Cell Structure Cell Structure. Cell Theory The cell is the structural and functional unit of all...
-
Upload
erica-roberts -
Category
Documents
-
view
221 -
download
0
Transcript of Cell Structure Cell Structure. Cell Theory The cell is the structural and functional unit of all...

Cell StructureCell Structure

Cell TheoryCell Theory
The cell is the structural and functional unit The cell is the structural and functional unit of all living organismsof all living organisms..

The Cell TheoryThe Cell Theory
Principal features of the cell theory are:Principal features of the cell theory are:
The cell is the fundamental unit of structure The cell is the fundamental unit of structure and function in living things.and function in living things.
All cells come from pre-existing cells by All cells come from pre-existing cells by
division. division.
Cells contain hereditary information which is Cells contain hereditary information which is passed from cell to cell during cell division passed from cell to cell during cell division

All cells are basically the same in chemical All cells are basically the same in chemical composition. composition.
All known living things are made up of cells. All known living things are made up of cells.
Some organisms are unicellular, made up of Some organisms are unicellular, made up of only one cell. Others are multicellular, only one cell. Others are multicellular, composed of countless number of cells. composed of countless number of cells.

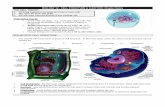
Typical animal cell Typical animal cell (copied from the internet)(copied from the internet)

Typical Plant Cell Typical Plant Cell (copied from the internet)(copied from the internet)

Diagram of nucleus Diagram of nucleus (copied from the internet)(copied from the internet)

Bacterial cellBacterial cell

Structure and Function of OrganellesStructure and Function of Organelles Nucleus: Nucleus: Typically the most prominent organelle in the Typically the most prominent organelle in the
cell. cell.
It is usually spherical or oval in shape and It is usually spherical or oval in shape and averages 5 µm in diameter.averages 5 µm in diameter.
Most cells have one nucleus. Most cells have one nucleus.
The nuclear envelope consists of two The nuclear envelope consists of two membranes that separate the nuclear contents membranes that separate the nuclear contents from the surrounding cytoplasm. from the surrounding cytoplasm.

These membranes are separated by 20-40 These membranes are separated by 20-40 nm. nm.
At intervals the membranes come together At intervals the membranes come together to form nuclear pores. to form nuclear pores.
Nuclear pores regulate the passage of Nuclear pores regulate the passage of materials between nucleoplasm and materials between nucleoplasm and cytoplasm.cytoplasm.

Most of the cell’s DNA is located inside Most of the cell’s DNA is located inside the nucleus. the nucleus.
DNA is associated with proteins, forming a DNA is associated with proteins, forming a complex called chromatin, which is complex called chromatin, which is granular granular
In dividing cells, the chromatin condenses In dividing cells, the chromatin condenses and becomes visible as distinct threadlike and becomes visible as distinct threadlike structures called chromosomes.structures called chromosomes.

Most nuclei have one or more densely Most nuclei have one or more densely packed structures called nucleoli. packed structures called nucleoli.
A nucleolus is not membrane bound and A nucleolus is not membrane bound and stains differently than the chromatin. stains differently than the chromatin.
Each nucleolus contains chromosomal Each nucleolus contains chromosomal DNA encoding instructions for making the DNA encoding instructions for making the type of RNA in ribosomes. type of RNA in ribosomes.
This ribosomal RNA is synthesized in the This ribosomal RNA is synthesized in the nucleolus. nucleolus.

Diagram of Ribosome Diagram of Ribosome (copied from the internet)(copied from the internet)

Made up of Made up of 65% ribosomal RNA and 35% 65% ribosomal RNA and 35% ribosomal proteins ribosomal proteins arranged into small and large arranged into small and large subunitssubunits..
Ribosomes consist of two subunits that fit Ribosomes consist of two subunits that fit together and work as one to translate the mRNA together and work as one to translate the mRNA into a polypeptide chain during protein synthesis. into a polypeptide chain during protein synthesis.
The active part of the ribosome is RNAThe active part of the ribosome is RNA

Prokaryotes Ribosomes:Prokaryotes Ribosomes:
Prokaryotes have 70S ribosomes, each Prokaryotes have 70S ribosomes, each consisting of a small (30S) and a large (50S) consisting of a small (30S) and a large (50S) subunit. subunit.
Their large subunit is composed of a 5S RNA Their large subunit is composed of a 5S RNA subunit (consisting of 120 nucleotides), a 23S subunit (consisting of 120 nucleotides), a 23S RNA subunit (2900 nucleotides) and 34 proteins. RNA subunit (2900 nucleotides) and 34 proteins.
The 30S subunit has a 1540 nucleotide RNA The 30S subunit has a 1540 nucleotide RNA subunit (16S) bound to 21 proteins subunit (16S) bound to 21 proteins

