Chapter 10 Immunologic Tolerance General Features and Mechanisms T Lymphocyte Tolerance B Lymphocyte...
-
Upload
ira-jenkins -
Category
Documents
-
view
314 -
download
2
Transcript of Chapter 10 Immunologic Tolerance General Features and Mechanisms T Lymphocyte Tolerance B Lymphocyte...

Chapter 10Chapter 10 Immunologic Immunologic ToleranceTolerance
General Features and Mechanisms
T Lymphocyte Tolerance
B Lymphocyte Tolerance
Tolerance induced by Foreign Protein Antigens
Homeostasis in the Immune System

Immunologic Tolerance—— an antigen induced specific unresponsivenessunresponsiveness
Tolerogens Immunogens
Self-tolerance Autoimmunity
Tolerance induced by foreign antigens
What is Immunologic Tolerance?
FailureFailure

General Features and Mechanisms
Immunologically specificImmunologically specific A result of antigen recognition by specific A result of antigen recognition by specific
lymphocyteslymphocytes

Neonate
Adult
Skin graft rejection + +_
Studies of graft rejection in inbred mice
Immunologically specific
a result of the recognition of antigens by specific lymphocytes
During lymphocyte maturation in the generative lymphoid organs, all lymphocytes pass through a stage in which encounter with Ag leads to tolerance
Strain A Strain A Strain A

General Features and Mechanisms
Immunologically specificImmunologically specific Central tolerance:Central tolerance:
induced in generative lymphoid organs immature self-reactive lymphocyte
The repertoire of mature lymphocytes cannot recognize ubiquitous or widely disseminated self antigens
The repertoire of mature lymphocytes cannot recognize ubiquitous or widely disseminated self antigens

Burnet: Clonal selection hypothesis

General Features and Mechanisms
Immunologically specificImmunologically specific Central tolerance:Central tolerance:
generative lymphoid organs immature self-reactive lymphocyte
Peripheral tolerance:Peripheral tolerance: peripheral sites mature self-reactive lymphocytes
The repertoire of mature lymphocytes cannot recognize ubiquitous or widely disseminated self antigens
The repertoire of mature lymphocytes cannot recognize ubiquitous or widely disseminated self antigens
Important for maitaining unresponsiveness to self antigens that are not expressed in the generative lymphoid organs.

Peripheral tolerance is induced when mature lymphocytes recognize antigens without adequate levels of the costimulators.

The principal mechanisms of lymphocyte tolerance
Deletion: apoptotic cell death
Anergy: functional inactivation without cell death
Treg
Central tolerance
Peripheral tolerance

Apoptosis

Immunologic Immunologic ToleranceTolerance
General Features and Mechanisms
T Lymphocyte Tolerance
B Lymphocyte Tolerance
Tolerance induced by Foreign Protein Antigens
Homeostasis in the Immune System

T Lymphocyte Tolerance
Central T Cell Tolerance Peripheral T cell Tolerance

Maturation of T cells in the thymus

Negative selection: Development of central tolerance
High affinity
High concentration

Self antigens expressed in the thymus
ubiquitous self-antigen: widely expressed in the body
tissue-specific antigenautoimmune regulator gene, AIRE

Natural Tregs arise in the thymus


T Lymphocyte Tolerance
Central T Cell Tolerance Peripheral T cell Tolerance

Peripheral T cell Tolerance
Antigen recognition without adequate costimulationUse CTLA-4 to recognize costimulators on APCsActivation induced cell death (AICD)Regulatory T LymphocytesFactors that determine the tolerogenicity of self antigens

Peripheral T cell Tolerance
Antigen recognition without adequate costimulationUse CTLA-4 to recognize costimulators on APCsAICDTregFactors that determine the tolerogenicity of self antigens

Sig2
(co-stimulation)
1975 Lafferty & Cunningham
T helper cells die when they see antigen unless rescued by co-stimulation(signal two) from APCs.
Two Signal model

co-stimulatory signal

Figure 8-20Gowth factor: IL-2

Anergy is induced when mature lymphocytes recognize antigens without adequate levels of the costimulators.

