched in sphingolipids, cholesterol and
membrane proteinsmembrane proteins► Long saturated FA chain of sphingolipids = attractive forces that Long saturated FA chain of sphingolipids = attractive forces that
hold adjacent molecules togetherhold adjacent molecules together► Thicker than other parts of bilayerThicker than other parts of bilayer► able to accommodate membrane proteins concentrating for able to accommodate membrane proteins concentrating for
transport or to enable proteins to function togethertransport or to enable proteins to function together
The Lipid BilayerThe Lipid Bilayer
Membrane asymmetryMembrane asymmetry► Phospholipid distribution: Phospholipid distribution:
phosphatidylcholine and sphingomyelin confined to outer monolayer phosphatidylcholine and sphingomyelin confined to outer monolayer phosphatidylethanolamine and phosphatidylserine are on inner phosphatidylethanolamine and phosphatidylserine are on inner
monolayer monolayer ► Charge Charge ► Proteins Proteins ► Impt to function (ie, apoptosis and translocation of phosphatidylserine) Impt to function (ie, apoptosis and translocation of phosphatidylserine) ► glycolipids glycolipids
The Lipid BilayerThe Lipid Bilayer
Glycolipids Glycolipids ► Sugar containing lipid molecules w/ Sugar containing lipid molecules w/
most extreme assemmetry in most extreme assemmetry in distributiondistribution
► Found exclusively on Found exclusively on noncytoplasmic monolayernoncytoplasmic monolayer
► On surface of all plasma membranesOn surface of all plasma membranes► gangliosides= most complex, sialic gangliosides= most complex, sialic
acid containing oligosaccharides, acid containing oligosaccharides, net negative chg, most abundant in net negative chg, most abundant in pm of nerve cellspm of nerve cells
► Function- protection, cell Function- protection, cell recognition, transmission of recognition, transmission of electrical impulseselectrical impulses
Membrane ProteinsMembrane Proteins
Proteins Carry Out Specific Functions of Membrane
►Give ea type of membrane characteristic functional properties
►Amts and types of proteins highly variable
►By mass proteins represent 50% lipids 50%; lipids small thus 1 protein/ 50 lipid molecules
►Associate w/ membrane in various ways depending on function: transmembrane, integral, peripheral
Membrane ProteinsMembrane ProteinsTransmembrane Proteins Typically Cross as Alpha HelixTransmembrane Proteins Typically Cross as Alpha Helix► Unique orientation reflection syn and insertion in ER and functionUnique orientation reflection syn and insertion in ER and function► Membrane spanning doamin comprised of nonpolar aa 20-30Membrane spanning doamin comprised of nonpolar aa 20-30► Alpha helix is predominate conformation but beta shees form Alpha helix is predominate conformation but beta shees form
closed beta barrels that can span membrane as wellclosed beta barrels that can span membrane as well► Can predict membrane spanning regions via hydropathy plotCan predict membrane spanning regions via hydropathy plot
Membrane ProteinsMembrane Proteins
Beta Barrels form Transmembrane ChannelsBeta Barrels form Transmembrane Channels► Tend to be more rigidTend to be more rigid► Comprised of 8-22 strandsComprised of 8-22 strands► Some pore forming proteins generating water-filled channels for Some pore forming proteins generating water-filled channels for
select hydrophilic solutesselect hydrophilic solutes► Polar side chains line channel on inside; nonpolar side chains project Polar side chains line channel on inside; nonpolar side chains project
out interact w/hydrophobic core of lipid bilayerout interact w/hydrophobic core of lipid bilayer
Membrane ProteinsMembrane Proteins
Many Membrane Proteins are Glycolslated
►Majority of transmembrane proteins in animal cells are glycolsylated
►Sugars added in lumen of ER and golgi
►Oligosaccharide chains always present on noncytosolic side
Membrane ProteinsMembrane Proteins
Membrane Proteins can be Solubilized and Purified in Detergents
Distrupt hydrophobic interactions
Bind to hydrophobic regions of membrane and displace lipid molecules
SDS, triton
Membrane ProteinsMembrane Proteins
Red Blood Cells
Model system for studying membranes
Available in lg numbers
Easy to isolate uncontaminated from other cell types
No nucleus or internal organelles
Can prepare ghosts and in-side-out vesicles
Membrane ProteinsMembrane Proteins
Ghosts and InSide-Out RBCsGhosts and InSide-Out RBCsGhosts= empty RBCs Ghosts= empty RBCs
prepared by placing cells in soln of low salt to cause water to move into and lyse cellsprepared by placing cells in soln of low salt to cause water to move into and lyse cellscan reseal or be studied while leakycan reseal or be studied while leaky
Inside-Out VesiclesInside-Out Vesicles