RibosomesRibosomes
Eukaryotes Ribosomes:Eukaryotes Ribosomes:
Eukaryotes have 80S ribosomes, each Eukaryotes have 80S ribosomes, each consisting of a small (40S) and large (60S) consisting of a small (40S) and large (60S) subunit. subunit.
Their large subunit is composed of a 5S RNA Their large subunit is composed of a 5S RNA (120 nucleotides), a 28S RNA (4700 (120 nucleotides), a 28S RNA (4700 nucleotides), a 5.8S subunit (160 nucleotides) nucleotides), a 5.8S subunit (160 nucleotides) and ~49 proteins. and ~49 proteins.
The small subunit has a 1900 nucleotide (18S) The small subunit has a 1900 nucleotide (18S) RNA and ~33 proteins RNA and ~33 proteins

Ribosomes contain the enzyme necessary Ribosomes contain the enzyme necessary for the formation of peptide bondsfor the formation of peptide bonds
They are tiny manufacturing plants that They are tiny manufacturing plants that assemble proteins. assemble proteins.

Diagram of ER Diagram of ER (copied from the internet)(copied from the internet)

Endoplasmic ReticulumEndoplasmic Reticulum::
This is a maze of parallel internal This is a maze of parallel internal membranes that encircle the nucleus and membranes that encircle the nucleus and extend into many regions of the cytoplasm. extend into many regions of the cytoplasm.
This complex network of membranes This complex network of membranes makes up a significant part of the makes up a significant part of the cytoplasm in many cells. cytoplasm in many cells.

Many ER membranes consist of a series of Many ER membranes consist of a series of tightly packed and flattened, sac-like tightly packed and flattened, sac-like structuresstructures
They form interconnected compartments They form interconnected compartments within the cytoplasm. within the cytoplasm.
The internal space enclosed by the The internal space enclosed by the membranes is called the ER lumen.membranes is called the ER lumen.

In most cells the ER lumen is continuous with In most cells the ER lumen is continuous with the space between the inner and outer the space between the inner and outer membranes of the nuclear envelope. membranes of the nuclear envelope.
The ER membranes and lumen contain a The ER membranes and lumen contain a large variety of enzymes that catalyse many large variety of enzymes that catalyse many chemical reactions. chemical reactions.
ER can be distinguished into rough and ER can be distinguished into rough and smooth ER.smooth ER.

Their functions are different but their Their functions are different but their membranes are connected and their internal membranes are connected and their internal spaces are continuous.spaces are continuous.
Rough ER has ribosomes attached and hence Rough ER has ribosomes attached and hence is rough in appearance in electron is rough in appearance in electron micrographs. micrographs.
The rough ER plays a central role in the The rough ER plays a central role in the synthesis and assembly of proteinssynthesis and assembly of proteins

Many proteins that are exported from the Many proteins that are exported from the cell and others destined for other organelles cell and others destined for other organelles are synthesized on ribosomes attached to are synthesized on ribosomes attached to ER. ER.
A tunnel within the ribosome connects to an A tunnel within the ribosome connects to an ER pore or translocon. ER pore or translocon.
Proteins are transported through the tunnel Proteins are transported through the tunnel into the lumen of the ER. into the lumen of the ER.

where the proteins may be modified by where the proteins may be modified by enzymes that add complex carbohydrates enzymes that add complex carbohydrates or lipids to them.or lipids to them.
Other enzymes in the ER lumen catalyse Other enzymes in the ER lumen catalyse
the efficient folding of the proteins into the efficient folding of the proteins into proper conformations (chaperones). proper conformations (chaperones).
The proteins are then transferred to other The proteins are then transferred to other compartments by small transport vesicles.compartments by small transport vesicles.

These vesicles bud off from the ER These vesicles bud off from the ER membrane and then fuse with the membrane and then fuse with the membrane of some target membrane.membrane of some target membrane.
The smooth ER is more tubular and has no The smooth ER is more tubular and has no ribosomes. ribosomes.
Smooth ER is the primary site of lipid and Smooth ER is the primary site of lipid and steroid synthesis.steroid synthesis.

