Chapter 1-2 Convection and the Mantle. Heat always moves from warmer to cooler Three types of heat...
-
Upload
bruce-hart -
Category
Documents
-
view
222 -
download
3
Transcript of Chapter 1-2 Convection and the Mantle. Heat always moves from warmer to cooler Three types of heat...

PLATE TECTONICSChapter 1-2
Convection and the Mantle

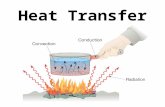
Types of Heat Transfer
Heat always moves from warmer to cooler
Three types of heat transfer
Radiation – transfer of energy through space No direct contact between heat source and
object Ex. Sunlight, heat from an open fire

Conduction – transfer within a material or between materials touching Ex. Metal spoon in a pot of hot soup – you touch
the spoon and the heat conducts from the spoon to your skin.
Convection – transferred by the movement of fluids. Movement of currents within a fluid
Figure 8, p. 15

Convection Currents
Convection Current – the flow that transfers heat within a fluid
Continue as long as heat is added. Heat from the core and the mantle itself
causes convection currents in the mantle.
Figure 9, p. 16

Convection Currents in Earth
Heat from the core and the mantle cause convection currents in the mantle.
The mantle flows very slowly
Heats up at the bottom of the mantle, rises up, cools, sinks back down.
Figure 10, p. 17