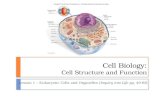
CHAPTER 7 CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTION PGS. 168 - 199 CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTION.
Cell structure function 2.2(k)
description
Transcript of Cell structure function 2.2(k)

Ch. 2.2:Cell Structure
& Function
http://koning.ecsu.ctstateu.edu/cell/cell.html

Focus Questions
1. What is the difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
2. What are the major cell parts/organelles and their functions? (see table)

1. What is the difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?

Prokaryotic Cells
• Do not have structures surrounded by membranes
• DNA is not surrounded by a membrane (no nucleus)
• Single-celled organisms only (Bacteria)
http://library.thinkquest.org/C004535/prokaryotic_cells.html

Eukaryotic Cells• Contain organelles surrounded by membranes• DNA is surrounded by a membrane (nucleus)• Includes all multicellular organisms
Plant Animal
http://library.thinkquest.org/C004535/eukaryotic_cells.html

“Typical” Animal Cell
http://web.jjay.cuny.edu/~acarpi/NSC/images/cell.gif

http://waynesword.palomar.edu/images/plant3.gif
“Typical” Plant Cell

2. What are the major cell parts/organelles and their functions?
(see table)

Surrounding the Cell

Cell Membrane
• Protects the inside of a cell from the outside environment
• Controls movement of materials in and out of the cell
• Found in all cells types
http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html

Cell Wall• Stiff structure outside
of cell membrane that supports & protects cells
• Found in prokaryotes & plant cells only
http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html

ONE OF THE DIFFERENCES BETWEEN PLANT AND ANIMAL CELLS IS THAT PLANT CELLS
HAVE:
A. B. C. D. E.
0 0 000
A. CHROMOSOMES
B. GENES
C. CELL WALLS
D. NUCLEI
E. VACUOLES
Non-Response Non-Response GridGrid
CountdownCountdown
45

The cells in your body have cell walls.
A. B.
00
A. True
B. FalseNon-Response Non-Response
GridGrid
CountdownCountdown
45

Inside the Cell

Organelle
• Structures within a cell that have specialized functions
• Most are surrounded by a membrane

Nucleus
• Directs cell activities
• Contains genetic info stored in DNA
• Found only in eukaryotic cells (plant & animal cells)

DNA • Stores genetic
information• Located in the
nucleus only in eukaryotes (plant & animal cells)
• Prokaryotes – floats around in cytoplasm

THE GENETIC INFORMATION FOR AN ORGANISM IS FOUND IN THIS ORGANELLE.
A. B. C. D. E.
0 0 000
A. NUCLEAR MEMBRANES
B. NUCLEUS
C. VACUOLE
D. MITOCHONDRIA
E. CHLOROPLAST Non-Response Non-Response GridGrid
CountdownCountdown
45

Cytoplasm• A gel-like substance inside of a cell that
contains water, salt & other molecules
• Contains a cell’s cytoskeleton
• Found in all cell types

Cytoskeleton• Network of threadlike proteins that are joined
together
• Provides a framework that gives a cell its shape & helps it move
• Found in all cells

A JELLYLIKE MATERIAL THAT HOLDS THE ORGANELLES IN PLACE IS CALLED THE:
A. B. C. D. E.
0 0 000
A. CRYOGENICS
B. CYTOPLASM
C. CYTOSKELETON
D. ORGANELLE GEL
E. MICROPLASMNon-Response Non-Response
GridGrid
CountdownCountdown
45

Endoplasmic Reticulum• Rough ER: produces
proteins• Smooth ER: makes
lipids & removes harmful substances from a cell
• Found in plant & animal cells
http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html

Ribosomes
• Each cell contains thousands (no membrane)
• Make proteins
• Found on Rough ER & floating throughout the cell
• Found in all cell types
http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html

Mitochondria
• Produces energy through chemical reactions – breaking down fats & carbohydrates
• Stores energy in ATP• Found in plant & animal
cells
http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html

Golgi Apparatus• Prepares proteins for
specific jobs & packages them into vesicles
• Protein “packaging” center
• Found in plant & animal cells
http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html

Lysosome• Contains enzymes
that break down & recycle cell components
• Cell breaks down if lysosome explodes
• Found in plant & animal cells
http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html

Which organelle produces energy and stores it as ATP?
A. B. C. D. E.
0 0 000
A. Endoplasmic Reticulum
B. Golgi Apparatus
C. Mitochondria
D. Nucleus
E. RibosomeNon-Response Non-Response
GridGrid
CountdownCountdown
45