Diagram of Golgi Apparatus Diagram of Golgi Apparatus (copied from the (copied from the
internet)internet)

Golgi apparatusGolgi apparatus: :
In many cells this consists of stacks of In many cells this consists of stacks of
flattened membranous sacs called flattened membranous sacs called cisternae. cisternae.
In some cases these sacs are filled with In some cases these sacs are filled with cellular products. cellular products.
Each flattened sac has an internal space Each flattened sac has an internal space (lumen). However unlike the ER most of (lumen). However unlike the ER most of these internal spaces are not continuous. these internal spaces are not continuous.

Each golgi stack has three areas: cis, Each golgi stack has three areas: cis, trans and medial regions. trans and medial regions.
The cis is located nearest the nucleus The cis is located nearest the nucleus and functions to receive materials and functions to receive materials transported by vesicles from the ER.transported by vesicles from the ER.

The trans face, nearest to the cytoplasmic The trans face, nearest to the cytoplasmic membrane, packages molecules in vesicles membrane, packages molecules in vesicles and transport them out of the Golgi. and transport them out of the Golgi.
As the proteins move through the Golgi As the proteins move through the Golgi apparatus they are modified resulting in the apparatus they are modified resulting in the formation of complex biological moleculesformation of complex biological molecules

Glycoproteins are packaged in secretory Glycoproteins are packaged in secretory vesicles in the trans region. vesicles in the trans region.
These vesicles pinch off from the Golgi These vesicles pinch off from the Golgi membrane and transport their contents to membrane and transport their contents to a specific destination. a specific destination.

Diagram of Lysosomes Diagram of Lysosomes (copied from the internet)(copied from the internet)

LysosomeLysosome These are small sacs of digestive enzymes These are small sacs of digestive enzymes
dispersed in the cytoplasm of most dispersed in the cytoplasm of most eukaryotic cells. eukaryotic cells.
These enzymes breakdown complex These enzymes breakdown complex molecules that originate inside or outside molecules that originate inside or outside the cell. the cell.
40 different enzymes have been identified, 40 different enzymes have been identified, most active under acidic conditions. most active under acidic conditions.

Under normal conditions the lysozyme Under normal conditions the lysozyme confines its enzymes and actions. confines its enzymes and actions.
Primary lysozymes are formed by the Primary lysozymes are formed by the budding from the Golgi apparatus. budding from the Golgi apparatus.
Their hydrolytic enzymes are formed in the Their hydrolytic enzymes are formed in the rough ER. rough ER.

As they pass through the lumen of the As they pass through the lumen of the ER sugars are added to each molecule ER sugars are added to each molecule identifying it as bound for a lysosome. identifying it as bound for a lysosome.
This signal allows the Golgi to This signal allows the Golgi to appropriately sort the enzyme to a appropriately sort the enzyme to a lysosome rather than transport it from the lysosome rather than transport it from the cell. cell.

Lysosomes degrade bacteria ingested by Lysosomes degrade bacteria ingested by scavenger cells. scavenger cells.
The ingested matter is enclosed in a vesicle The ingested matter is enclosed in a vesicle formed from the plasma membrane. formed from the plasma membrane.
One or more primary lysosome then fuse One or more primary lysosome then fuse with the vesicle containing the ingested with the vesicle containing the ingested material forming a larger secondary material forming a larger secondary lysosome.lysosome.

PeroxisomesPeroxisomes
Are membrane-bound organelles Are membrane-bound organelles containing enzymes that catalyse an containing enzymes that catalyse an assortment of metabolic reactions in which assortment of metabolic reactions in which hydrogen is transferred from a variety of hydrogen is transferred from a variety of compounds to oxygen. compounds to oxygen.
Hydrogen peroxide is produced as a Hydrogen peroxide is produced as a byproduct. byproduct.

Peroxisomes contain the enzyme catalase Peroxisomes contain the enzyme catalase that splits hydrogen peroxide rendering it that splits hydrogen peroxide rendering it harmless. harmless.
Peroxisomes are found in large numbers in Peroxisomes are found in large numbers in cells that synthesize, store or degrade cells that synthesize, store or degrade lipids. lipids.
Glyoxysomes are specialized peroxisomes Glyoxysomes are specialized peroxisomes in seeds which contain enzymes which in seeds which contain enzymes which convert stored fats into sugars. convert stored fats into sugars.

Peroxisomes may also contain an Peroxisomes may also contain an enzyme for the degradation of alcohol.enzyme for the degradation of alcohol.

