Ch. 14 Light and Reflection. Spherical aberrations – a blurred image produced from rays that...
-
Upload
marshall-taylor -
Category
Documents
-
view
216 -
download
0
Transcript of Ch. 14 Light and Reflection. Spherical aberrations – a blurred image produced from rays that...

Ch. 14
Light and Reflection

Spherical aberrations – a blurred image produced from rays that reflect at points on a mirror far from the principle axis.

Parabolic mirrors eliminate spherical abberationsAre segments of a paraboloid (a three-dimensional parabola)All rays parallel to the
principle axis converge at the focal point.
Good for flashlights headlights

Reflecting telescopes use parabolic mirrorscan reflect and focus electro-
magnetic radiation of different wavelengths

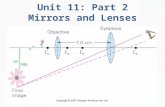
Other type of telescopeRefracting telescope
– uses a combination of lenses to form an image

ColorObjects absorb certain wavelengths from the light falling on them and reflect the rest.The color of an object depends on which wavelengths of light shine on the object and which wavelengths are reflected.Ex. Green leaves absorb
all colors except green. Green is reflected and that is what we see

Additive Primary colorsRed, blue, greenProduce white light
when combinedComplementary colors
are cyan, magenta, and yellow

Additive Primary colorsTwo primary colors
combine to produce a complementary color
Additive colors are used to color glass, produce images on television.
The human eye has cone cells that are sensitive to red, blue and greenLight of different wavelengths stimulate a combination of these receptors so a wide range of colors can be perceived.

Subtractive primary colorsCyan, magenta, and
yellowLight is absorbed or
subtracted from incoming light
Complementary colors are red, blue, and green

Subtractive primary colorsWhen pigments are
mixed, each one subtracts certain colors from white light and the resulting color depends on the frequencies that are not absorbed.

Polarization of LightAllows some light to be filtered by certain materialsMost light consists of waves that have electric fields oscillating in random directions (unpolarized)
They are combinations of vertical and horizontal electric field oscillations

Light whose electric field waves are oriented in the same direction have linear polarizationLight can be linearly polarized through transmission by being passed through certain transparent crystals

The light is passed through the crystal.The crystal will only allow certain parts of light to go throughThe light must pass through the transmission axisAny light waves that are linearly polarized with respect to the transmission line will pass through

Light can be polarized by reflection and scatteringWhen light is reflected at a certain angle from a surface, the reflected light is completely polarized parallel to the reflecting surface









![Visual and Refractive Outcomes following Bilateral ...downloads.hindawi.com/journals/joph/2018/7321794.pdfgression of age due to spherical aberrations [4, 5]. Since the spherical IOLs](https://static.fdocuments.net/doc/165x107/5edd681dad6a402d66687d22/visual-and-refractive-outcomes-following-bilateral-gression-of-age-due-to-spherical.jpg)