Vacuoles
• Store food, water, & waste material
• Contains water solution
• Help plants maintain shape
• Found in plant & animal cells (one large one in plant cells)
http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html

WHICH ORGANELLE IS THE POWERHOUSE OF THE ANIMAL
CELL?
A. B. C. D. E.
0 0 000
A. VACUOLE
B. NUCLEUS
C. ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM
D. MITOCHONDRIA
E. RIBOSOMESNon-Response Non-Response
GridGrid
CountdownCountdown
45

Chloroplast
• Contains green chlorophyll
• Use light energy to make food (sugar) from water & CO2 through photosynthesis
• Found in plant cells
http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html

Photosynthesis takes place in the…
A. B. C. D.
0 000
A. Mitochondria
B. Nucleus
C. Chloroplast
D. Endoplasmic Reticulum
Non-Response Non-Response GridGrid
CountdownCountdown
45

THE HEREDITARY INFORMATION, DNA, IS FOUND IN WHICH PART?
A. B. C. D. E.
0 0 000
A. PROTOPLASM
B. CYTOPLASM
C. VACUOLE
D. NUCLEUS
E. FLAGELLA Non-Response Non-Response GridGrid
CountdownCountdown
45

Frogs are green because they have chloroplasts.
A. B.
00
A. True
B. False
Non-Response Non-Response GridGrid
CountdownCountdown
45

Which is NOT part of the cell theory?
A. B. C. D.
0% 0%0%0%
A. All cells come from preexisting cells
B. All cells contain a nucleus
C. All living things have cells
D. Cells are the smallest unit of life
Non-Response Non-Response GridGrid
CountdownCountdown
45

Which 2 macromolecules store energy?
A. B. C. D.
0% 0%0%0%
A. Carbohydrates & Proteins
B. Lipids & Proteins
C. Nucleic Acids & Lipids
D. Lipids & Carbohydrates
Non-Response Non-Response GridGrid
CountdownCountdown
45

Which of these refers to changes in an organism’s environment?
a) b) c) d)
0 000
a) External stimuli
b) Homeostasis
c) Internal stimuli
d) Development
Non-Response Non-Response GridGrid
CountdownCountdown
30

Homeostasis refers to an organism’s ability to maintain what kind of conditions?
a) b) c) d)
0 000
a) External
b) Internal
c) Cellular
d) Environmental
Non-Response Non-Response GridGrid
CountdownCountdown
30

Which characteristic of life does this example refer to:
a tadpole changing into a froga tadpole changing into a frog?
a) b) c) d)
0 000
a) Growth & development
b) Organization
c) Reproduction
d) Homeostasis
Non-Response Non-Response GridGrid
CountdownCountdown
30

Which characteristic of life does this example refer to:
a bacterium dividing into 2 bacteriaa bacterium dividing into 2 bacteria?
a) b) c) d)
0 000
a) Growth & development
b) Organization
c) Reproduction
d) Energy
Non-Response Non-Response GridGrid
CountdownCountdown
30

Which characteristic of life does this example refer to:
eating because you feel hungryeating because you feel hungry?
a) b) c) d)
0 000
a) Response to stimuli
b) Organization
c) Reproduction
d) Homeostasis
Non-Response Non-Response GridGrid
CountdownCountdown
30

Which characteristic of life does this example refer to:
your body temperature staying the sameyour body temperature staying the same?
a) b) c) d)
0 000
a) Energy
b) Response to stimuli
c) Reproduction
d) Homeostasis
Non-Response Non-Response GridGrid
CountdownCountdown
30

Which characteristic of life does this example refer to:
what you need for doing all activitieswhat you need for doing all activities?
a) b) c) d)
0 000
a) Growth & development
b) Energy
c) Reproduction
d) Homeostasis
Non-Response Non-Response GridGrid
CountdownCountdown
30

Which characteristic of life does this example refer to:
groups of cells working togethergroups of cells working together?
a) b) c) d)
0 000
a) Growth & development
b) Organization
c) Response to stimuli
d) Homeostasis
Non-Response Non-Response GridGrid
CountdownCountdown
30

What term refers to things that have all the characteristics of life?
a) b) c) d)
0 000
a) cells
b) unicellular organisms
c) organisms
d) multicellular organisms
Non-Response Non-Response GridGrid
CountdownCountdown
30