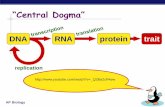
Central Dogma of Molecular Biology DNA –Stored information inside nucleus –Copied to make new...
-
date post
19-Dec-2015 -
Category
Documents
-
view
221 -
download
0
Transcript of Central Dogma of Molecular Biology DNA –Stored information inside nucleus –Copied to make new...

Central Dogma of Molecular Biology• DNA
– Stored information inside nucleus– Copied to make new cells = REPLICATION
• RNA– Copied from a piece of DNA (GENE) to make
a single protein = TRANSCRIPTION– Moves information from nucleus to cytoplasm
• Protein – Information from a single RNA used to make a
single protein = TRANSLATION

Base Pairing
• Complementary bases– A bonds to T– C bonds to G
• Complementary strands– Opposite strands of DNA
that can completely base pair to form a double helix

DNA Double Helix

Chromatin and Chromosomes
• Chromatin– DNA associated with proteins– Organizes and packages DNA
• Chromosome– Tightly coiled chromatin– Many cells have more than one chromosome– Humans – 46 chromosomes



DNA Replication
• Each strand of DNA can act as a template for the complementary strand
• Enzymes guide replication

• Enzymes pull apart the DNA strands• Enzymes add complementary nucleotides to
each strand
DNA Replication


Transcription
• Part of the DNA molecule is copied to make an RNA molecule

The Genetic Code and Genetics
• How does DNA encode for protein?– DNA – nucleotide subunits
• Nitrogenous bases = information
• 4 different nitrogenous bases
– Protein – amino acid subunits• 20 different amino acids

How are four nitrogenous bases translated into 20 different amino acids?
• Nucleotides form “words” called codons– Each codon codes for a different amino acid– A codon consists of 3 nitrogenous bases– 64 different combinations of codons– Only 21 needed (20 amino acids, 1 stop)

How is the code read?

Transfer RNA’s
• “Read” codons
• Bring amino acids to the ribosome








Mutations• Changes in DNA often but not always cause
changes in the protein for which it codes.
• Changing a single nucleotide has the potential to dramatically change a protein.

Gene

Homologous Chromosomes

Vocabulary• Allele
– Different versions of a gene– Make different versions of a protein
• Homozygous– Same allele on both homologous chromosomes
• Heterozygous– Different allele on each homologous chromosome– Often referred to as a hybrid
• Genotype– Total set of alleles which can be passed to the next
generation
• Phenotype– Observable appearance caused by different alleles

Naming Genes• All alleles of a gene use the same root letter or
word to indicate that it is the same gene• Dominant allele
– Phenotype expressed in heterozygous individual– Capitalized letter or word = dominant gene
• Recessive allele– Phenotype only expressed in homozygous
individual– Lower case letter or word = recessive gene

Gregor Mendel’s Law of Segregation
• Alleles of a gene segregate from one generation to another
• Exact reason not known by Mendel• Today we know assortment occurs during meiosis

Garden Pea
• Self-fertilize– Pollen from same flower
• Cross-fertilize– Pollen from different flower
• To cross is to fertilize (mate)


Heterozygous Cross
• Alleles– P
• Dominant
• Phenotype purple
– p• Recessive
• Phenotype white

Genotype Vs. Phenotype Ratio

Test Cross
• To cross an organism with an unknown genotype with an organism with a known phenotype
• PP or Pp X pp– Purple flower could be either PP or Pp– White flower must be pp

Multiple Alleles

Incomplete Dominance

Linked Genes
• Genes close together on the same chromosome
• Sort together during Meiosis
• Inherited together

Gregor Mendel’s Law of Independent Assortment
• Traits are transmitted to offspring independently of one another
• Traits that sort independently are on different chromosomes

Dihybrid Cross
• Seed Texture– R=round– r=wrinkled
• Seed Color– Y=yellow– y=green

Sex Chromosomes
• Humans– 46 total chromosomes
– 23 pairs• 22 pairs are called autosomes
– common to both males and females
• 1 pairs are called sex chromosomes– Females
» 2 X-chromosomes
– Males
» 1 X-chromosome and 1 Y-chromosome

Sex Determination
• SRY gene present on Y-chromosome triggers male pathway
• Female pathway is the default
• Hormones determine male and female sex characteristics

X-Linked Traits
• Male inherits only one X-chromosome– From which parent?– Males are Hemizygous for genes on X-
chromosome
• Female inherits two X-chromosome– One from each parent

Queen Victoria Pedigree

Dosage Compensation
• Both males and females require the same amount of protein coded for in their X-chromosomes– However…
• Females 2 X-chromosome
• Males 1 X-chromosomes

X-inactivation
• Female embryos inactivate one X-chromosome at random in each cell when they are 12-16 days old.
• Inactive X-chromosome is called a Barr Body
• Females are a mosaic

Calico Cats• Gene for coat color on X-chromosome
• Two alleles Brown and Black

Anhydrotic Dysplasia
• Sweat gland do not develop
• Heterozygous females are mosaics
![[PPT]DNA Replication - Rothology - homereplication.pptx · Web viewDNA Replication copyright cmassengale Replication Facts DNA has to be copied before a cell divides DNA is copied](https://static.fdocuments.net/doc/165x107/5aa6232f7f8b9a7c1a8e5563/pptdna-replication-rothology-home-replicationpptxweb-viewdna-replication.jpg)