Cervical Spine Injuries. The Cervical Spine Vertebrae –7 cervical –12 thoracic –5 lumbar –5...
-
Upload
janiya-fluck -
Category
Documents
-
view
235 -
download
0
Transcript of Cervical Spine Injuries. The Cervical Spine Vertebrae –7 cervical –12 thoracic –5 lumbar –5...
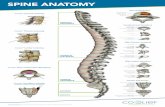
The Cervical SpineThe Cervical Spine
• VertebraeVertebrae
– 7 cervical7 cervical
– 12 thoracic12 thoracic
– 5 lumbar5 lumbar
– 5 sacral5 sacral
– 4 coccyx4 coccyx
Anatomy of Cervical VertebraeAnatomy of Cervical Vertebrae
Body of Axis
Odontoid Process
(Dens) of Axis Anterior Arch of Atlas
Posterior Arch of Atlas
C1-C2 Facet
Lamina
Bifid Spinous Process
Transverse ProcessTransverse
Foramen
Inferior Articular Process
Superior ArticularFacet
• Facet Joint InjuryFacet Joint Injury
– Mechanism of InjuryMechanism of Injury
• Generally the same mechanism as a strainGenerally the same mechanism as a strain
• More violentMore violent
• Involves a snapping of the head and neck Involves a snapping of the head and neck
• Ligaments injuredLigaments injured
• Signs and SymptomsSigns and Symptoms
• Similar signs and symptoms to a strain Similar signs and symptoms to a strain
• Tenderness facet joints and ligamentsTenderness facet joints and ligaments
• Pain will usually arise the day after the trauma Pain will usually arise the day after the trauma
• Muscle spasmsMuscle spasms
Cervical SprainCervical Sprain
• ManagementManagement
– Severe injuriesSevere injuries
• Activate EMSActivate EMS
• Refer to MD Refer to MD
– RICE for first 48-72 hoursRICE for first 48-72 hours
– Bed rest if severe Bed rest if severe
– RehabilitationRehabilitation
• StrengtheningStrengthening
• Restore ROMRestore ROM
• Review tackling techniques for football Review tackling techniques for football playersplayers
Cervical (Sprain)Cervical (Sprain)
Brachial Plexus InjuriesBrachial Plexus Injuries(Burner/Stinger)(Burner/Stinger)
• Mechanism of InjuryMechanism of Injury
– Lateral flexionLateral flexion
• Result of Result of
– Stretching of the brachial plexus or Stretching of the brachial plexus or
– Compression of the brachial plexus Compression of the brachial plexus
– Disrupts peripheral nerve functionDisrupts peripheral nerve function
Brachial Plexus Injury (Burner/Stinger)Brachial Plexus Injury (Burner/Stinger)
• Signs and SymptomsSigns and Symptoms• Burning sensationBurning sensation
• Numbness and tingling from the shoulder into the handNumbness and tingling from the shoulder into the hand
• Pain extending from the shoulder into the handPain extending from the shoulder into the hand
• Some loss of function of the arm and hand for several minutesSome loss of function of the arm and hand for several minutes
– Dead arm feeling by athleteDead arm feeling by athlete
• Symptoms rarely persist for several daysSymptoms rarely persist for several days
• Repeated injury can result in permanent damage Repeated injury can result in permanent damage
Brachial Plexus Neurapraxia Brachial Plexus Neurapraxia (Burner/Stinger)(Burner/Stinger)
• ManagementManagement
– Assessment by medical personnelAssessment by medical personnel
– IceIce
– RestRest
– Strengthening and stretching programStrengthening and stretching program
– Return to activity once signs and symptoms have returned to normalReturn to activity once signs and symptoms have returned to normal
– Padding to limit neck ROM during impactPadding to limit neck ROM during impact
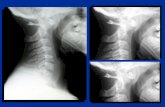
Cervical FracturesCervical Fractures
• Mechanism of InjuryMechanism of Injury
– Usually axial load w/ some degree of cervical flexionUsually axial load w/ some degree of cervical flexion
– SpearingSpearing
• PreventionPrevention
– Teach Teach proper tackling technique proper tackling technique
– (See what you hit)(See what you hit)
Cervical FracturesCervical Fractures• Signs and SymptomsSigns and Symptoms
– Neck point tendernessNeck point tenderness
– Restricted motionRestricted motion
– Cervical muscle spasmCervical muscle spasm
– Cervical painCervical pain
– Pain in the chest and extremitiesPain in the chest and extremities
– Numbness in the trunk and or limbsNumbness in the trunk and or limbs
– Weakness in the trunk and/or limbsWeakness in the trunk and/or limbs
– Loss of bladder and bowel controlLoss of bladder and bowel control
• ManagementManagement
– Activate EMS (911)Activate EMS (911)
– Treat like an unconscious athlete Treat like an unconscious athlete
– Use extreme careUse extreme care
– X-ray and physician referralX-ray and physician referral
– Transport with extreme caution Transport with extreme caution
– Minimize movement of cervical spineMinimize movement of cervical spine
• Cervical extrication collarCervical extrication collar
• Spine Board Spine Board
• Mechanism of InjuryMechanism of Injury– Usually violent flexion and rotation of the headUsually violent flexion and rotation of the head
Cervical DislocationCervical Dislocation
• Signs and SymptomsSigns and Symptoms
– Considerable painConsiderable pain
– NumbnessNumbness
– Weakness or paralysisWeakness or paralysis
• ManagementManagement
– Extreme care must be usedExtreme care must be used
– Do not straighten athletes neckDo not straighten athletes neck
– Activate EMS (911) Activate EMS (911)
– More likely to cause spinal cord injury More likely to cause spinal cord injury than a fracturethan a fracture
Cervical DislocationCervical Dislocation
Stabilize Head and NeckStabilize Head and Neck
5 Man Lift5 Man Lift
Log Roll onto Spine BoardLog Roll onto Spine Board
Facemask RemovalFacemask Removal
Strap to BoardStrap to Board
Log Roll onto Spine BoardLog Roll onto Spine BoardLifting Spine BoardLifting Spine Board
1
2a
2b
2b
3
4
5
5
5
Strengthening ExercisesStrengthening Exercises• Initiated when near normal range has been achievedInitiated when near normal range has been achieved
• Should be performed pain freeShould be performed pain free
• Exercise progressionExercise progression
• Isometric Isometric
• Isotonic exercisesIsotonic exercises