Figure 8-12CTLA-4/B7 initiate the inhibitory signal

Anergy may be induced if T cells use CTLA-4 to recognize costimulators on APCs

Question
Recognize the same B7 with CTLA-4 (inhibitory receptor)
Factors
?
?
Tolerance
Immune response
?
?T cells recognize B7 molecules
with CD28 (active receptor)
?T cells
?
?
T cells?

Making and breaking tolerance
The nature of tissue APCs is an important determinant of whether self-tolerance or autoimmunity develops.

Peripheral T cell Tolerance
Antigen recognition without adequate costimulationUse CTLA-4 to recognize costimulators on APCsAICDTregFactors that determine the tolerogenicity of self
antigens

Activation induced cell death
Repeated stimulation of T cells by persistent antigen results in death of the activated cells by a process of apoptosis

AICD is a form of apoptosis induced by signals from membrane death receptors
Fas-mediated activation-induced cell death

activation activation
The net effect is that the population of mature lymphocytes is depleted of antigen specific lymphocytes by repeated stimulation.

Peripheral T cell Tolerance
Antigen recognition without adequate costimulationUse CTLA-4 to recognize costimulators on APCsAICDRegulatory T Lymphocytes (Treg)Factors that determine the tolerogenicity of self antigens

Immunity 2009; 30: p626
Treg cell development

T cell-mediated suppression

Mechanisms of action of regulatory T cells

Peripheral T cell Tolerance
Antigen recognition without adequate costimulationUse CTLA-4 to recognize costimulators on APCsAICDRegulatory T Lymphocytes (Treg)Factors that determine the tolerogenicity of self antigens

Factors That Determine the Immunogenicity and Tolerogenicity of Protein
Factor Factors that favor stimulation of immune response
Factors that favor tolerance
Amount Optimal doses that vary for different antigens
High doses
Persistence Short-lived(eliminated by immune response)
Prolonged (AICD)
Portal of entry; location
Subcutaneous, intradermal; absence from generative organs
Intravenous, oral; presence in generative organs
Presence of adjuvants
Antigens with adjuvants: stimulate helper T cells
Antigens without adjuvants:
Properties of APCs
High levels of costimulators Low levels of costimulators and cytokines

Immunologic Immunologic ToleranceTolerance
General Features and Mechanisms
T Lymphocyte Tolerance
B Lymphocyte Tolerance
Tolerance induced by Foreign Protein Antigens
Homeostasis in the Immune System

B Lymphocyte Tolerance
Central B Cell Tolerance Peripheral B cell Tolerance
Checkpoints during B cell maturation and activation at which encounter self Ags may abort these process

B cell development in bone marrow


Central tolerance in B cells
• Immature B cells that recognize self antigens in the in the bone marrowbone marrow with high affinityhigh affinity are deleted or change their specificity.
• multivalent self antigens: cell membrane molecules 、 polymeric molecules


HEL transgenic
What is the result of self antigen recognition in generative lymphoid organ?
Down-regulation of antigen receptor expression
Change in receptor specificity (receptor editing)

B Lymphocyte Tolerance
Central B Cell Tolerance Peripheral B cell Tolerance


B7 CD28
T-B Collaboration


Peripheral tolerance in B cells
• Mature B cells that recognize self antigens in peripheral tissues in the absence of specific helper T cells may be rendered functionally unresponsive.
If anergic B cells do encounter any antigen-specific helper T cells, what
happened?
The B cells maybe killed by FasL on the T cells engaging Fas on the B cells.

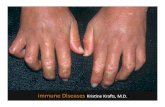
头发 Hair脱发 alopecia
脑 Brain癫痫 seizures精神病 psychosis头痛 headache
脸 Face颊部红斑 malar rash盘状红斑 discoid rash
心 Heart心包炎 pericarditis心肌炎 myocarditis心内膜炎 endocarditis肺动脉高压 pulmonary hypertension
小肠 Intestines血管炎 vasculitis
手 Hands雷诺氏现象 Raynauds phenomenonJaccoud 关节病
关节 Joints关节炎 arthritis
肺 Lungs胸膜炎 pleurisy间质性肺炎 interstitial pneumonia
血液、血管 Blood & Vessels血管葱皮样改变 onion-skin like artery贫血 anemia血栓 thrombosis
肾 Kidneys蛋白尿 proteinuria管型 casts
足 Feet血管炎 vasculitis
systemic lupus erythematosus systemic lupus erythematosus

