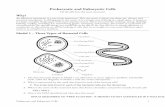
Cell Structures, Functions and Transport. Types of Cells Prokaryotic cells Eukaryotic cells.
-
Upload
madyson-wickwire -
Category
Documents
-
view
245 -
download
0
Transcript of Cell Structures, Functions and Transport. Types of Cells Prokaryotic cells Eukaryotic cells.

Cell Structures, Functions and Transport

Types of Cells
Prokaryotic cells Eukaryotic cells

Prokaryotic cells
Simplest cells No membranes around their
nuclear material (DNA and RNA, genetic material)
Prokaryotes include bacteria and some pond scum

Eukaryotic cells
Eukaryotic cells have membranes around their nuclear material
Membrane bound organelles Eukaryotes include protists, fungi,
plants, and animals (almost all organisms)

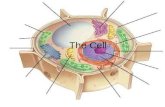
Section 7-2
Figure 7-5 Plant and Animal Cells
Go to Section:
Animal Cell

Section 7-2
Figure 7-5 Plant and Animal Cells
Go to Section:
Animal Cell
Cell Membrane

Cell membrane

Eukaryotic Cell Organelles and Function
1. Cell Membrane Nickname: “The Gatekeeper” Function: forms outer boundary of
the cellallows only certain
materials tomove into and out of the
cell
Parts: made up of a double layer of fats with some proteins scattered
throughout

Section 7-2
Figure 7-5 Plant and Animal Cells
Go to Section:
Animal Cell
Cell Membrane
Cytoplasm

Cell membrane
Cytoplasm

Eukaryotic Cell Organelles and Function
2. Cytoplasm Gel-like material inside the cell
membrane and outside the nucleus Function: contains water, chemicals,
and the various cell organelles Cytoplasm constantly moves or
streams

Section 7-2
Figure 7-5 Plant and Animal Cells
Go to Section:
Animal Cell
Nucleus
Nucleolus
Cell Membrane
Cytoplasm
Nuclear Membrane

Cell membrane
Cytoplasm
Nucleus
Nucleolus
Nuclear envelope/membrane

Eukaryotic Cell Organelles and Function
3. Nucleus Nickname: “The Control Center” Function: holds the DNA Parts:
1. Nucleolus: dark spot in the middle of the nucleus that helps make ribosomes
2. Nuclear envelope/membrane: surrounds nucleus in eukaryotic cells, has pores to let material in and out of the nucleus

Eukaryotic Cell Organelles and Function
3. Nucleus Parts:
3. Chromatin: Strands of genetic material found in the nucleus, made of protein and DNA

Section 7-2
Figure 7-5 Plant and Animal CellsAnimal Cell
Nucleus
Nucleolus
Mitochondria
Cell Membrane
Cytoplasm
Nuclear Membrane

Cell membrane
Cytoplasm
Nucleus
Nucleolus
Nuclear envelope/membrane
Mitochondria

Eukaryotic Cell Organelles and Function
8. Mitochondria Nickname: “The Powerhouse” Function: Energy formation
Breaks down food to make ATP ATP: is the major fuel for all cell
activities that require energy



Section 7-2
Figure 7-5 Plant and Animal Cells
Go to Section:
Animal Cell
Nucleus
Nucleolus Ribosomes
Cell Membrane
Cytoplasm
Nuclear membrane
Ribosomes
Mitochondria

Cell membrane
Cytoplasm
Nucleus
Nucleolus
Nuclear envelope/membrane
Mitochondria
Ribosomes

Eukaryotic Cell Organelles and Function
4. Ribosomes Function: makes proteins Found in all cells, prokaryotic and
eukaryotic

Section 7-2
Figure 7-5 Plant and Animal Cells
Go to Section:
Animal Cell
Nucleus
Nucleolus
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
Cell Membrane
Cytoplasm
Ribosomes
Nuclear Membrane
Ribosomes
Mitochondria

Cell membrane
Cytoplasm
Nucleus
Nucleolus
Nuclear envelope/membrane
Mitochondria
Ribosomes
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum

Eukaryotic Cell Organelles and Function
5. Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) Nickname: “Roads” Function: The internal delivery
system of the cell

Endoplasmic Reticulum 2 Types:
1. Rough ER: Rough appearance because it has
ribosomes on its surface Function: helps make proteins, that’s
why it has ribosomes
2. Smooth ER: NO ribosomes Function: makes fats or lipids

Section 7-2
Figure 7-5 Plant and Animal Cells
Go to Section:
Animal Cell
Nucleus
Nucleolus
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
Ribosomes
Golgi Complex
Cell Membrane
Cytoplasm
Ribosomes
Nuclear membrane

Cell membrane
Cytoplasm
Nucleus
Nucleolus
Nuclear envelope/membrane
Mitochondria
Ribosomes
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
Golgi Body

Eukaryotic Cell Organelles and Function
6. Golgi Complex (Golgi Body) Nickname: The shippers Function: packages, modifies, and
transports materials to different location inside/outside of the cell
Appearance: stack of pancakes Structure: stack of membrane-
covered sacs



