Cell structure and function biology
-
Upload
greencycle -
Category
Education
-
view
1.094 -
download
10
description
Transcript of Cell structure and function biology

Muskaan company presents
ing anil shokeen – writter
ing archana shokeen-co-operator
ing ansh shokeen –fighting with me
ing muskaan shokeen –main director and everything
Cell structure and function

What is a cell?
A cell may be defined as the smallest structural
and functional unit of an organism.

Unicellular organisms
Bodies of organisms may consist of one or many cells.Organisms whose body consists a single
cell are called unicellular organisms.

Functions of unicellular organism
In an unicellular organism, a single cell
performs all vital activities such as
feeding, movement, respiration, and reproduction.

Examples of unicellular organisms
Amoeba , paramaecium ,
euglana , bacteria.

Multicellular organisms
Organisms whose body consists of many cell are
called multicellular organisms.

Functions of multicellular cell
In multicellular organisms , cells
represent the lowest level of organization.
Other levels of organization include tissues, organs, and
organ systems. The organ systems get together to
form a complete organism.

Variation in shape
Cells exist in different shapes.
Some of examples are muscle cell,nerve
cell,skin cell.

Nerve cell
Nerve cell carry messages between different part of the
body. Hence, they are elongated in shape.

Muscle cell
Muscle cell help in movement through
contraction and expansion. Hence , they
are thin and long.

Skin cells
Skin cells cover a large area. Hence , they are
flat in shape.

Microscope

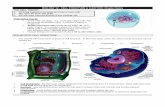
Organelles
The living parts of the cell that have a definite shape , structure , and
function are called organelles.

Parts of cells are :
1.Cell membrane2.Cytoplasm
3.Nucleus

Cell membrane

Cell membrane or plasma membrane
It is the outermost covering of a cell. It is
porous membrane through which select
substances can enter or leave the cell. The cell
membrane is also called plasma membrane.

Cytoplasm

Cytoplasm
It is jelly like fluid that fills up the part of the cell between the cell membrane and the nucleus. Several
organelles are embedded in the cytoplasm.

Nucleus

Nucleus It is considered to be the brain of the
cell. Nucleus is surrounded by a membrane called the nuclear
membrane and is filled with a semi solid substance called the
nucleoplasm thread like structures called chromosomes are in the
nucleoplasm. Chromosomes carry genes, which transfer the
characteristics of a cell to the new cells that are formed during cell division. Also present inside the nucleus is a round granule called
nucleolus, which contains a network of fibrous materials called chromatin
fibres.

Golgi apparatus – it is made of tubules (long tube like structures), vesicles (small vessels), and vacuoles and is responsible for the secretion of chemical substances such as enzymes, hormones and proteins.
Golgi body

It is a fluid filled space enclosed in a membrane. Vacuoles store excess water, useful minerals, pigments and many other substances.
Vacuoles

Lysosome contains chemical substances called enzymes that are capable of digesting cells and variety of intra and extra cellular materials (intra; internal) and (extra; external).
In times of emergency, lysosomes burst and destroy the cell.
Hence, they are also called suicide bag of the cells.
Lysosome

It is a network of tubules and channels and is involved in the synthesis, storage, and transport of the cell products.
Endoplasmic reticulum

These are small granular structures scattered in the cytoplasm that act as sites of protein synthesis.
Ribosomes

This structure is present only in animal cells. The main function of centrosomes is to initiate and regulate the cell division.
Centrosomes

These are present only in plant cells. Plastid contains certain pigments that have a specific role to play in the functioning of the plant. Depending on the pigment, color, plastids are of three types:
Chloroplast – this contains the green pigment chlorophyll which helps plants in making food.
Chromoplasts – this contains non green pigment that gives color to flowers and fruits.
Leucoplasts – these are colorless and store food in the form of carbohydrates, fats and proteins.
Plastid

1.Chloroplasts
2.Chromoplasts
3.leucoplasts
Plastids are of three kind

These are tiny spherical or rod shaped bodies. They act as sites of energy production and are , therefore, called the power house of the cell.
Mitochondria

Plant cell

Animal cell

Plant cell1.Cell wall is present.
2.Cytoplasm is not as dense as in an animal cell.
3.A large vacuole is present.
4.Plastids are usually present.
5.Centrosome is absent.
Differences between plant and animal cell.

Animal cell1.Cell wall is absent.
2.Cytoplasm is dense.
3.Vacuoles are generally absent . If present, they are small in size.
4.Palstids are absent.
5.Centrosome is present.
Differences between plant and animal cell.

Cells that lack a well defined nucleus surrounded by a nuclear membrane are called prokaryotic cells. Organisms that have such cells are called prokaryotes. Examples of prokaryotes are bacteria, blue green algae, viruses.
Prokaryotes

Cells that have a well defined nucleus are called eukaryotic cells. Organisms that have such cells are called eukaryotes. All organisms apart from bacteria, blue green algae, and viruses are eukaryotes.
Eukaryotes

The food that we eat leads to an increase in the size of cells. After reaching a certain size, a cell divides into two by a process called cell division. Increase in the numbers of cell division is responsible for the growth in organisms. Cell division also replaces the dead or damaged cells with the new ones and is responsible for healing wounds.
Cell division and growth

Thank you so much.









![[PPT]Cell Structure & Function - Lepore's Life and Health · Web viewCell Structure & Function Cell Biology * G. Podgorski, Biol 1010 * Cell Biology * G. Podgorski, Biol 1010 * Cell](https://static.fdocuments.net/doc/165x107/5aa4d86e7f8b9a517d8c79f5/pptcell-structure-function-lepores-life-and-health-viewcell-structure-function.jpg)