The Cell History, Microscopes & Cell Theory. Cell Organism’s basic unit of structure and function…
Cell History & Structure
description
Transcript of Cell History & Structure

Cell History & Structure
Ms. MezzettiLynn English High School
Science Department

Early ContributorsRobert Hooke - The first person to see cells, he was looking at cork and noted that he saw "a great many boxes. (1665)Anton van Leeuwenhock - Observed living cells in pond water, which he called "animalcules" (1673)Theodore Schwann - zoologist who observed that the tissues of animals had cells (1839)Mattias Schleiden - botanist, observed that the tissues of plants contained cells ( 1845)Rudolf Virchow - also reported that every living thing is made of up vital units, known as cells. He also predicted that cells come from other cells.


THE CELL THEORY1. Every living organism is made of one or
more cells.2. The cell is the basic unit of structure and
function. It is the smallest unit that can perform life functions.
3. All cells come from preexisting cells.

Prokaryotic Cells• Prokaryotes are:
very simple cells a membrane (sometimes a cell wall)cytoplasm strand of DNA RibosomesAre bacteria-unicellular
Prokaryotic cells do not contain membrane bound organeles or nucleusThe word "prokaryote" means "before the nucleus"

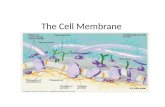
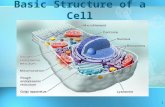
EUKARYOTIC CELLSThe eukaryotic cell is composed of 4 main parts: 1. cell membrane - outer boundary of the cell2. cytoplasm - jelly-like fluid interior of the cell3. nucleus - the "control center" of the cell,
contains the cell's DNA (chromosomes) 4. organelles - "little organs" that carry out cell
functions-membrane bound organelles

ANIMAL CELL

PLANT CELL

2.2: PROKARYOTES/EUKARYOTESCompare and contrast, at the cellular level, prokaryotes and eukaryotes (general structures and degrees of complexity).
PROKARYOTES BOTH EUKARYOTESNo nucleus DNA Membrane bound
nucleusNo membrane bound organelles
Ribosomes Membrane bound organelles-ER; golgi bodies; mitochondria; lysosome
Bacteria Plasma membrane
Animal, plant, protist and fungi cells
Simple cells Cytoplasm Complex cells