Case Study: Lessons learned from the assistance to the 2010 Earthquake in Haiti Kae Yanagisawa JICA...
-
Upload
arron-mclaughlin -
Category
Documents
-
view
221 -
download
0
Transcript of Case Study: Lessons learned from the assistance to the 2010 Earthquake in Haiti Kae Yanagisawa JICA...

Case Study:Lessons learned from the assistance to the 2010
Earthquake in Haiti
Kae YanagisawaJICA
October 22, 2015


Damage
Earthquake in HaitiJanuary, 2010
M 7.2 in richter scaleDepth of the epicenter : 10km
Distance from the caiptal :17km
212,000 persons were killed 300,000 persons were injured
Government buildings were destroyed,Killing government officials
PKO (MINUSTA) headquarter building was Destroyed, killing SRSG and 8 Chinese
UN POL officers
Earthquake in ChileFebruary, 2010
M 8.8Depth of the epicenter: 35km
Distance from the Capital :300km
528 persons were killed

JICA

Haiti before the disasterPolitically, Supported by the UN stabilization mission (MINUSTAH), after long years of dictatorship and political turbulance. National military and police were under re-organization with the support of MINUSTAHEconomically, Poorest country in the Western hemisphereIn addition, Infrastructure had already been damaged by hurricanes in previous years.
A typical case of “fragile state”

Challenges to international humanitarian assistance
• Weak leading role of the government• Security concern Even before the earthquake, safety and security were at stake. UNDAC team requested every SAR team to arrange force protection.• Logistic difficulties The international airport was the sole entry point and controlled by the US Air Force. Due to congestion, many relief teams made a detour via Dominican republic.

Japan’s engagement
•A civilian medical team (JDR team) was deployed, succeeded by a medical unit of the JSDF (JDR team), and then, Japan Red Cross (NGO)
•The Government of Japan decided to participate in the MINUSTAH to assist recovery and reconstruction and deployed engineering corps of JSDF


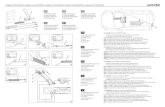
Cluster Meeting
UNOCHA DPKOUS
GovernmentUN CMCoord
Officer
In NY In Washington DC
UN CMCoord Officer
US Southern Command
UN CMCoordTeam
Joint Operations and Tasking Centre
Foreign military
Foreign military
Foreign militaryCivilian HA
organization
Civilian HA organization
Civilian HA organization
In Miami
In Port au Prince
Humanitarian Exchange Magazine
Coordination framework

Lessons learned
• Coordination among “enlightened” humanitarian workers, both civilians and militaries, was made relatively well.
But without the strong presence of the Haitian Government
• Overall, response was rather chaotic because of the influx of unregulated assistance.
Some NGOs were believed to be there just to show their presence to donors for fundraising. Some 1,800 rescue workers were on the scene, but their
size and capability were uneven. Some medical care did not fit local conditions and was not sustainable.

Changes brought by the lessons
•USAR coordination cell was devised as sub-component of UNDAC team to further facilitate coordination among SAR teams.
•Classification and standardization of foreign medical teams are in progress, with a proposal of registration and monitoring on the ground.
They were tested during the earthquake in Nepal.

Fragility and disasters•Weak governance of Haiti resulted in - lack of disaster prevention and preparedness - inefficient response - prolonged recovery• Cholera outbreak and political tension further
exacerbated the situation and delayed the recovery
Nevertheless, international assistance should be provided to support the Government, not replace it.