Cell organisation
Transcript of Cell organisation


Cell organization

Learning outcomes
• State the necessity for cell specialisation in multicellular organisms as compared to unicellular organisms
• Describe cell specialisation in multicellular organisms

Unicellular organism
• Small and simple organisms
• Vital function within a single cell
• Depends on cellular component---organelles
• Does not have any organs or systems
• Example: Amoeba sp




Amoeba sp.
• Live in freshwater environments and soil water
• Have plasma membrane
• Changing shape when meets obstacles and responds to stimuli eg acidic water and bright light

Amoeba’s movement
• Extending pseudopodia
• Anchoring tips on the ground
• Flow of cytoplasm into the projected pseudopodia
• Pseudopodia also used for feeding
• Feeding by phagocytosis


Phagocytosis
• Extending its pseudopodia
• Pseudopodia enclose the food and packaged in a food vacuoles
• Food vacuoles fuses with lysosome
• Food is digested by enzymes
• Absorbed nutrients into the cytoplasm



Amoeba sp. Feed(makan)-phagocytosis
Respire(bernafas)-exchange of gases
Excrete(membuang)-waste subtances by Diffusion through plasmamembrane
Move(gerak)-Pseudopodia
Reproduce(membiak)-asexually by binary fission-when environment is favourable

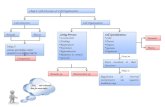
Multicellular organism

Multicellular organism• More than one cell eg human
Male gamete + Female gamete
Zygote
2 identical cells
4 cells
8 cellsEmbryo
White blood cellNerve cellsRed blood cellsSperm cells



![Cell Organisation in Plants [biology form 4 chapter 2]](https://static.fdocuments.net/doc/165x107/589cad591a28abbe4a8b52a9/cell-organisation-in-plants-biology-form-4-chapter-2.jpg)