Cells Chapter 3 Bio160. Plasma Membrane Plasma membrane – flexible yet sturdy barrier that...
-
Upload
lindsay-payne -
Category
Documents
-
view
219 -
download
0
Transcript of Cells Chapter 3 Bio160. Plasma Membrane Plasma membrane – flexible yet sturdy barrier that...

Cells
Chapter 3
Bio160

Plasma Membrane
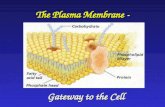
• Plasma membrane – flexible yet sturdy barrier that surrounds and contains the cytoplasm of a cell.
Fluid mosaic model
Lipid bilayer
Membrane proteins

Plasma Membrane
• Cytoplasm – Everything inside the cell including the fluid (cytosol) and organelles.
The plasma membrane is selectively permeable, which means that only certain substances can enter or leave the cell

Transport Across Membranes
Process Energy Source Description Examples
Passive processes
Simple diffusion Kinetic energy Net movement of particles (ions, molecules, etc.) from an area of their higher concentration to an area of their lower concentration, that is along their concentration gradient
Movement of fats, oxygen, carbon dioxide through the lipid portion of the membrane, and ions through protein channels under certain conditions
Osmosis Kinetic energy Simple diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane
Movement of water into and out of cells via membrane pores

Transport Across Membranes
Facilitated diffusion Kinetic energy Same as simple diffusion, but the diffusing substance is attached to a lipid-soluble membrane carrier protein
Movement of glucose into cells
Filtration Hydrostatic pressure
Movement of water and solutes through a semipermeable membrane from a region of higher hydrostatic pressure to a region of lower hydrostatic pressure, that is along a pressure gradient
Movement of water, nutrients, and gasses through a capillary wall; formation of kidney filtrate

Transport Across Membranes
Active processes
Active transport (solute pumping)
ATP (cellular energy)
Movement of a substance through a membrane against a concentration (or electrochemical gradient; requires a membrane carrier protein)
Movement of amino acids and most ions across the membrane
Bulk transport
Exocytosis ATP Secretion or ejection of substances from a cell; the substance is enclosed in a membranous vesicle, which fuses with the plasma membrane and ruptures, releasing the substance to the exterior
Secretion of neurotransmitters, hormones, mucus, etc.; ejection of cell wastes

Transport Across Membranes
Phagocytosis (endocytosis)
ATP “Cell eating”; A large external particle (proteins, bacteria, dead cell debris) is surrounded by a “seizing foot” and becomes enclosed in a plasma membrane
In the human body, occurs primarily in protective phagocytes (some white blood cells, macrophages)
Pinocytosis (endocytosis)
ATP “Cell drinking”; Plasma membrane sinks beneath an external fluid droplet containing small solutes; membrane edges fuse, forming a fluid-filled vesicle
Occurs in most cells; important for taking in solutes by absorptive cells of the kidney and intestine

Transport Across MembranesReceptor-mediated
endocytosisATP Selective
endocytosis process; external substance binds to membrane receptors, and coated pits are formed
Means of intake of some hormones, cholesterol, iron, and other molecules

Tonicity• Isotonic – concentrations of solutes are the
same on both sides of the membrane0.9% NaCl solution (normal physiological saline) is
isotonic for red blood cells (RBC)
• Hypotonic – a solution that has lower concentration of solutes than the cytosol
Lysis or hemolysis in RBC
• Hypertonic – a solution that has greater concentration of solutes than the cytosol
Crenation – cell shrinkage

Nucleus
• Nucleus – control center
contains chromosomes - heredity material-called chromatin when cell is not dividing
nucleolus - assembly plant for ribosomes
surrounded by nuclear membrane which has pores in it through which substances enter and exit

Ribosomes
• Ribosomes - contain both rRNA and ribosomal proteins
functions as the workbench for protein synthesis
some ribosomes are free ribosomes - no attachment to organelles - concerned primarily with synthesizing proteins for use inside cell

Ribosomes
some ribosomes are attached to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), hence rough ER, involved in the synthesis of proteins for insertion in the cell membrane or for export from the cell

Endoplasmic Reticulum
• Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) - system of membrane-enclosed channels continuous with nuclear membrane and Golgi complex
rough ER - has attached ribosomes - proteins synthesized are stored by the ER and sugar groups may be added to form glycoproteins - then transported from ER to Golgi

Endoplasmic Reticulum (2)smooth ER - no ribosomes attached - provides
a surface area for chemical reactions
– site of steroid, fatty acid, phospholipid synthesis (ex: in testis provides surface for enzymes involved in testosterone synthesis)
– site of carbohydrate synthesis, detoxification of alcohol, pesticides, carcinogens (ex: liver synthesis of glycogen)
– stores Ca++ in muscle (but called sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) in muscle)

Golgi Apparatus• Golgi apparatus - consists of stacks of flattened
sacs (like pancakes) that can form vesicles for exocytosis, lysosomes, or for storage (vesicles are membrane bound sacs that are smaller than vacuoles)
Golgi receives proteins, carbohydrates, lipids from vesicles made from ER and collects, sorts, packages as new vesicles, and delivers vesicles for storage, membrane use, or exocytosis, lysosomes

Lysosomes
• Lysosome - formed by Golgi and contain powerful digestive (hydrolytic) enzymes that:
recycle monomers in a cell from polymers (proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids)
destroy bacteria engulfed by white blood cells (WBC) when the phagocytic vesicle fuses with lysosome

Mitochondria
• Mitochondria - powerhouse of cell - double membraned - found in both animal and plant cells, but not in bacteria
Major site of chemical reactions that release energy from certain nutrient molecules and transfer it to ATP, a chemical form the cell can use.

Cytoskeleton
• Cytoskeleton - elaborate network of protein structures = "bones and muscles"
microfilaments - thin strands of actin - aid in cell movement (ex. amoeboid movement as in WBC), aid in cytokinesis
– most highly developed in muscles

Cytoskeleton
– provide monorail system to move organelles/vesicles
microtubules - hollow tubes formed of globular proteins called tubulins
– also in centrioles, cilia, spindle fibers

Centrosomes and Centrioles
• Centrioles - paired cylindrical bodies, each composed of microtubules
Organize spindle fibers and asters during mitosis in animal cells (may not be necessary for this purpose because plants produce spindle fibers during mitosis but they lack centrioles)
• Centrosomes – a structure near the Golgi and nucleus that contains two centrioles.

Centrosomes and Centrioles
– Having centrioles at each pole in mitosis provides a vehicle for transmission of centrioles to all cells
Form the bases of cilia and flagella

Cilia/Flagella
• Cilia/Flagella - Membrane bound sets of microtubules that move by means of ATP
cannot produce cilia/flagella without centrioles
– Cilia – tiny, hairlike structures that fringe the surface of some cells
– Flagellum – long, usually single extension, ex. tail of a sperm

![Plasma Membrane [7.2] Goals: Understand the concept of homeostasis in relation to the plasma membrane Demonstrate and understand how the plasma membrane.](https://static.fdocuments.net/doc/165x107/5697c01d1a28abf838cd0a9a/plasma-membrane-72-goals-understand-the-concept-of-homeostasis-in-relation.jpg)