Diagram of Vacuole Diagram of Vacuole (copied from the internet)(copied from the internet)

VacuolesVacuoles
Functions as the lysosomes in animal Functions as the lysosomes in animal cells.cells.
They are large, single, membrane-They are large, single, membrane-bounded sacs referred to as vacuole. bounded sacs referred to as vacuole.
The vacuolar membrane is called the The vacuolar membrane is called the tonoplast. tonoplast.

The vacuole has no internal structure. The vacuole has no internal structure.
Vacuoles are larger than vesicles and are Vacuoles are larger than vesicles and are sometimes formed by the merging of many sometimes formed by the merging of many vesicles. vesicles.
Vacuoles play a major role in the plant’s Vacuoles play a major role in the plant’s growth and development. growth and development.

An immature cell contains many vesicles An immature cell contains many vesicles which merge forming a small central which merge forming a small central vacuole. vacuole.
A plant cell normally enlarges by adding A plant cell normally enlarges by adding water to this central vacuole which can water to this central vacuole which can account for up to 90% of the cell volume. account for up to 90% of the cell volume.
The vacuole also contains stored foods, The vacuole also contains stored foods, salts, pigments and metabolic wastes. salts, pigments and metabolic wastes.

Functions of vacuoleFunctions of vacuole
Vacuoles serve as storage compartments Vacuoles serve as storage compartments for inorganic compounds for inorganic compounds
Recycle wastes or aggregate them into Recycle wastes or aggregate them into crystals, crystals,
Store compounds that are noxious to Store compounds that are noxious to herbivores, herbivores,

breakdown unneeded organelles and breakdown unneeded organelles and other cellular componentsother cellular components
maintenance of hydrostatic pressure in maintenance of hydrostatic pressure in the plant cell. the plant cell.

Mitochondria and chloroplastsMitochondria and chloroplasts
both have small amounts of DNA that both have small amounts of DNA that code for some of their proteins. code for some of their proteins.
They are able to grow and reproduce They are able to grow and reproduce independently of the cell. independently of the cell.

Diagram of Mitochondrion Diagram of Mitochondrion (copied from the (copied from the
internet)internet)

MitochondriaMitochondria
Mitochondria are found in eukaryotic cells. Mitochondria are found in eukaryotic cells.
These are the site of aerobic respiration, a These are the site of aerobic respiration, a process that includes most of the reactions process that includes most of the reactions that convert the chemical energy present in that convert the chemical energy present in certain foods to ATP. certain foods to ATP.
Mitochondria are most numerous in cells that Mitochondria are most numerous in cells that are very active and therefore have high are very active and therefore have high energy requirements. energy requirements.

They vary in size from 2-8 µm in length and They vary in size from 2-8 µm in length and are capable of changing shape and size are capable of changing shape and size rapidly. rapidly.
Each mitochondrion is bounded by a double Each mitochondrion is bounded by a double membrane which forms two different membrane which forms two different compartments: compartments:
the intermembrane space the intermembrane space and the matrix. and the matrix.

The intermembrane space is found The intermembrane space is found between the inner and outer mitochondrial between the inner and outer mitochondrial membranes. membranes.
The matrix is enclosed by the inner The matrix is enclosed by the inner membrane membrane
It contains enzymes that breakdown food It contains enzymes that breakdown food molecules and convert their energy to molecules and convert their energy to other forms of chemical energy.other forms of chemical energy.

The outer mitochondrial membrane is smooth and The outer mitochondrial membrane is smooth and allows the passage of small molecules through it. allows the passage of small molecules through it.
The inner membrane on the other hand has The inner membrane on the other hand has numerous folds and strictly regulates the types of numerous folds and strictly regulates the types of molecules that can move across it.molecules that can move across it.
The folds called cristaeThe folds called cristae
the inner mitochondrial membrane is the site of the inner mitochondrial membrane is the site of energy conversion from chemical energy to ATP. energy conversion from chemical energy to ATP.

Mitochondria also functions in aging.Mitochondria also functions in aging.
It also plays a role in apoptosis.It also plays a role in apoptosis.

Diagram of Chloroplast Diagram of Chloroplast (copied from the internet)(copied from the internet)

ChloroplastChloroplast
Are organelles that contain chlorophyll, Are organelles that contain chlorophyll,
Chlorophyll is a green pigment that traps Chlorophyll is a green pigment that traps light energy for photosynthesis. light energy for photosynthesis.
Chloroplasts also contain a variety of Chloroplasts also contain a variety of carotenoids (yellow and orange pigments) carotenoids (yellow and orange pigments) which also absorb light. Chloroplasts are which also absorb light. Chloroplasts are usually between 5-10 µm or longer. usually between 5-10 µm or longer.