Membrane ProteinsMembrane Proteins
Use of Sealed and Unsealed RBC ghostsUse of Sealed and Unsealed RBC ghosts Demonstrated some proteins extend across lipid bilayerDemonstrated some proteins extend across lipid bilayer Enabled sidedness of proteins to be determinedEnabled sidedness of proteins to be determined
Label intact sealed ghosts and inside-out vesicles w/ water Label intact sealed ghosts and inside-out vesicles w/ water solutble label that cannot penetrate lipid bilayer– perform SDS solutble label that cannot penetrate lipid bilayer– perform SDS PAGEPAGE
Exposed internal or external surface to proteolytic enzymes that Exposed internal or external surface to proteolytic enzymes that are membrane impremeant (transmembrane protein will be are membrane impremeant (transmembrane protein will be partially digested from both sidespartially digested from both sides
Labeled antibodies Labeled antibodies
Membrane ProteinsMembrane Proteins
Studies of RBC Plasma Membrane Proteins by SDS Studies of RBC Plasma Membrane Proteins by SDS PAGEPAGE
15 major protein bands btwn 15,000-250,000 daltons15 major protein bands btwn 15,000-250,000 daltons 3 most prominent comprose more than 65% protein mass; ea 3 most prominent comprose more than 65% protein mass; ea
arranged differently in membranearranged differently in membrane SpectrinSpectrin GlycophorinGlycophorin Band 3Band 3
Membrane ProteinsMembrane Proteins
Spectrin= Cytoskeletal Protein Assoc. w/ Cytosolic Side of Spectrin= Cytoskeletal Protein Assoc. w/ Cytosolic Side of MembraneMembrane
Most proteins are peripheral and assoc w/ cytosolic sideMost proteins are peripheral and assoc w/ cytosolic side Spectrin most abundantSpectrin most abundant Long, thin, flexible rod 100 nm length, constitutes 25% protein massLong, thin, flexible rod 100 nm length, constitutes 25% protein mass 2.5 x 102.5 x 1055 copies/cell copies/cell Principle component of cytoskeleton underlying RBC, maintains Principle component of cytoskeleton underlying RBC, maintains
structural integrity and biconcave shapestructural integrity and biconcave shape Heterodimer formed from 2 lg structurally similar subunits that assoc Heterodimer formed from 2 lg structurally similar subunits that assoc
head to head to form 200 nm long tetramerhead to head to form 200 nm long tetramer Tail ends of 4-5 tetramers linked by binidng short actin filaments and Tail ends of 4-5 tetramers linked by binidng short actin filaments and
other cytoskeletal components forming meshwork other cytoskeletal components forming meshwork Abnormalities in spectrin results in anemia and spherical shaped RBCs Abnormalities in spectrin results in anemia and spherical shaped RBCs
that are fragilethat are fragile Ankyrin binds spectrin and band 3 to membraneAnkyrin binds spectrin and band 3 to membrane
Membrane ProteinsMembrane Proteins
GlycophorinGlycophorin sm singlepass glycoprotein of 131 aasm singlepass glycoprotein of 131 aa Most of mass on external surface of Most of mass on external surface of
membranemembrane 100 sugar residues on 16 diff side chains 100 sugar residues on 16 diff side chains
which account for 60% protein masswhich account for 60% protein mass >90% sialic acid most of negative chg >90% sialic acid most of negative chg
on surface of RBCon surface of RBC 1 million molec/cell1 million molec/cell Function unknownFunction unknown
Membrane ProteinsMembrane Proteins
Band 3Band 3 Multipass membrane proteinMultipass membrane protein Catalyzes couple transport of anionsCatalyzes couple transport of anions 930 aa thought to extend across bilayer 12X930 aa thought to extend across bilayer 12X Allows HCOAllows HCO33 to cross membrane in exchg for Cl to cross membrane in exchg for Cl--
increasing amt of COincreasing amt of CO22 delivered to lungs delivered to lungs
Membrane ProteinsMembrane Proteins
Bacteriorhodopsin is a Proton Pump
Halobacterium salinarum “purple membrane”
7 transmembrane helices of 25 aa
Retinal light absorbing chromophore linked to lys side chain
Light excites chromophore causing conf chg which results in transfer of H+ from inside to outside cell
Electrochemical gradient used to syn ATP
Can pump up to 100 H+/sec
Membrane ProteinsMembrane Proteins
Membrane Proteins Often Function as Lg ComplexesMembrane Proteins Often Function as Lg Complexes
Membrane ProteinsMembrane Proteins
Membrane Proteins Diffuse in Plane of Membrane Proteins Diffuse in Plane of
Membrane but Do Not Flip-FlopMembrane but Do Not Flip-Flop
Membrane ProteinsMembrane Proteins
Techniques for Measuring the Lateral Techniques for Measuring the Lateral
Diffusion of Membrane ProteinsDiffusion of Membrane Proteins
Membrane ProteinsMembrane Proteins
Confining Proteins and Lipids to Confining Proteins and Lipids to Specific Specific
Regions of the MembraneRegions of the Membrane