Cell Biology Structure & Function
Transcript of Cell Biology Structure & Function

Origin of Cells
Cell BiologyStructure & Function
Types of Cells
Organelles
Viruses

Review from Last Week
1

Assignment

Origin of Cells
3

Atmospheric Gases: Methane, H2O Vapor, Ammonia, H2, CO2
Extremely hot due to the volcanic and meteoric activities
Water vapor condensed to create oceans

● Urey-Miller Theory- Life comes from life● Simulate early earth conditions in a lab● Designed an apparatus to model the conditions● Methane, Hydrogen, Ammonia (gases)● Clearly demonstrated that biomolecules can
form on early earth conditions● Turned a portion of speculation of life coming
from chemistry into testable science
Urey-Miller Theory

Requirements of Life
4


Prokaryotes v. Eukaryotes
5

Prokaryotes● A prokaryote is a simple,
single-celled organism without a nucleus or membrane-bound organelles.
● Most of the DNA of a prokaryotic cell is in its nucleoid, consisting of a single large loop called a circular chromosome.

● Prokaryotes are very small, ranging from 0.1-5.0 micrometers in diameter.
● Critical thinking question: Why do cells need to remain small?

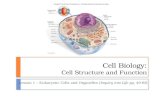
Eukaryotes● Eukaryotic cells are
cells that contain a nucleus and organelles, and are enclosed by a plasma membrane.

● They also have multiple linear chromosomes.
● Examples of eukaryotes include plants, animals, and you!


Endosymbiotic Theory
6

What is the Endosymbiotic Theory?● endo • symbiotic ● This theory proposes that organelles like the
mitochondria and chloroplast were once free-living prokaryotic cells that were engulfed by a larger host cell. Over a long time, the prokaryote and the host prokaryote evolved together, until one could not function without the other.


● Evidence includes:○ The fact that the mitochondria and
chloroplasts contain their own DNA, suggesting they originated from prokaryotic organisms.
○ ribosomes are structurally similar to prokaryotic cells.
What is the Evidence?


Organelles
7

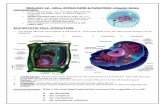
Plant vs. Animal Cells Plant Cells Animal Cells -Cells are large and have fixed rectangular shapes -Have cell walls and chloroplasts-Few mitochondria -Have one large vacuole -Nucleus lies on one side of the cell
-Small and irregularly shaped -Have lysosomes -Lots of mitochondria-Have many small vacuoles-Nucleus lies in the center

The town hall -> nucleus •All important meetings and decisions are made at the townhall, just like all important decisions regarding cell activity and growth are made at the nucleus •The town hall is in the center of the town and is home to the mayor, just like the nucleus is in the center of a cell and is home to the nucleolus
The parts of a cell, or should I say a city?

Mayor -> nucleolus •The mayor directs all of the towns activity and makes all important decisions for the town•The nucleolus directs all of the cell’s activity and makes all important decisions for the cell

Security around town hall -> nuclear envelope•Security stands outside the town hall to protect the town hall and regulate who can go in to the town hall•The nuclear envelope is right outside the nucleus and protects the inside and regulates what can enter and exit the nucleus

Mail man -> Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) •The mail man collects and drops of things from one parts of the city to other parts•The ER similarly collects and processes specific proteins from one parts of the cell to other parts

Post office -> smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)•The post office ships out mail that was processed to other parts of the town or outside the town•The smooth ER sends out specific proteins to other parts of the cell or outside the cell

Power Plant -> mitochondria•A power plant generates power for the city to function•The mitochondria similarly generates the energy needed for the cell to function

Train system -> golgi apparatus•The train system transports people all throughout the city•The golgi apparatus transports protein all throughout the cell

Construction workers -> ribosomes•Construction workers build structures that helps the city function•Ribosomes build all the protein that helps the cell function

Farmer -> chloroplasts•Farmers produce all the food for the city•The chloroplasts produce all the food for the cell

Storage units -> vacuole•Storage units hold all the city’s things•The vacuole stores all the cell’s things like food

Trash company -> lysosomes•The trash company collects trash from the people and cleans the city•Lysosomes clean the cell and recycle old cell material

Police department -> cytoskeleton•The police department maintains order in the city and keeps the town people in following the laws•The cytoskeleton protects the cell and maintains the cell’s structure

City border -> cell membrane•The city border controls who enters and exits the city•The cell membrane controls what can enter and exit the cell

City wall -> cell wall•Not all cities have a wall around them, like not all cells have a cell wall around them (only plants cells do)•The city wall protects the city from intruders•Similarly, the cell wall protects the cell from intruders in addition to providing the cell its structure and form

Phospholipid Bilayer
8

What is the Phospholipid Bilayer?
● Selective Permeability

Hydrophobic vs Hydrophilic

Composition● Membrane Proteins
● Cholesterol and permeability
● Tags/Markers
● Fluid Mosaic Model

Viruses
9

Viruses are NOT Living● Characteristics of Life
○ made of cells○ obtain and use
energy○ grow and develop○ have DNA○ sense and
respond to change
○ reproduce
● Characteristics of Viruses○ acellular - NOT made
of cells○ obtain and use
energy○ cannot grow and
develop○ DNA or RNA○ sense and respond to
change○ intracellular obligate
parasites - reproduce inside a HOST CELL
this is what a real virus looks like!

Structure
host cell membrane
surface proteins
outer envelope
genetic material
capsid

Virus Types & Transmission● virus: package of genetic material protected by a
protein shell for delivery into a host cell for expression● species specific
○ bacteriophages - infect bacteria○ 20 nm in diameter ~ SMALLER than ribosomes
● transmission○ inhalation○ ingestion this is what a
bacteriophage looks like!

Lytic Cycle● Step 1: viruses enters cell● Step 2: virus releases DNA● Step 3: uses host nutrients to synthesize proteins● Step 4: viruses assemble● Step 5: lysis
host cell membrane
host cell membrane
inside cell
host cell membrane
inside cell
host cell membrane
inside cell

Lysogenic Cycle● Step 1: viruses enters cell● Step 2: virus releases DNA● Step 3: viral DNA becomes a part of host DNA
○ everytime the host cell divides, the viral DNA is also duplicated
● Step 4: in stressful conditions, viral DNA is released from host DNA, and the virus enters step 3 of the lytic cycle
binary fission


Retroviruses● viruses need to eventually convert their genetic
material to DNA so it can interact with the host DNA● retroviruses: RNA-based viruses
○ reverse transcription turns RNA into DNA■ this process can result in frequent mutations
○ after reverse transcription, the virus go into the lytic or lysogenic cycle
DNA RNA PROTEINRNA

Problem Solving
Why is there no cure for
the influenza virus?

Post-Survey & Future Workshops● post-survey: bit.ly/CB1PS● August: Cell Biology
○ lectures & kitchen labs: 8/9, 8/16○ practical: 8/23
● September: DNA○ lectures & kitchen labs: 9/6, 9/13, 9/20○ practical: 9/27

THANK YOU!Does anyone have any final
questions?
G L E E

THE END.