Chloroplasts are typically disc-shaped structures Chloroplasts are typically disc-shaped structures and have a complex system of folded membranes. and have a complex system of folded membranes.
The chloroplast is bounded by two membranes and The chloroplast is bounded by two membranes and the inner membrane encloses a fluid-filled space the inner membrane encloses a fluid-filled space called the stroma. called the stroma.
The stroma contains enzymes necessary for the The stroma contains enzymes necessary for the production of carbohydrates from carbon dioxides production of carbohydrates from carbon dioxides and water using energy trapped from sunlight. and water using energy trapped from sunlight.
Suspended in the stroma is a system of Suspended in the stroma is a system of interconnected flat disc-like sacs called thylakoids. interconnected flat disc-like sacs called thylakoids. The thylakoids are arranged in stacks called grana.The thylakoids are arranged in stacks called grana.

The space inside the thylakoid is called the The space inside the thylakoid is called the thylakoid lumen and is the innermost thylakoid lumen and is the innermost compartment of the chloroplast. compartment of the chloroplast.
The thylakoid membranes, in which The thylakoid membranes, in which chlorophyll is found, are similar to the inner chlorophyll is found, are similar to the inner mitochondrial membrane in that it is the site mitochondrial membrane in that it is the site of ATP synthesis. of ATP synthesis.
Energy absorbed from sunlight by chlorophyll Energy absorbed from sunlight by chlorophyll molecules is used to excite electrons. molecules is used to excite electrons.

The energy in these excited electrons is The energy in these excited electrons is then used to form ATP and other then used to form ATP and other molecules that can transfer chemical molecules that can transfer chemical energy. energy.
This chemical energy is used to produce This chemical energy is used to produce carbohydrate from carbondioxide and carbohydrate from carbondioxide and water in the stroma.water in the stroma.

In 1935 Dawson and Danielli proposed that the In 1935 Dawson and Danielli proposed that the cell membrane is a phospholipids bilayer coated cell membrane is a phospholipids bilayer coated with protein molecules on both surfaces.with protein molecules on both surfaces.
the electron microscope inventedthe electron microscope invented
In 1959 Robertson put forward In 1959 Robertson put forward the unit the unit membranemembrane hypothesis which proposed that the hypothesis which proposed that the three layers seen by electron microscopy three layers seen by electron microscopy arranged as proposed by Dawson and Danielle.arranged as proposed by Dawson and Danielle.

Freeze fracturing reveals the presence of Freeze fracturing reveals the presence of particles (mainly proteins) which penetrate into particles (mainly proteins) which penetrate into and sometimes right through the lipid bilayer. and sometimes right through the lipid bilayer.
The inner and outer surfaces of membranes also The inner and outer surfaces of membranes also differ in their particle distribution.differ in their particle distribution.
In 1972 Singer and Nicholson put forward the In 1972 Singer and Nicholson put forward the fluid mosaic model of membrane structure in fluid mosaic model of membrane structure in which a mosaic of protein molecules floats in a which a mosaic of protein molecules floats in a fluid lipid structure.fluid lipid structure.

Fluid mosaic model is a dynamic Fluid mosaic model is a dynamic structure in which:structure in which:
proteins can float like islandsproteins can float like islands
some molecules move about freely while some molecules move about freely while others are fixed in positionothers are fixed in position
Lipids also move about.Lipids also move about.

Hydrophilic (polar) regions of the protein Hydrophilic (polar) regions of the protein project from the inner or outer surface. project from the inner or outer surface.
Hydrophobic (nonpolar) regions are Hydrophobic (nonpolar) regions are embedded within the membrane.embedded within the membrane.

Fluid mosaic modelFluid mosaic model

ReferencesReferences
www.cartage.org.lb/.../Mitochondria.htmwww.cartage.org.lb/.../Mitochondria.htm
http://kvhs.nbed.nb.ca/gallant/biology/golgi_apparatus.htmlhttp://kvhs.nbed.nb.ca/gallant/biology/golgi_apparatus.html
www.microscopy.fsu.edu/cells/endoplasmicreticwww.microscopy.fsu.edu/cells/endoplasmicretic
www.emc.maricopa.eduwww.emc.maricopa.edu/.../BIOBK/BioBookCELL2.html/.../BIOBK/BioBookCELL2.html
www.harlem-school.com/10TH/sci_pdf/sci.htmlwww.harlem-school.com/10TH/sci_pdf/sci.html