CHAPTER 1. PRE-FERTILISATION: STRUCTURES AND EVENTS In the flower the male and female reproductive...
-
Upload
griffin-boone -
Category
Documents
-
view
224 -
download
6
Transcript of CHAPTER 1. PRE-FERTILISATION: STRUCTURES AND EVENTS In the flower the male and female reproductive...
CHAPTER 1 REPRODUCTION IN ORGANISMS
SEXUAL REPRODUCTION INFLOWERING PLANTSCHAPTER 1
flowers are morphological and embryological marvelsand the sites of sexual reproduction
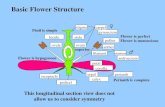
PRE-FERTILISATION: STRUCTURES AND EVENTSIn the flower the male and female reproductivestructures, the androecium and the gynoecium differentiate and develop.the androecium consists of a whorl of stamensrepresenting the male reproductive organ and the gynoecium representsthe female reproductive organ.Stamen, Microsporangium and Pollen Graintypical angiosperm anther is bilobed witheach lobe having two theca, i.e., they are dithecousfour microsporangia
Structure of microsporangiumMicrosporogenesisThe process of formation of microspores from a pollen mothercell through meiosis
pollen grains represent the male gametophytesPollen grainPollen grains are rich in nutrients
The Pistil, Megasporangium (ovule) and Embryo sacThe gynoecium represents the female reproductive part of the flower.monocarpellarymulticarpellarysyncarpous).apocarpous
The Megasporangium (Ovule)The ovule is a smallstructure attached to the placenta by means of a stalk called funicle.
MegasporogenesisThe process of formation of megaspores from the megaspore mother cell is called megasporogenesis
Autogamy- pollination is achieved in the same flowerPollinationChasmogamy- Oxalis
Cliestogamy- Oxalis
Geitonogamy- pollen from the anther to the stigma of another flower of the same plant.Xenogamy- between different plantsAgents of pollinationAbiotic and bioticWind pollination- pollen grains are light and non-sticky. Well exposed stamens
Water pollination- long ribben like, mucilage covering
Animal pollinatedFlowers are large, colorful, fragrant and rich in nectar.Small flowers are clustered into inflorescence
Yucca and moth Pollen robbersContinued self pollination result in inbreeding depression.Anther and stigma are placed in different positionsReceptivity is not synchronisedOutbreeding devicesSelf incomactibilityUnisexual flowers
Pollen pistil interactionIf the pollen is of the right type pistill will allow germintaion- communicate through chemicalsPollen grains are shed at two celled stage
Artificial hybridisationEmasculation and bagging
syngamy and triple fusion- embryo and edoseprmDouble fertilization
Post fertilization changesEndosperm, embryo development, maturation of ovules into seeds and ovary into fruitFree nuclear endospermEndosperm is completely used up- pea, groundnutEndosperm is not completely used up- coconut, castor
embryo
seedA fertilized ovuleAlbuminous and non albuminous seedsRemnants of nucellus- perisperm
FruitA mature ovarydormancyFalse fruits Pericarp- walls of fruit from integumentsParthenocarpic fruits
Apomixis and Polyembryony















![The “Early-Diverging” Flowering Plants Corolla [CO ...Androecium [A]: the stamens or male structures (#6-8) Gynoecium [G]: the carpels or pistils or female structures that contain](https://static.fdocuments.net/doc/165x107/5e776fae06490068f518a1ab/the-aoeearly-diverginga-flowering-plants-corolla-co-androecium-a-the-stamens.jpg)
![monograph of Psidium guajava l. leaves - · PDF fileFlower: Flowers occur ... flower opens, superior.[1] Androecium: Stamens indefinite, ... Figure 3: Diagram of a transverse section](https://static.fdocuments.net/doc/165x107/5ab3aa3f7f8b9ac3348e7789/monograph-of-psidium-guajava-l-leaves-flowers-occur-flower-opens-superior1.jpg)