蝶型红斑 ( Butterfly rash )

Homogenous pattern
Peripheral pattern
Speckled pattern

• Normal individals do not produce autoantibodies against self protein antigens, and this may be due to deletion or tolerance of helper T lymphocytes even if functional B cells are present.
• Defects in the maintenance of T cell tolerance may result in autoantibody production

FeatureFeature T lymphocyteT lymphocyte B lymphocyteB lymphocyte
Principal sites Principal sites Thymus (cortex);peripheral
Bone marrow; peripheral
Tolerance-Tolerance-sensitive stage sensitive stage
CD4+CD8+ thymocyte Immature B lymphocytes
Stimuli for Stimuli for tolerance tolerance inductioninduction
Central: high-avidity recognition of Ag in thymus
Central: high-avidity recognition of multivalent Ag in bone marrow
Peripheral: Ag presentation by APCs lacking costimulators; repeated stimulation by self Ag
Peripheral: Ag recognition without T cell helper
Principal Principal mechanisms of mechanisms of
tolerancetolerance
Central tolerance: clonal deletion (apoptosis)
Central tolerance: clonal deletion (apoptosis), receptor editing
Peripheral tolerance:: anergy, AICD, suppression
Peripheral tolerance: block inblock in signal transduction (anergy); failure to enter FC

Immunologic Immunologic ToleranceTolerance
General Features and Mechanisms
T Lymphocyte Tolerance
B Lymphocyte Tolerance
Tolerance induced by Foreign Protein Antigens
Homeostasis in the Immune System

Factors That Determine the Immunogenicity and Tolerogenicity of Protein
Factor Factors that favor stimulation of immune response
Factors that favor tolerance
Amount Optimal doses that vary for different antigens
High doses
Persistence Short-lived(eliminated by immune response)
Prolonged (AICD)
Portal of entry; location
Subcutaneous, intradermal; absence from generative organs
Intravenous, oral; presence in generative organs
Presence of adjuvants
Antigens with adjuvants: stimulate helper T cells
Antigens without adjuvants:
Properties of APCs
High levels of costimulators Low levels of costimulators and cytokines

Immunologic Immunologic ToleranceTolerance
General Features and Mechanisms
T Lymphocyte Tolerance
B Lymphocyte Tolerance
Tolerance induced by Foreign Protein Antigens
Homeostasis in the Immune System
Termination of normal immune response

Mechanisms of the decline of normal immune response (homeostasis)
CTLA-4 、 Fas 、 FasL

24 h
B7
CD28
Ag
TCR
B7
CTLA-4
Active signal
I T I MI TAM
Inhibitorysignal
T cell

Antibody feedback

The repertoire for TCR and BCR (Ab)
Ab1Ab2AgAg
Ab3
Ab1
Ab2
Niels Jerne: Network hypothesis
thresholdthreshold
Idiotype and anti-idiotypic
Reach a steady state at which the immune system is at homeostasis

Summary
What is immunologic tolerance?Central and peripheral toleranceTolerance in T and B cellsHomeostasis

Tolerance—— an antigen induced specific unresponsivenessunresponsiveness
Tolerogens Immunogens
Self-tolerance Autoimmunity
Tolerance induced by foreign antigens
What is Immunologic Tolerance?

FeatureFeature T lymphocyteT lymphocyte B lymphocyteB lymphocyte
Principal sites Principal sites Thymus (cortex);peripheral
Bone marrow; peripheral
Tolerance-Tolerance-sensitive stage sensitive stage
CD4+CD8+ thymocyte Immature B lymphocytes
Stimuli for Stimuli for tolerance tolerance inductioninduction
Central: high-avidity recognition of Ag in thymus
Central: high-avidity recognition of multivalent Ag in bone marrow
Peripheral: Ag presentation by APCs lacking costimulators; repeated stimulation by self Ag
Peripheral: Ag recognition without T cell helper
Principal Principal mechanisms of mechanisms of
tolerancetolerance
Central tolerance: clonal deletion (apoptosis)
Central tolerance: clonal deletion (apoptosis), receptor editing
Peripheral tolerance:: anergy, AICD, suppression
Peripheral tolerance: block inblock in signal transduction (anergy); failure to enter FC

THANK THANK YOUYOU
THANK THANK YOUYOU