Comparative Vertebrate Physiology Vertebrate Respiration Systems.
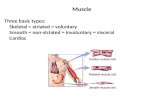
Ch 36 Musculoskeletal System AP lecture Three vertebrate muscles Skeletal – A.k.a striated –...
-
Upload
amanda-bradford -
Category
Documents
-
view
219 -
download
0
Transcript of Ch 36 Musculoskeletal System AP lecture Three vertebrate muscles Skeletal – A.k.a striated –...
• Cardiac – Involuntary – Beating of the heart– Appears striated because of myosin
and actin – Smaller than skeletal – Cells attached by gap junctions
• Smooth – Involuntary –Movement of internal organs– Internal organs controlled by ANS – Smaller than skeletal –Do not appear striated because of
the actin and myosin arrangements
Muscle contraction
• Skeletal muscle cells and muscle fibers are bundled together by connective tissue
• Interactions between actin and myosin – Every muscle fiber is made of
myofibrils- actin and myosin in repeating segments called sarcomeres
Muscle
voluntary, striated
involuntary, striatedauto-rhythmic
involuntary, non-striatedevolved first
multi-nucleated
digestive systemarteries, veins
heartmoves bone
Actin
• Thin filaments • Long chains of actin monomers
twisted around each other. • Twisted around that chain is
tropomyosin and attached to that is troponin. – These control contractions and
relaxation
Myosin
• Two long polypeptide chains coiled together. Each ends in a large globular head.
• Myosin filaments have many myosin molecules
• http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0072495855/student_view0/chapter10/animation__myofilament_contraction.html
ATP feeds the contractions
• Immediate system uses ATP • Glycolytic system metabolizes
carbohydrates to lactate and pyruvate
• Oxidative system metabolizes carbohydrates or fats into water and carbon dioxide
Where is ATP needed?
3
4
1 2
1
1
1
Cleaving ATP ADP allows myosin head to bind to actin filament
thin filament(actin)
thick filament(myosin)
ATP
myosin head
formcrossbridge
binding site
ADP
releasecrossbridge
shortensarcomere
1
Vertebrate skeleton
• 206 bones • Axial skeleton – Skull, vertebral column ,sternum
and ribs
• Appendicular skeleton – Pectoral girdle, pelvic girdle, arm,
leg, hands and feet bones
Bone growth
Joints
• Two bones join and muscles work in antagonistic pairs – Flexor – Extensor
• Types of joints – Ball and socket – Pivot –Hinge
• Tendon • Ligament