Section 7-2
Figure 7-5 Plant and Animal Cells
Go to Section:
Animal Cell
Nucleus
Nucleolus
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
Ribosomes
Golgi Body
Cell Membrane
Cytoplasm
Ribosomes
Nuclear Membrane Mitochondria

Cell membrane
Cytoplasm
Nucleus
Nucleolus
Nuclear envelope/membrane
Mitochondria
Ribosomes
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
Golgi Body
Lysosome

Eukaryotic Cell Organelles and Function
7. Lysosomes: circular, but bigger than ribosomes
Nickname: “Clean-up Crews” Function: to break down food into
particles the rest of the cell can use and to destroy old cells

Cell membrane
Cytoplasm
Nucleus
Nucleolus
Nuclear envelope/membrane
Mitochondria
Ribosomes
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
Golgi Body
Lysosome
Vacuole

Eukaryotic Cell Organelles and Function
9. Vacuoles Function: Help store things Vacuoles in animal cells are usually
small sacs

Animal Cell
Nucleus
Nucleolus
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
Ribosomes
Golgi Bodies
Mitochondria
Cell Membrane
Cytoplasm
Ribosomes
Nuclear Membrane
Centrioles

Cell membrane
Cytoplasm
Nucleus
Nucleolus
Nuclear envelope/membrane
Mitochondria
Ribosomes
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
Golgi Body
Lysosome
Centriole (only 1 is shown)

Eukaryotic Cell Organelles and Function
10. Centrioles Function: Help with cell division Only found in animal cells Look like two small bundles of
spaghettiarranged perpendicularto each other

Now let’s talk about structures only found in PLANT Cells!!

Section 7-2
Figure 7-5 Plant and Animal Cells
Go to Section:
Plant Cell
Cell Membrane
Vacuole

Eukaryotic Cell Organelles and Function
11. Vacuoles Function: stores water
This is what makes lettuce crisp When there is no water, the plant wilts
Animal cells have vacuoles to provide temporary storage
Vacuoles in animal cells are smaller than plant vacuoles

Vacuole

Section 7-2
Figure 7-5 Plant and Animal Cells
Go to Section:
Plant Cell
Cell Membrane
Vacuole
Chloroplasts

Vacuole
Chloroplast

Eukaryotic Cell Organelles and Function
12. Chloroplasts Function: traps energy from the sun
to produce food for the plant cell Green in color because of
chlorophyll, which is a green pigment

Chloroplasts

Section 7-2
Figure 7-5 Plant and Animal Cells
Go to Section:
Plant Cell
Cell Membrane
Vacuole
Chloroplasts
Cell Wall

Cell wall

Eukaryotic Cell Organelles and Function
13. Cell Wall Function: provides support and
protection to the cell membrane Found outside the cell membrane in
plant cells

Plant Cell
Cell Membrane
Vacuole
Chloroplasts
Cell Wall
Nucleolus
Nucleus
Rough ER
Smooth ER
Golgi Bodies
Mitochondria
Ribosomes
Cytoplasm
Rough ER
Nuclear Membrane

Cell wall
Cell membrane
Vacuole
Nucleus
Nucleolus
Nuclear envelope/membrane
Chloroplast
Mitochondria Golgi Bodies
Ribosomes
Smooth ER
Rough ER
Lysosome
Cytoplasm

Comparing Plant and Animal CellsPlant Animal

Comparing Plant and Animal CellsPlant Animal
Cell WallChloroplastsLarge vacuole
CentriolesSmall vacuole
Cell MembraneCytoplasmNucleusNucleolusNuclear membraneMitochondriaRibosomesRough Endoplasmic ReticulumSmooth Endoplasmic ReticulumGolgi BodiesLysosomesVacuoles

Cell Transport
It’s a question of control.

Who’s in control?
Cells get nutrients, etc. from environment
Release waste into same environment

Moving along…or not!
Selective permeability: property of a cell membrane which allows some materials to pass through while keeping others out.

Diffusion
Molecules move constantly Move from crowded
conditions to less crowded conditions
Particles diffuse in liquids and in gases

Diffusion cont’d
Equilibrium: molecules of a substance are spread evenly throughout a space
Molecules continue to move during equilibrium

Osmosis—Diffusion of H2O
The diffusion of water through a cell membrane
Most cells surrounded by water molecules and contain water molecules

Osmosis Cont’d What happened to egg cells
in lab? If cells aren’t surrounded by
pretty pure water, they’ll lose the water.
No water molecules in corn syrup around eggs—so ….

Water tended to move out of the cells and dilute the corn syrup
Cells became shriveled and yolks became firm

Place eggs in pure water and the process is reversed
The eggs swell up and the yolks slosh around inside

Moving on… Particle movement across cell
membrane by diffusion is called passive transport because…
Cell doesn’t use energy to move the materials

Active transport: energy required to move large molecules through cell membrane
Need help of transport proteins

Active transport is required to move substances from where there are small amounts to where there are large amounts

Cell membrane Cell membrane is composed
of a double layer (bilayer) of phospholipids with protein molecules scattered throughout
Phospholipids make a bilayer with polar heads facing out and hydrophobic tails facing in

Cell membrane model

Lipids