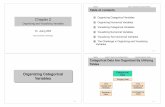
Categorical vs. Quantitative Variables
description
Transcript of Categorical vs. Quantitative Variables

Categorical vs. QuantitativeVariables
Identifying the Difference

Introduction to Statistics--Variables
2
Variables Come in 2 Varieties
1. Categorical (or __________)
2. Quantitative (or __________)

Introduction to Statistics--Variables
3
Categorical Variable Characteristics
• Recorded usually with words
• Records which of several groups an individual belongs to
• Count data in each group, but you logically should not average it
• Can calculate %age distributions
• Includes all yes/no questions
• Graphing: best illustrated with a pie chart(but could also be a bar graph)

Introduction to Statistics--Variables
4
Quantitative Variable Characteristics
• Possible responses are numerical in nature
• Includes values for which it makes sense to do operations like adding, totaling and averaging
• Includes answers to how much/how many questions
• Always includes ‘units’
• Graphing: best illustrated with a bar chart

Introduction to Statistics--Variables
5
2 Types of Quantitative Variables
1. __________ If the Q variable is a set of isolated points on thenumber line, we call it this. (i.e., it’s a number but it only comes in certain values) Usually a variable that can be ‘counted’.
2. __________ If the Q variable forms an entire interval along the number line, we call it this. (i.e., it’s a number & it can be any value) Usually a variable that can be ‘measured’.

Introduction to Statistics--Variables
6
Diagram of Variable Types
Categorical(Qualitative)
Variables Discrete
Quantitative(Numerical)
Continuous

Introduction to Statistics--Variables
7
Categorical or QuantitativeIf Categorical, one possible category?
If Quantitative, Continuous or Discrete? Units?
1) Length of a pen?
2) Type of pen?
3) Number of pens in box?
4) Maker of pen?5) Flow of ink in ml/sec?
6) Color of pen’s ink?
7) Point size of pen?
Subject of a book? Number of pages in the
book? Area of each page of
book? Number of letters on a
page? Number of weeks on
best seller list?

Introduction to Statistics--Variables
8
Categorical or QuantitativeIf Categorical, one possible category?
If Quantitative, Continuous or Discrete? Units?
1) Style of pants?
2) Color of pants?3) Number of pairs of
pants you own?
4) # of pockets on pants?
5) Size of pants?
6) Maker of the pants?7) Length of inseam on the
pants?

Introduction to Statistics--Variables
9
Reviewing Variable Types
1. __________ (or __________)
2. __________ (or __________)

Introduction to Statistics--Variables
10
Reviewing ________ Variables
• Possible responses are ________ in nature• Includes values for which it makes sense to do
operations like ________, ________ and ________.
• Includes answers to ________/________ questions
• Includes ‘________’• Usually—best illustrated with a ________, but
___________________________________.

Introduction to Statistics--Variables
11
2 Types of __________ Variables
1. __________ If the Q variable forms an entire interval _______________,
we call it this. (i.e., it’s a number & it can be any value).
2. __________ If the Q variable is a set of isolated ___________
_________, we call it this. (i.e., it’s a number but it only comes in certain values)

Introduction to Statistics--Variables
12
Classwork & Homework
• Use the terms you’ve learned to analyze the types of variables you encounter in the samples
• Answer some the ‘usual’ questions about the nature of this survey using the data and your powers of analysis.

Introduction to Statistics--Variables
13
Answers to Fill in Blanks

Finding Individuals & Variables in a List
State Region Population Males Females
AlabamaAlaska
SouthWest
15.6m5.4m
8.3m2.5m
7.2m2.9m
Arizona West 10.2m 5.1m 5.1m
Introduction to Statistics--Variables
14
Individuals in Sample—Usually in 1st ColumnVariables—Usually in 2nd and succeeding columns
Number of in Sample = 3Who’s in Sample? Alabama, Alaska, Arizona
Variable = Region = CategoricalVariable = Population = Discrete QuantitativeVariable = Males = Discrete QuantitativeVariable = Females = Discrete Quantitative
Look for Variable Names in Column Headings

Introduction to Statistics--Variables
15
Variables Come in 2 Varieties
1. Categorical (or Qualitative)
2. Quantitative (or Numerical)

Introduction to Statistics--Variables
16
2 Types of Quantitative Variables
1. Discrete If the Q variable is a set of isolated points on the
number line, we call it this. (i.e., it’s a number but it only comes in certain values)
2. ContinuousIf the Q variable forms an entire interval along the number line, we call it this.
(i.e., it’s a number & it can be any value).

Introduction to Statistics--Variables
17
Categorical or QuantitativeIf Categorical, one possible category? If Quantitative, Continuous or Discrete?
1) Length of a pen?
2) Type of pen?
3) Number of pens in box?
4) Maker of pen?5) Flow of ink in ml/sec?
6) Color of pen’s ink?
Quantitative, Continuous
Categorical
Quantitative, Discrete
Categorical
Quantitative, Continuous
Categorical

Introduction to Statistics--Variables
18
Categorical or QuantitativeIf Categorical, one possible category? If Quantitative, Continuous or Discrete?
Subject of a book? Number of pages in the
book? Area of each page of
book? Number of letters on a
page? Number of weeks on
best seller list?
Categorical
Quantitative, Discrete
Quantitative, Continuous
Quantitaitve, Discrete
Quantitative, Discrete

Introduction to Statistics--Variables
19
Categorical or QuantitativeIf Categorical, one possible category? If Quantitative, Continuous or Discrete?
1) Style of pants?
2) Color of pants?3) Number of pairs of
pants you own?
4) # of pockets on pants?
5) Size of pants?
6) Maker of the pants?7) Length of inseam on the
pants?
Categorical
Categorical
Quantitative, Discrete
Quantitative, Discrete
Quantitative, Discrete
Categorical
Quantitative, Continuous

Introduction to Statistics--Variables
20
Reviewing Variable Types
1. Categorical (or Qualitative)
2. Quantitative (or Numerical)

Introduction to Statistics--Variables
21
Reviewing Quantitative Variables
• Possible responses are numerical in nature• Includes values for which it makes sense to do
operations like adding, totaling and averaging.• Includes answers to how much/how many
questions• Includes ‘units’• Usually—best illustrated with a bar graph, but
pie chart is also possible.

Introduction to Statistics--Variables
22
Reviewing Categorical Variables• Recorded usually with words
• Records which of several categories an individual belongs to
• Count data in each group, but you logically should not average it
• Can calculate percentage distributions
• Includes all yes/no questions
• Usually—best illustrated with a pie chart.

Introduction to Statistics--Variables
23
2 Types of Quantitative Variables2. Continuous If the Q variable forms an entire
interval along the number line, we call it this.
(i.e., it’s a number & it can be any value).
2. Discrete If the Q variable is a set of isolated points on thenumber line, we call it this.
(i.e., it’s a number but it only comes in certain values)